胫骨平台骨折是常见的主要承重关节的关节内骨折。治疗的关键是获得一个稳定、对位良好、活动正常且无痛的膝关节,以最大限度地减少膝关节创伤性关节炎的发生
[4-5]。胫骨上端周围皮质骨较为薄弱,具有纵向骨小梁,向上至同侧平台软骨下皮质骨,在平台皮质骨下方,有横行联合形骨小梁,与纵行骨小梁交叉状排列。胫骨平台的关节软骨下皮质骨较股骨髁薄弱,故骨的支撑力相应的减弱,暴力使胫骨平台和股骨髁相互撞击时,常引起胫骨平台骨折。由于外侧平台骨小梁分布密度不及内侧平台密集,骨支撑力相对较弱,膝外侧容易遭受侧方暴力,故外侧平台骨折多见。
人体膝关节主要负荷的直接承重部位是髁的中心区,胫骨软骨下的骨强度最大,但髁的前部骨强度相对较弱。近端胫骨的骨强度在内髁的中央部分最大,在外髁和周边的软骨部分骨强度呈下降趋势[4]。内侧平台关节面以及支撑该关节面的内侧部分比外侧部分要坚强,因此内侧平台骨折少见,但当一旦内侧平台发生骨折,往往是收到更为严重的暴力。但是,随着近年来高能损伤的增多,胫骨平台骨折的病理变化也越来杂越复,致使治疗十分困难,存在的主要问题是骨折难以满意复位、骨折碎片不稳定、不能有效固定、难以早期锻炼和术后感染。
胫骨内外两侧平台关节面呈鞍状。正位观略呈凹形,侧位观,平台关节面略呈凸形。内侧平台较大。外侧平台较小但比内侧平台高,这一解剖特点在固定时注意以免从外侧进入的螺钉进入内侧关节面。胫骨隆突位于内外两侧平台之间,不参与关节面的构成。此处向后顺序附有内侧半月板前角、前交叉韧带,外侧半月板前角,胫骨棘,外侧半月板后角,内侧半月板后角和后交叉韧带。胫骨上端周围皮质骨较为薄弱,具有纵向骨小梁,向上至同侧平台软骨下皮质骨,在平台皮质骨下方,有横行联合形骨小梁,与纵行骨小梁交叉状排列。胫骨平台的关节软骨下皮质骨较股骨髁薄弱,故骨的支撑力相应的减弱,暴力使胫骨平台和股骨髁相互撞击时,常引起胫骨平台骨折。由于外侧平台骨小梁分布密度不及内侧平台密集,骨支撑力相对较弱,膝外侧容易遭受侧方暴力,故外侧平台骨折多见。
人体膝关节主要负荷的直接承重部位是髁的中心区,胫骨软骨下的骨强度最大,但髁的前部骨强度相对较弱。近端胫骨的骨强度在内髁的中央部分最大,在外髁和周边的软骨部分骨强度呈下降趋势[4]。内侧平台关节面以及支撑该关节面的内侧部分比外侧部分要坚强,因此内侧平台骨折少见,但当一旦内侧平台发生骨折,往往是受到更为严重的暴力。后内侧平台骨折为屈曲位所导致的损伤,一般为冠状位骨折块。胫骨内侧髁关节面呈卵圆形并微凹,外侧髁的关节面呈三角形并微凸,胫骨两髁的关节面与股骨两髁不完全相称,其连接借助于其间的半月板。由内侧半月板所围绕的圆形区域是外侧半月板围绕区的大约1倍,股骨内侧髁与胫骨内侧髁在临近胫骨内侧髁间结节处的接触面较为宽大,而股骨外侧髁与胫骨外侧髁在临近胫骨外侧髁间结节处的接触面较为窄小。胫骨上端的关节面与胫骨干并不垂直,而是向后倾斜。Chiu等[6]报道胫骨平台内侧后倾角为(15.02±4.20)°,外侧后倾角为(11.74±3.80)°,无论正常或退变关节的胫骨平台后倾角,内侧大于外侧。Chiu等[6]通过尸体解剖和X射线影像学研究认为内侧平台后倾角与胫骨平台后倾角有紧密相关性,而外侧平台后倾角与胫骨平台后倾角无相关性。
由于胫骨平台约10°后倾角的存在[7],当胫骨固定时,股骨髁有后移的趋势。垂直于胫骨平台的力使胫骨平台发生应变,产生骨折。
平行于胫骨平台的力可使股骨髁在胫骨平台上向后滑动,决定胫骨平台骨折发生的位置。这两个力决定于:①膝关节受力的大小。②膝关节受力时的位置。③膝关节对抗股骨髁在胫骨平台上后移的组织力量的大小(伸膝装置、前交韧带等)。④胫骨平台骨的强度的大小。
