中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (17): 2625-2629.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1683
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞对心脏死亡脂肪变供肝移植后肝功能的保护
蔡秋程,范洪凯,熊日晖,江 艺
- 中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第900医院肝胆外科,福建省福州市 350025
Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects liver function following fatty liver transplantation from donors after cardiac death
Cai Qiucheng, Fan Hongkai, Xiong Rihui, Jiang Yi
- Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the 900th Hospital of PLA Joint Service Support Force, Fuzhou 350025, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 转氨酶:是人体肝脏正常运转过程中必不可少的“催化剂”,肝细胞是转氨酶的主要生存地。当肝细胞发生炎症、中毒、坏死时会导致肝细胞受损,转氨酶便会释放到血液里,使血清转氨酶升高。 边缘供肝:供肝短缺是当今制约临床肝移植进一步发展的瓶颈,如何扩大供肝来源,挖掘潜在边缘供肝,成为肝移植工作者极为感兴趣又急需解决的现实问题。边缘供肝一般是指肝移植后存在原发性移植肝无功能或功能低下以及迟发性移植物失活风险的肝移植供者。
摘要
背景:公民逝世后供肝捐赠者由于脂肪肝的高发病率,以及较长热缺血时间、组织低灌注时间等损害,移植后并发症发生率明显增加。理论上间充质干细胞可以促进移植器官细胞的再生,减轻器官移植后的缺血再灌注损伤和各种免疫损伤,从而起到对移植器官功能的保护作用。
目的:探讨骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠心脏死亡脂肪变供肝移植后肝功能的保护作用。
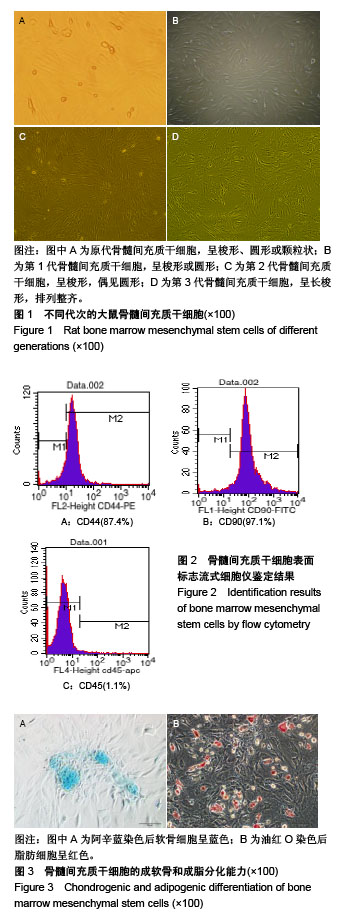
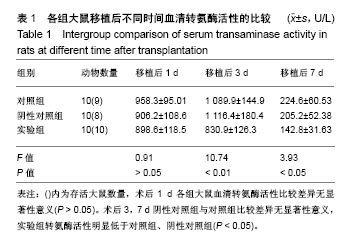
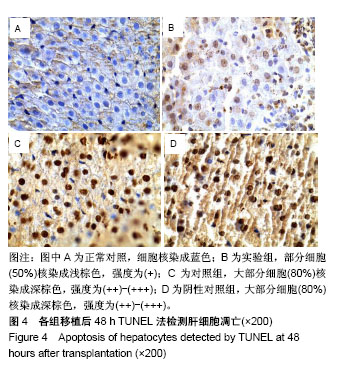
方法:应用密度梯度离心法分离、培养纯化大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞;将供体大鼠给予高脂饲料喂养8周致中-重度脂肪肝,然后诱导大鼠心脏死亡。将受体大鼠随机分为3组:①对照组(n=10):心脏死亡脂肪变供肝移植;②阴性对照组(n=10):心脏死亡脂肪变供肝移植,移植术中经门静脉注射生理盐水1 mL;③实验组(n=10):心脏死亡脂肪变供肝移植,术中经门静脉注射1 mL(约1.0×106个细胞)PBS配备的骨髓间充质干细胞悬液。移植后第1,3,7天检测血清转氨酶活性。移植后48 h,采用Tunel法检测肝细胞凋亡情况。
结果与结论:①移植后第1天,3组转氨酶活性比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);移植后第3,7天,实验组转氨酶活性低于对照组和阴性对照组(P < 0.05);②实验组肝细胞凋亡指数低于对照组和阴性对照组,组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);对照组和阴性对照组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③结果表明,骨髓间充质干细胞移植能够抑制肝细胞凋亡,有利于脂肪变供肝移植后肝功能的恢复。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3086-6687(蔡秋程)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)