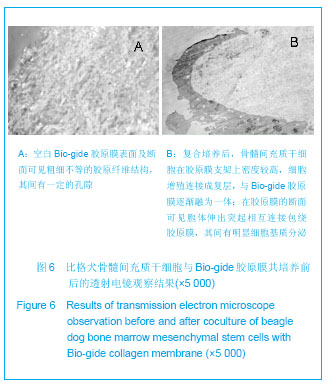
| [1] Zhao D,Wang B,Guo L,et al.Will a Vascularized Greater Trochanter Graft Preserve the Necrotic Femoral Head? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010;468: 1316-1324.[2] Li Y,Han R,Geng C,et al. A new osteonecrosis animal model of the femoral head induced by microwave heating and repaired with tissue engineered bone. Int Orthop.2009;33(2):573-580. [3] Peng J,Wen C,Wang A,et al. Micro-CT-based bone ceramic scaffolding and its performance after seeding with mesenchymal stem cells for repair of load-bearing bone defect in canine femoral head.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2011;96(2):316-325.[4] Hartman GA,Arnold RM,Mills MP,et al.Clinical and histologic evaluation of anorganic bovine bone collagen with or without a collagen barrier.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2004; 24(2):127-135.[5] Nevo Z,Robinson D,Horowitz S,et al.Collagen membranes at immediate implants: a histomorphometric study in dogs.Clin Oral Implants Res.Ceu Transplantation.1998;7(1): 63-70.[6] Wakitani S, Goto T, Young RG,et al.Repari of large full-thickness articular cartilage defects with allograft artichlar chondrocytes embedded in a collagengel.Tissue Eng.1998; 4(4): 429-444.[7] Marc L,Camelo M, Samuel E, et al. Evaluation of periodontal regeneration following grafting intrabony defects with bio-oss collagen:a human histologic report. Int J Periedonties Restorative Dent.2003;23(1):9-17. [8] 张志兴,詹暶,赵欣,等.不同浓度的骨髓基质细胞裸鼠体内成骨能力的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(6):720-722.[9] 张向荣,郭光华,刘德伍,等. 人骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养及BrdU标记鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(19): 3618-3622.[10] Barone FC,Arvin B,White RF,et al.T umor necrosis factor-alpha. a mediator necrosis factor-alpha.a mediator of focal ischemic brain injury.Storke.1997;28(6):1233-1244.[11] Lee HS,Huang GT,Chiang H,et al. Multi-potential mesenchymal stem cells from femoral bone marrow near the site of osteonecrosis. Stem cells.2003;21: 190-199.[12] Lin Z,Willers C,Xu J,et al. The chondrocyte: biology and clinical application.Tissue Eng. 2006;12(7):1971-1984.[13] 潘思年,杜敏联,马华梅,等. 大鼠胫骨生长板软骨细胞的体外培养及鉴定[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2009,30(45):1-5.[14] 赵德伟,胡永成. 成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志,2012,6(3):479-484.[15] Sekiya JK,Ruch DS,Hunter DM,et al. Hip arthroscopy in staging avascular necrosis of the femoral head. South Orthop Assoc.2000;9(4):3-9.[16] Urbaniak JR,Coogan PG,Gunneson EB,et al.Treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head with free vascularized fibular grafting: a long-term follow-up study of on e hundred and three hips. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1999;577(6): 681- 694.[17] Mats Brittberg. 细胞载体作为软骨修复中的下一代细胞疗法[J].中华关节外科杂志,2011,5(6):796-812.[18] Abelow SP,Guillen P,Ramos T. Arthroscopic technique for matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for the treatment of large chondral defects in the knee and ankle. Oper Tech Orthop.2006; 16: 257-261. [19] Amin AA,Bartlett W,Gooding CR,et al. The use of autologous chondrocyte implantation following and combined with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Int Orthop.2006; 30(1):48-53. [20] Bachmann G,Basad E,Lommel D,et al. MRT in the follow-up of matrix-guided autologous chondrocyte implantation ( MACI ) and microfracture. Radiologe.2004; 44(8): 773-782. [21] Bartlett W,Gooding CR,Carrington RWJ,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation at the knee using a bilayer collagen membrane with bone graft. