| [1] Pratt A J, Getzoff E D, Perry J J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: update and new developments. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis.2012;2012(2):1-14.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23019386[2] Benkler C, Offen D, Melamed E, et al. Recent advances in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis research: perspectives for personalized clinical application. EPMA J.2010;1(2):343-361.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23199069[3] Venkova-Hristova K, Christov A, Kamaluddin Z, et al. Progress in therapy development for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurol Res Int. 2012;2012:187234.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22830014[4] Naganska E, Matyja E. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis - looking for pathogenesis and effective therapy. Folia Neuropathol.2011;49(1):1-13.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21455838[5] Thonhoff JR, Ojeda L, Wu P. Stem cell-derived motor neurons: applications and challenges in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009;4(3):178-199.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19492980[6] Hefferan MP, Galik J, Kakinohana O, et al. Human neural stem cell replacement therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by spinal transplantation. PLoS One.2012;7(8):e42614.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22916141[7] Wang DB, Gitcho MA, Kraemer BC, et al. Genetic strategies to study TDP-43 in rodents and to develop preclinical therapeutics for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci.2011;34(8):1179-1188.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21777407[8] Rosen DR. Mutations in CuZn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature.1993;362:59-62.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8446170[9] Turner BJ, Talbot K. Transgenics, toxicity and therapeutics in rodent models of mutant SOD1-mediated familial ALS. Prog Neurobiol.2008;85(1):94-134.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18282652[10] Julien J. Mouse models of amyotrophic lateralsclerosis. Drug Discovery Today: Disease Models. 2006;3(4):331-339.http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1740675706000727[11] Mali Y, Zisapel N. A novel decoy that interrupts G93A-superoxide dismutase gain of interaction with malate dehydrogenase improves survival in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis cell model. J Med Chem. 2009;52(17):5442-5448.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19670830[12] Koh SH, Lee YB, Kim KS, et al. Role of GSK-3beta activity in motor neuronal cell death induced by G93A or A4V mutant hSOD1 gene. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22(2):301-309.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16045483[13] Gurney ME, Pu H, Chiu AY. moter neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science. 1994;5166(264):1772-1775.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8209258[14] Joyce PI, Fratta P, Fisher EM, et al. SOD1 and TDP-43 animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: recent advances in understanding disease toward the development of clinical treatments. Mamm Genome.2011;22(7-8):420-448.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21706836[15] Rj M, Ej B, Aj K, et al. Optimised and Rapid Pre-clinical Screening in the SOD1G93A Transgenic Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Plos One. 2011;6(8):e23244.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21876739[16] Huang H, Zhang C, Xi J, et al. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2006;26(3):258-260.黄慧,张成,席静,等. 家族性肌萎缩侧索硬化症转基因鼠的繁殖和鉴定[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2006,26(3):258-260.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DYJD200603002.htm[17] Guo YS, Yu JX, Duan WS, et al. Nao yu Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 郭艳苏,于继徐,段伟松,等. SOD1-G93A转基因小鼠的鉴定方法比较[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志,2009;17(4): 268-270.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LYSJ200904009.htm[18] Henriques A, Pitzer C, Schneider A. Characterization of a novel SOD-1(G93A) transgenic mouse line with very decelerated disease development]. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e15445.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21102999[19] Qian Y, Ye BQ, Geng JG, et al. Shiyan Dongwu yu Bijiao Yixue. 2009;29(2):124-126.钱云,叶步青,耿建国,等. DNA检测技术在基因剔除小鼠保种中的初步应用[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,2009,29(2):124-126.http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=30139998[20] Alves C J, de Santana L P, Dos S A, et al. Early motor and electrophysiological changes in transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and gender differences on clinical outcome. Brain Res. 2011;1394:90-104.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21354109[21] Bame M, Pentiak P A, Needleman R, et al. Effect of Sex on Lifespan, Disease Progression, and the Response to Methionine Sulfoximine in the SOD1 G93A Mouse Model for ALS. Gend Med. 2012;9(6):524-535.