胫骨平台后内侧骨折是膝关节屈曲位时,胫股关节面接触在胫骨平台后内侧,膝关节内翻,由强大的外力造成胫骨平台后内侧骨发生应变,造成骨质破坏。因为应力特点为垂直暴力为主,所以大部分骨折为后侧冠状面的劈裂骨折,同时由于骨的强度不同,可以出现劈裂塌陷型骨折。虽然膝关节外侧胫骨平台后倾角较内侧小,但膝关节总体后倾,膝关节外翻时时可造成后外侧胫骨平台的冠状骨折,二者的创伤机制相似,常常共同发生。二者治疗也相似,有些学者将二者共同研究。
在胫骨平台后内侧骨折的创伤机制的认识上曾经有过误区,Bhattacharyya等[8]报道1例前交叉韧带胫骨处止点撕脱合并胫骨后内侧的劈裂骨折的患者,认为此处骨折为撕脱性骨折。由于对其创伤机制的模糊认识,有人将其称为神秘骨折。在使膝关节屈曲60°-80°时,予以内翻应力,总是造成胫骨旋转,然后是膝关节前脱位或半脱位,先造成前交叉韧带损伤,最后造成胫骨平台后内侧骨折,有的骨折反而是半膜肌腱附着处骨折。他认为这种骨折是由于胫骨受内翻应力同时合并胫骨外旋应力造成了股胫关节内侧室的碰撞挤压和胫骨前移形成的。
国内外对胫骨平台骨折固定方法的临床报告较多, 张殿英等[9]采用AO技术治疗46例胫骨平台骨折,B1型行AO拉力螺钉固定;B2型行撬拨植骨加压螺钉内固定;B3型撬拨植骨复位后用T型或L型钢板固定;C1和C2型先用加压螺钉固定平台折块后,再用一两块T 型或L型钢板固定干骺端;C3型因无法行坚强内固定,则采用平台加压螺钉固定后再行跨膝桥形外固定架固定。随访39例,结果优良34例,可差5例。认为良好复位,稳妥固定,有效植骨支撑和早期功能锻炼,是膝关节顺利康复的重要因素。
李永山等[10]按Schatzker[11]分类,治疗43例胫骨平台骨折,其中Ⅰ型行切开复位松质骨螺钉内固定;Ⅱ、Ⅲ型行切开复位植骨钢板螺钉内固定; Ⅳ、Ⅴ、Ⅵ型行切开复位支持钢板加螺栓、螺钉内固定。对内固定稳妥者,内固定后即行CPM锻炼膝关节,否则以管型石膏固定4-6周,结果35例获得随访,优16例,良13例,中4例,差2例。认为正确复位操作和坚强内固定以及必要的植骨是维持胫骨平台关节面解剖或近解剖复位的关键。
胫骨平台骨折通常是以下暴力作用的结果:①直接作用于膝部的内翻或外翻暴力。②轴向压缩暴力以及侧向暴力同时作用。③轴向压缩应力。受伤时股骨髁对胫骨平台同时产生剪切力和压缩力,因此劈裂和压缩与劈裂合并压缩骨折最为常见,单纯的劈裂骨折常见于年轻患者,因为他们的胫骨髁坚强的骨质能够耐受住股骨髁对其施加的压缩暴力,随着年龄的增长,骨质开始变得疏松,其物理强度开始下降,它不能够再耐受股骨髁对其施加的压缩暴力。因此,劈裂压缩骨折多见于50岁以上的患者,且通常是低能量损伤引起。外侧平台骨折是由强大的外翻应力合并轴向负荷所引起,而内侧平台骨折则是由强大的内翻应力合并轴向负荷引起。冠状位的后内侧劈裂骨折是膝屈曲时遭受内翻和轴向负荷所引起。
骨折的形态同样能反映暴力的倾向,Kennedy和Bailey[12]在对死尸的膝部施加1 600-8 000 N的内(或外)翻暴力结合轴向负荷可以产生临床上常见的大多数骨折类型。2 250-3 750 N的内外翻负荷可以产生不同程度的关节塌陷和髁的分离。在高能量损伤中,暴力强大以致平台暴裂形成大量的碎骨片。生物力学研究证明,当轴向负荷超过8 000 N时,则产生严重的粉碎性骨折。这一机制的典型病例见子从高处坠落或车祸时轴向负荷作用于伸直的膝关节的患者。
由于内、外侧股骨髁的外形有所不同,外侧髁的前后径较内侧髁大,外侧髁的前后轴线基本上是矢状走向,而内侧髁的前后轴线通常与矢状面成22°左右夹角。所以屈曲90°时外髁要比内髁高,而膝关节的平面大致水平,所以内外髁的底在大致一个水平面上。所示当从上面予以轴向载荷时内外髁象两个楔子一样撞击胫骨平台,而膝关节有内翻的趋势,所以能先造成内侧平台骨折。