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005; 87: 330-332. [22] Bartlett W,Krishnan SP,Skinner JA,et al. Collagen-covered versus matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for osteochondral defects of the knee. A comparison of tourniquet times. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2006; 16: 315-317. [23] Bartlett W,Skinner JA,Gooding CR,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation versus matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for osteochondral defects of the knee: a prospective,randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(5): 640-645. [24] Behrens P,Bitter T,Kurz B,et al. Matrix-associated autologous chondrocyte transplantation /implantation ( MACT/MACI)-5-year follow-up. Knee.2006; 13(3): 194-202. [25] Cherubino P,Grassi FA,Bulgheroni P,et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation using a bilayer collagen membrane: a preliminary report. J Orthop Surg.2003; 11(1): 10 -15. [26] D’Anchise R,Manta N,Prospero E,et al. Autologous implantation of chondrocytes on a solid collagen scaffold: clinical and histological outcomes after two years of follow-up. J Orthopaed Traumatol.2005; 6: 36-43. [27] Macarini L,Murrone M,Marini S,et al. Aspects of magnetic resonance in the surgical treatment of osteochondral lesions of the knee. Radiol Med.2003; 106(1-2) : 74-86. [28] Marlovits S,Striessnig G,Kutscha-Lissberg F,et al. Early postoperative adherence of matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for the treatment of full-thickness cartilage defects of the femoral condyle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2005; 13(6) : 451-457. [29] Marlovits S,Striessnig G,Resinger CT,et al. Definition of pertinent parameters for the evaluation of articular cartilage repair tissue with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol.2004; 52(3):310-319. [30] Ronga M,Grassi FA,Bulgheroni P. Arthroscopic autologous chondrocyte implantation for the treatment of a chondral defect in the tibial plateau of the knee. Arthroscopy.2004; 20(1):79-84. [31] Ronga M,Grassi FA,Manelli A,et al. Tissue engineering techniques for the treatment of a complex knee injury. Arthroscopy.2006; 22(5):576.e1-576 e3. [32] Ronga M,Grassi FA,Montoli C,et al. Treatment of deep cartilage defects of the ankle with matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation ( MACI).Foot Ankle Surg.2005; 11: 29-33. [33] Trattnig S,Ba-Ssalamah A,Pinker K,et al. Matrix-based autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage repair: noninvasive monitoring by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging.2005; 23(7):779- 787. [34] Zhang Z,Ye Q,Yang Z,et al. Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation for treatment of chondral defects of knee: a preliminary report. J Musculoskel Res.2006; 10: 95-101. [35] Zheng MH,Willers C,Kirilak L,et al. Matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation ( MACI) : biological and histological assessment. Tissue Eng.2007; 13(4): 737-746. [36] 荆志成.心脏胶原网络及其病理学意义[J].中国循环杂志,1998, 13(3):187-188.[37] 贺冬冬,曾令员,向川,等.Ⅰ/Ⅲ型胶原膜联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔膝关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(38): 7031-7036.[38] Vander Kraan PM , Buma P, Van Kuppevelt T, et al . Interaction of chondrocytes, extracellular matrix and growth factors :relevance for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002; 10(8): 631-637. |
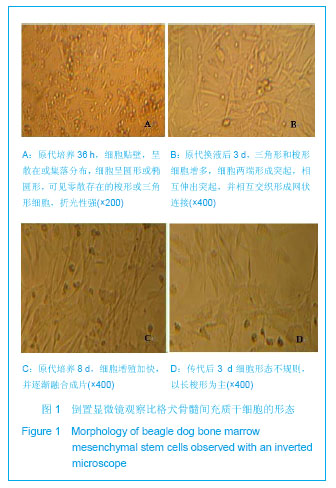
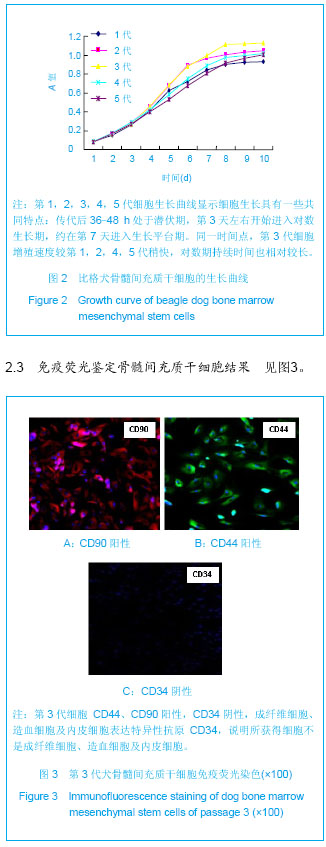
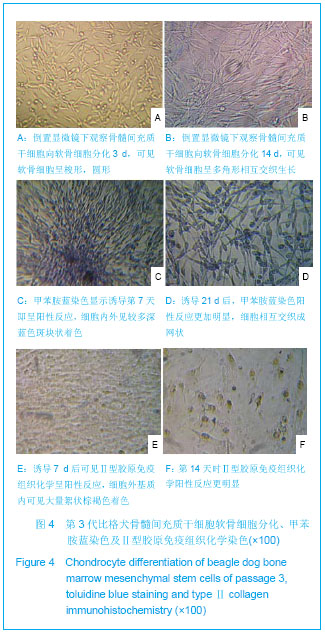
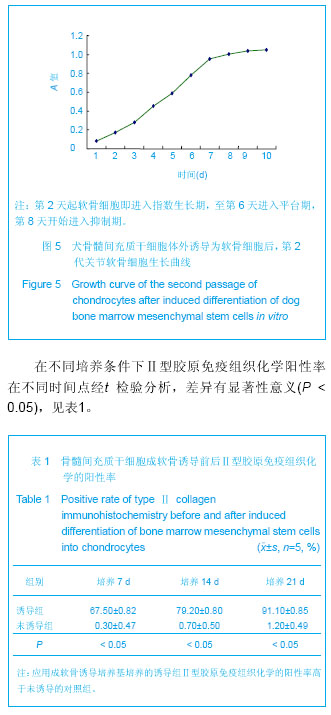
.jpg)