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23217569[22] Herron LR, Miles GB. Gender-specific perturbations in modulatory inputs to motoneurons in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroscience. 2012;226:313-323.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23000617[23] Huisman MH, de Jong SW, van Doormaal PT, et al. Population based epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using capture-recapture methodology. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82(10):1165-1170.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21622937[24] Manjaly ZR, Scott KM, Abhinav K, et al. The sex ratio in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A population based study. Amyotroph Lateral Scler.2010;11(5):439-442.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20225930[25] Miller RG, Anderson FJ, Bradley WG, et al. The ALS patient care database: goals, design, and early results. ALS C.A.R.E. Study Group. Neurology. 2000;54(1):53-57.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10636125[26] Choi CI, Lee YD, Gwag BJ, et al. Effects of estrogen on lifespan and motor functions in female hSOD1 G93A transgenic mice. J Neurol Sci. 2008;268(1-2):40-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18054961[27] Bromberg M B. Pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a critical review. Curr Opin Neurol.1999;12(5):581-588.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10590895[28] de Jong S, Huisman M, Sutedja N, et al. Endogenous female reproductive hormones and the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol,2012.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22972621[29] Czlonkowska A, Ciesielska A, Gromadzka G, et al. Estrogen and cytokines production - the possible cause of gender differences in neurological diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2005;11(8):1017-1030.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15777251[30] Popat RA, Van Den Eeden SK, Tanner CM, et al. Effect of reproductive factors and postmenopausal hormone use on the risk of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology. 2006;27(3):117-121.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16946622[31] Xiao AQ. Shengwuxue Jiaoxue. 2009;34(4):69.肖安庆.动物"杀婴"为哪般?[J]. 生物学教学,2009,34(4):69.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWJX200904041.htm[32] Günther R, Suhr M, Koch JC, et al. linical testing and spinal cord removal in a mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). J Vis Exp. 2012;(61). pii: 3936.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22453893[33] Knippenberg S, Thau N, Dengler R, et al. Significance of behavioural tests in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Behav Brain Res. 2010;213(1):82-87.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20450936[34] Kafkafi N, Yekutieli D, Yarowsky P, et al. Data mining in a behavioral test detects early symptoms in a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Behav Neurosci. 2008;122(4):777-787.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18729631[35] 鲁绍雄,毛华明,鲁立刚,等. 不同初始基因频率下闭锁群体遗传漂变的模拟[J]. 江苏农业学报,2009(5):991-996.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JSNB200905008.htm[36] Tonsor S J. Population genomics and the causes of local differentiation[J]. Mol Ecol,2012,21(22):5393-5395.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23281496[37] Willi Y, Griffin P, Van Buskirk J. Drift load in populations of small size and low density. Heredity (Edinb). 2013;110(3):296-302.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23211785[38] Niemann H, Lucas-Hahn A. Somatic cell nuclear transfer cloning: practical applications and current legislation. Reprod Domest Anim. 2012;47 Suppl 5:2-10.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22913555[39] Zheng S, Geghman K, Shenoy S, et al. Retake the center stage--new development of rat genetics. J Genet Genomics. 2012;39(6):261-268.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22749013[40] Devoy A, Bunton-Stasyshyn R K, Tybulewicz V L, et al. Genomically humanized mice: technologies and promises. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13(1):14-20.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22179716[41] Xu P, Liu LJ, Yu LL, et al. Zhongguo Bijiao Yixue Zazhi. 2009;19(8):9-14.徐平,刘丽均,郁丽丽,等. 系统低温生物学技术在实验小鼠资源保存中的建立与应用[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2009,19(8):9-14.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDX200908004.htm[42] Saragusty J, Arav A. Current progress in oocyte and embryo cryopreservation by slow freezing and vitrification. Reproduction. 2011;141(1):1-19.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20974041[43] Leibo SP. Cryopreservation of oocytes and embryos: optimization by theoretical versus empirical analysis. Theriogenology. 2008;69(1):37-47.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18023472 |

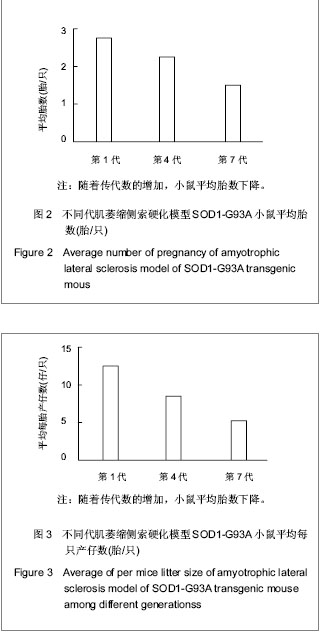
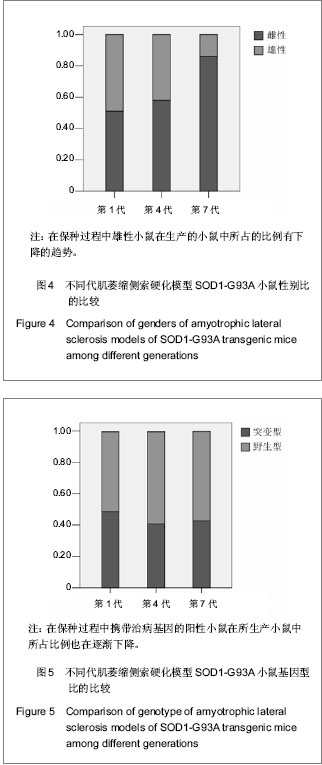
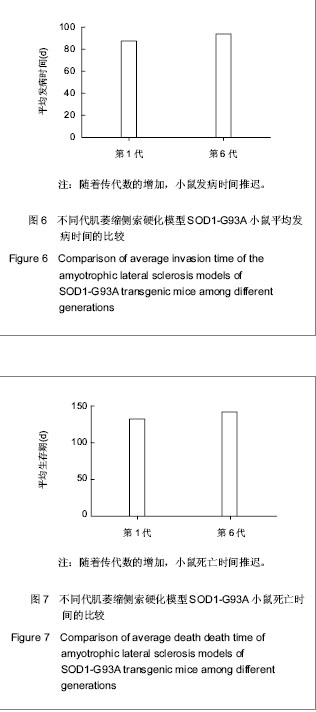
.jpg)