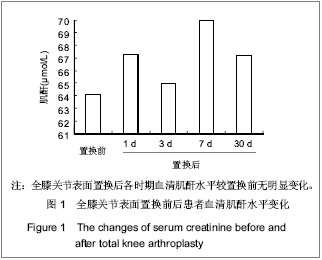
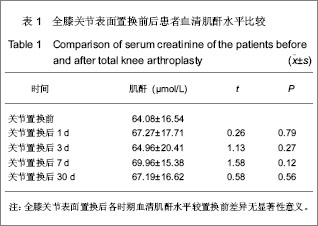
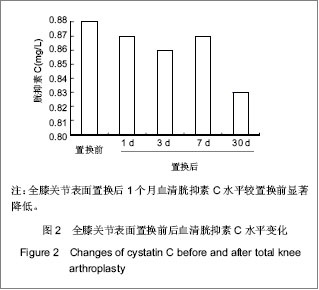
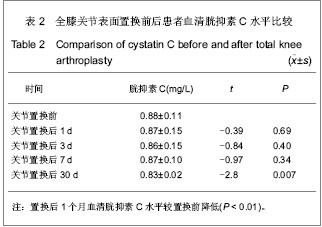
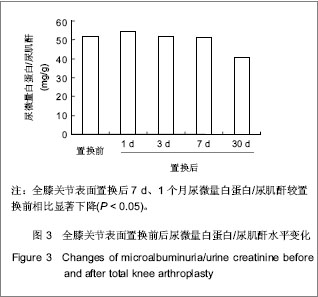
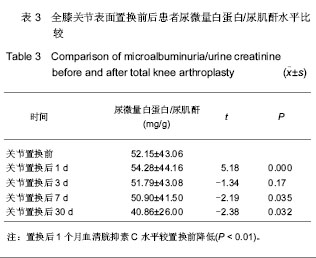
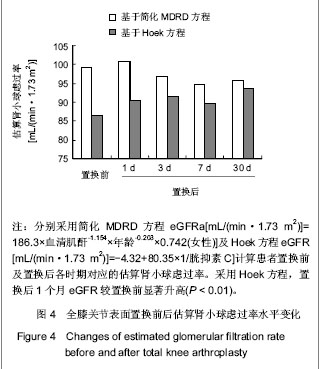
| [1]Lachiewicz PF, Soileua ES. Fifteen-year survival and osteolysis associated with a modular posterior stabilized knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(6):1419-1423.[2]Alan Cheung, Seo Kiat Goh, Andrew Tang, et al. Complications of total knee arthroplasty. Current Orthopaedics. 2008;22:274-283 .[3]Pavone V, Johnson T, Saulog PS, et al. Perioperative Morbidity in Bilateral One-Stage Total Knee Replacements.CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH.2004;421: 155-161. [4]Curtis JM, Sternhagen V, Batts D. Acute renal failure after placement of tobramycin-impregnated bone cement in an infected total knee arthroplasty. Pharmacotherapy. 2005; 25(6):876-80.[5]Dovas S, Liakopoulos V, Papatheodorou L, et al. Acute renal failure after antibiotic-impregnated bone cement treatment of an infected total knee arthroplasty. Clinical Nephrology. 2008; 69(3): 207-212.[6]Lapsley M, Sansom PA, Marlow CT, et al. Beta 2-glycoprotein-1 (apolipoprotein H) excretion in chronic renal tubular disorders: Comparison with other protein markers of tubular malfunction. J Clin Pathol.1991;44(10):612-816.[7]Li HX,Zhang CL,Xu GB,et al.Zhonghua Jianyan Yixue Zazhi. 2006;29:970- 974.李海霞,张春丽,徐国宾,等.健康人群血清半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂C与肌酐分布及其评价慢性肾脏病患者肾小球滤过率功能的比较研究[J].中华检验医学杂志, 2006, 29:970- 974. [8]Yang YS,Peng CH,Liu CK, et al.Use of serum CysC to detect early decline of glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetes.J Intern Med.2007;46(12):801-806.[9]Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury .2012; 2:8-12[10]Liu FX,Zhu GY,Su DL.Zhonghua Shiyong Zhenduan yu Zhiliao Zazhi. 2012;26(1):23-24.刘富新,朱国勇,苏大林.血清胱抑素-C水平在骨性关节炎诊断中价值[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2012,26(1):23-24.[11]Li JC,Chao SB,Chen XW.Shiyong Linchuang Yixue. 2010; 11(7):11-12.李建春,巢时斌,陈小文.胱抑素C联合尿微量白蛋白检测对早期肾功能损害的研究[J].实用临床医学,2010,11(7):11-12.[12]Nergelius G, Lidgren L, Grubb A, et al.Renal dysfunction after total knee replacement is not aggravated by bone cement. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.1998; 42: 974-981.[13]Fernando José Abelha, Miguela Botelho, Vera Fernandes ,et al. Determinants of postoperative acute kidney injury. Critical Care. 2009;13(3):R79.[14]Tang I, Murray PT. Prevention of perioperative acute renal failure: what works? Best Prac Res Clin Anaesth.2004; 18: 91-111.