| [1] Hofbauer LC, Schoppet M. Clinical implications of the steoprotegerin/RANKL/RANK system for bone and vascular diseases.JAMA. 2004;292(4):490-495. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15280347 [2] Brad B , Victoria S , Paul JK, et al . Osteoprotegerin , an endogenous antiosteoclast factor for protecting bone in rheumatoid arthritis. Aethritis Rheum. 2002;46(12):3121-3135. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12483715[3] Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastgenesis , lymphocyte development and lympya - node organogenesis. Nature. 1999;39(7):315-323. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=9950424[4] Soysa NS, Alles N. NF-KB functions in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;378(1):1-5. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=18992710[5] Bocyce BF, Xing L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;473(2):139-146. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=18395508 [6] Naoko Y, Tohru T, Haruyasu U, et al. Down-regulationg of osteoprotegerin production in bone marrow macrophages by macrophage colony stimulating factor. Cytokine. 2005;31(28):288-297. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15996478[7]. Teitelbaum SL.Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science(Washington DC). 2000; 289(5484) : 1504-1508. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10968780[8].. Rodan GA, Martin TJ.Therapeutic approaches to bone diseases. Science. 2000; 289 (5484) : 1508-1514. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10968781[9]. Cheng T, Dai M, Fan HX, et al. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2007;24(1):113.程涛, 戴闽, 范红先, 等.氧化铝陶瓷和高分子聚乙烯颗粒诱导体内生物学效应和细胞凋亡的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(1):113.http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91364X/200701/23832376.html [10].Battaglino R,Kim D,Fu J,et al.C-myc is required for osteoclast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(5):763-773. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12009006[11].Kieslinger M, Folberth S, Dobreva G, et al. EBF2 regulates osteoblast dependent differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2005; 9(6): 757-767. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=16326388[12]. Tsubaki M, Kato C, Manno M, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha MIP-1alpha enhances a receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand RANKL expression in mouse bone marrow stromal cells and osteoblasts through MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;304(1-2):53-60. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17549607[13].Takeshita S,Kaji K,Kudo A. Identification and characterization of the new osteoclast progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(8):1477-1488. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10934646[14].Monici M,Fusi F,Paglierani M,et al. Modeled gravitational unloading triggers differentiation and apoptosis in preosteoclastic cells. Cell Biochem. 2006;98(1): 65-80. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=16365883 [15].Ishizuka S,Kurihara N,Hiruma Y,et al. 1alpha 25-Dihydroxy vitamin D(3)-26,23-lactam analogues function as vitamin D receptor antagonists in human and rodent cells. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008;110(3-5):269-277. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=18501591[16].Kobayashi Y,Mizoguchi T,Take I,et al. Prostaglandin E2 enhances osteoclastic differentiation of precursor cells through protein kinase A - dependent phosphorylation of TAK1. Biol Chem. 2005;280(12):1395-1403. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=15647289 [17].Xiao XH, Liao EY, Dong YY. Nanhua Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2008;36(3):282-285.肖新华,廖二元,董源媛. 小鼠单核细胞RAW264.7的细胞生物学特征[J]. 南华大学学报: 医学版, 2008,36(3):282-285.http://www.cqvip.com/qk/96889A/200803/28165868.html [18].Geng DC,Xu YZ,Yang HL,et al. Cannabinoid receptor-2 selective antagonist negatively regulates receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand mediated osteoclastogenesis. Chin Med. 2011;124(4):586-590. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=21362286 [19]. Liu C,Walter TS,Huang P,et al. Structural and functional insights of RANKL-RANK interaction and signaling. J Immunol. 2010;184(12):6910-6919. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=PMID%3A%2020483727 [20] Tsurukai T, Udagawa N, Matsuzaki K. Role of macrophage-colony stimulating factor and osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis. Bone Miner Metab. 2000;12(18):177. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=10874596[21] Lee SW, Kwak HB, Chung WJ, et al. Participation of protein kinase Cβin osteoclast differentiation and function. Bone. 2003;32 (17):217-227. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12667549[22] Udagawa N,Takahashi N,Akatsu T,et al.Origin of osteoclasts:mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,1990,87(18);7260-7264. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=2169622[23] Lee SE, Chung WJ, Kwak HB, et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Supports the Survival of Osteoclasts through the Activation of Akt and ERK. Biol Chem. 2001;276(52) :49343-49349. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=11675379http://www.jbc.org/content/276/52/49343.long [24].Takahashi N,Udagawa N,Kobayashi Y,et al. Generation of osteoclasts in vitro and assay of osteoclast activity. Methods Mol Med. 2007;135:285-301. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=17951666[25].He X,Andersson G,Lindgren U,et al. Resveratrol prevents RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of murine osteoclast progenitor RAW 264.7 cells through inhibition of ROS production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401(3):356-362. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=20851107 [26].Hu L,Lind T,Sundqvist A,et al. Retinoic acid increases proliferation of human osteoclast progenitors and inhibits RANKL-stimulated osteoclast differentiation by suppressing RANK. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):13305. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=20949013[27].Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL.Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003; 423(6937): 337-342. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=12748652[28].Ferlin A, Pepe A, Facciolli A, et al. Relaxin stimulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Bone. 2010; 46(2): 504-513. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=19833242[29] Wu HY, Li J, Tang ZG. Zhongguo Kangfu Yixue Zazhi. 2005;20(4):248-250.吴贺勇,李娟,唐井钢.补肾中药对破骨细胞骨吸收功能的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2005,20(4):248-250.http://wzhz.cqvip.com/hzpinglaoshi/qk/90850X/200504/15704606.html [30] Zhan HS, Shi YY, Zhao YF. Zhongyao Xinyao yu Linchuang Yaoli. 2001;12(5):326-328.詹红生, 石印玉, 赵咏芳.含补肾益精方的切卵大鼠血清对破骨细胞骨吸收功能的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2001, 12(5):326-328.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zyxyylcyl200105005.aspx [31] Chen M, Zheng Q, Fang ZH, et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2008;16(4):282-284.陈明,郑琼,方真华,等. 阿伦膦酸钠对骨髓生成破骨细胞骨吸收作用的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(4):282-284.http://www.cqvip.com/qk/97753A/200804/26610447.html |



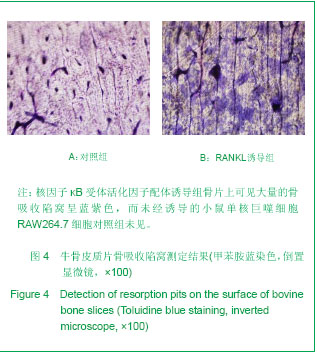
.jpg)