正常膝关节股胫关节负荷面伸直时平均为 20.13 cm2,股、胫骨髁接触面位于关节前面附近,屈曲时负荷面后移至关节面后方并面积减少。沈扬等[13]认为膝关节伸屈运动轨迹以股胫2∶1的关节面长度作滚动和滑动,亦即随着膝屈曲度增加,股骨髁在胫骨髁关节面上相对应位置也逐渐向后移。如膝屈曲在30°-45°时股胫对应位置在胫骨平台中1/3,在60°以上时股胫对应位置在胫骨平台后1/3。
正常情况下股骨在矢状方向上可发生前后移位,但由于交叉韧带的制导作用,其范围不应超过3-5 mm;胫骨相对固定,胫骨平台后倾角的存在,使股骨髁在承受轴向载荷时有向后“下坡”的趋势;随着载荷的增大,当其后移的分力超过股骨髁在与胫骨髁之间的摩擦力时,整个膝关节发生应变,首先股骨后移,前交叉韧带发生应变,当达到其极限载荷时,前交叉韧带破坏;膝关节此时只有股骨髁后部与后侧胫骨平台关节面接触,所以应变在此处发生。由于股骨髁的强度大于胫骨,其应变也大于胫骨,当载荷达到极限点时,则出现破坏,即胫骨平台后内侧骨折。而此时股骨髁由于载荷作用与破坏的胫骨平台形成新的角度。当载荷向后的分力不能克服股骨髁在与胫骨髁之间的摩擦力及前交叉韧带的拉应力,使股骨髁向后的位移较小时,则应变有可能稍靠前发生。由于膝关节内翻,压力载荷内倾,致胫骨平台内髁压力大于外髁,故全部标本均出现胫骨平台后内侧骨折。而外侧胫骨平台骨折只有5例。在膝关节屈曲90°时前交叉韧带与关节面几近平行,而且最紧张。但仔细分析,在伸直时,仅前部纤维紧张;开始屈曲时,胫骨内旋,前部纤维松弛,而中部纤维紧张;完全屈曲时,后外侧纤维变为紧张。Kenedy等[14]发现膝关节在完全伸直、屈曲5°及20°时,前交叉韧带紧张。在屈曲40°及50°时最为松弛,但当屈曲70°-90°时又变为紧张。在所有屈曲位置下,胫骨内旋均使前交叉韧带紧张。
在实验中,胫骨固定,股骨由于受力有向后“下坡”的趋势,胫骨相对于股骨向前,使前交叉韧带紧张,随着应力的增大,当超过其极限载荷时,则发生破坏。实验中发现有7例前交叉韧带损伤。前交叉韧带的极限载荷略小于胫骨平台的极限载荷,前交叉韧带断裂后膝关节失去“制导”作用,股骨髁在胫骨平台上滑动,而此时载荷不能造成骨折,载荷在此时停止上升趋势,在时间—载荷曲线上则表现为前交叉韧带损伤时间段的载荷平台期,因此前交叉韧带在胫骨平台后内侧骨折的创伤机制中扮演着重要的角色。
胫侧副韧带在屈曲时后部纤维紧张,载荷加大时可造成其损伤,但由于其极限载荷较小,在时间-载荷曲线曲线不能显现。腓侧副韧带在膝关节屈曲时松弛,当压应力达到一定程度,内翻达到一定程度时才出现损伤。同样由于其极限载荷较小,在时间-载荷曲线上不表现。膝关节屈曲时,两个半月板均向后移动,但程度不同,内侧半月板仅向后移动几毫米,但外侧半月板向后至少1 cm。完全屈曲时,两个半月板的后部正位于股骨髁及胫骨髁之间。在过度屈曲时,其向后滑动甚至可突出于胫骨的后缘1 cm,其形状亦相应发生改变,外侧半月板更是如此。
实验时,由于膝关节内翻,内侧半月板挤压在股骨髁于胫骨髁之间,外侧半月板受力相对较小,所以内侧半月板较易受伤,外侧半月板损伤的概率则较少。由于实验标本剔除了周围的肌肉等软组织,使损伤机制简单化。实际上,该损伤机制发生前还有一个重要的保护机制,既伸膝装置。屈曲时它可限制胫骨前移,胫骨固定时可限制股骨后移,此时膑骨及膑韧带上有一个拉应力,由于股四头肌张力较大,伸缩性好,所以并不出现明显的伸膝装置损伤。
由以上综合分析可知,由于胫骨平台后倾角的存在,当胫骨固定时,股骨髁有后移的趋势。垂直于胫骨平台的力使胫骨平台发生应变,产生骨折。平行于胫骨平台的力可使股骨髁在胫骨平台上向后滑动,决定胫骨平台骨折发生的位置。这两个力决定于:①膝关节受力的大小。②膝关节受力时的位置。③膝关节对抗股骨髁在胫骨平台上后移的组织力量的大小(伸膝装置、前交韧带等)。④胫骨平台骨的强度的大小。