[15]Mangano CM, Diamondstone LS, Ramsay JG,et al. Renal dysfunction after myocardial revascularization: risk factors, adverse outcomes and hospital resource utilization. The Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group. Ann Intern Med.1998; 128:194-203.[16]Ma WH,Zhang SD,Wang SJ,et al.Zhonghua Guanjie Waike Zazhi:Dianziban. 2011;5(6):728-732.马卫华,张树栋,王诗军,等.止血带的使用方式对膝关节置换术失血量和手术时间的影响[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011, 5(6):728-732.[17]Yang TD,Tao J.Zhongqing Yixue. 2006;35(8):673-674.杨天德,陶军,吴悦维,等.术中使用骨水泥引起的严重心血管功能紊乱[J].重庆医学,2006,35(8):673-674.[18]Orsini EC, Byrick RJ, Mullen JBM, et al. Cardiopulmonary function and pulmonary microemboli during arthroplasty using cemented or non-cemented components.Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1987;69-A: 822-832.[19]Nolan JP. Arterial oxygenation and mean arterial blood pressure in patients undergoing total hip replacement: cemented versus uncemented components. Anaesthesia. 1994;49: 293-299.[20]Dai YJ,Wang JR,Ma YL,et al.Hulixue Zazhi. 2010,25(2):49-51.代永静,王建荣,马燕兰,等.液体温度对双侧人工关节置换患者术中肾功能的影响[J].护理学杂志,2010,25(2):49-51.[21]Gee R, Munk P, Keogh C, et al. Radiography of the PROSTALAC (Prosthesis with Antibiotic-Loaded Acrylic Cement) orthopedic implant. Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180:1701-1706.[22]Belt H, Neut D, Schenk W, et al. Infection of orthopedic implants and the use of antibiotic-loaded bone cement. Acta Orthop Scand .2001;72:557-571.[23]Bertazzoni Minelli E, Benini A, Magnan B, et al. Release of gentamicin and vancomycin from temporary human hip spacers in two stage revision of infected arthroplasty.J Antimicrob Chemother.2004;53:329-334.[24]Sterling GJ, Crawford S, Potter JH, et al. The pharmacokinetics of Simplex-tobramycin bone cement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85B:646-649.[25]Goetz MB, Sayers J. Nephrotoxicity of vancomycin and aminoglycoside therapy separately and in combination. J Antimicrob Chemother .1993;32:325-334.[26]Namba RS, Chen Y, Paxton EW, et al.Outcomes of Routine Use of Antibiotic-Loaded Cement in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J The Journal of Arthroplasty. 2009 ;24(6):44-47.[27]Hermann M, Shaw S, Kiss E ,et al. Selective COX-2 inhibitors and renal injury in salt-sensitive hypertension. 2005; 45(2): 193-197.[28]Fu ZQ,Lv GY,Deng NF.Zhongri Youhao Yiyuan Xuebao. 2007; 21(3):178-180.付志强,吕国义,邓廼封.氟比洛芬酯的药理及临床应用[J].中日友好医院学报,2007,21(3):178-180. [29]Nishikawa T, Edelstein D, Du XL, et al. Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathway of hyperglycaemic damage. J Nature,2002;404: 787-790.[30]van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, et al. Intensive insulin therapy in the critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 2001; 345:1359-1367.[31]Huang SJ.Guowai Yixue:Yaoxue Fence. 2000,27(1):21-24.黄世杰.肾保护作用和抗高血压药物的现况[J].国外医学:药学分册.2000,27(1):21-24. |