胫骨平台后内侧骨折是膝关节屈曲位时,胫股关节面接触在胫骨平台后内侧,膝关节内翻,由强大的外力造成胫骨平台后内侧骨发生应变,造成骨质破坏。因为应力特点为垂直暴力为主,所以大部分骨折为后侧冠状面的劈裂骨折,同时由于骨的强度不同,可以出现劈裂塌陷型骨折。虽然膝关节外侧胫骨平台后倾角较内侧小,但膝关节总体后倾,膝关节外翻时时可造成后外侧胫骨平台的冠状骨折,二者的创伤机制相似,常常共同发生。二者治疗也相似,有些学者将二者共同研究。
在胫骨平台后内侧骨折的创伤机制的认识上曾经有过误区,Bhattacharyya等[15]报道1例前交叉韧带胫骨处止点撕脱合并胫骨后内侧的劈裂骨折的患者,认为此处骨折为撕脱性骨折。由于对其创伤机制的模糊认识,有人将其称为神秘骨折。在使膝关节屈曲60°-80°时,予以内翻应力,总是造成胫骨旋转,然后是膝关节前脱位或半脱位,先造成前交叉韧带损伤,最后造成胫骨平台后内侧骨折,有的骨折反而是半膜肌腱附着处骨折。他认为这种骨折是由于胫骨受内翻应力同时合并胫骨外旋应力造成了股胫关节内侧室的碰撞挤压和胫骨前移形成的。Gardner等[16]报道软组织损伤的几率为77%。胫骨平台后内侧骨折为高能量损伤,其合并软组织损伤的几率更大。从以上创伤机制可知,胫骨平台后内侧骨折发生前,前方软组织已经损伤。Vanek[17]报道1例病例也有前交叉韧带损伤,而他的19具标本实验中,均有前交叉韧带损伤,他认为这种创伤机制是必然合并前交叉韧带的损伤。正是由于胫骨平台内后侧损伤对膝关节稳定性的严重破坏,所以对其妥善的复位和固定对恢复膝关节功能相当重要。
三种固定方式生物力学特点:
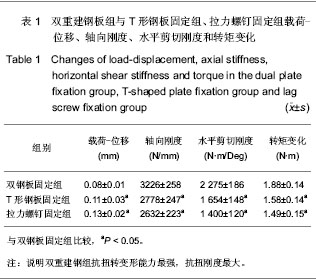
不同方式固定胫骨平台后内侧骨折的载荷-位移:胫骨平台在生理载荷作用下,载荷-位移关系成线性规律变化,随着载荷的加大,位移不断增加。载荷在1 000 N时,双重建钢板组位移比较小,占有一定的优势,与T形钢板固定组、拉力螺钉固定组比较呈显著性差异(t=2.769,P < 0.05)。这与双重建钢板提供了双轴力学支持有关。
不同方式固定胫骨平台后内侧骨折的刚度:胫骨平台上的轴向刚度仍然以双重建钢组最大(3 226 N/mm),其次是T型钢板固定组(2 778 N/mm),而拉力螺钉固定组(2 632 N/mm)最小。三者相比,双重建钢板组与T形钢板固定组、拉力螺钉固定组比较统计有显著性差异(t=3.149,P < 0.05)。证明采用双重建钢板固定胫骨平台内后侧骨折是十分稳固的,抗变形能力很强。这与双重建钢板为骨折块提供了“梁网状”结构有关,同时与双重建钢板应用了比T型钢板多一倍的螺钉有关。
胫骨平台固定后的抗扭力学性能:胫骨平台内外侧骨折3种固定方法中,若以胫骨平台内外侧骨折3种固定方法的抗扭转变形能力来比较,即抗扭刚度(GJρ)的大小来比较的话,双重建钢板组GJ为7.83 N·m/Deg,T形钢板固定组为6.21 N·m/Deg,拉力螺钉固定组为6.58 N·m/Deg。对3组扭转刚度进行比较,结果显示双重建钢组组抗扭转变形能力最强,抗扭刚度最大,统计表明三者差异显著性意义(t=2.342,P < 0.05)。由于双重建钢板远端采用两排3枚3.5 mm皮质骨螺钉不同方向上进行固定,从而更能产生较强的抗扭力学性能。双重建钢板良好可塑性,增加了其与骨质的摩擦力。
综上所述,双重建钢为胫骨平台内后侧骨折提供了持续、稳定的固定,有效的防止了骨折再次蹋陷和移位,可以提高胫骨平台内外侧骨折的手术效果,值得推荐。
.jpg)