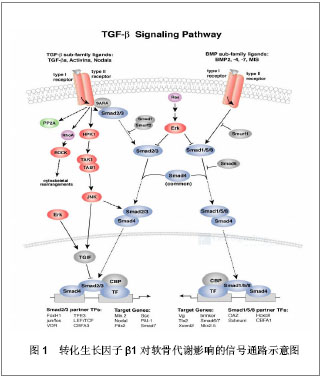
| [1] Li H, Haudenschild DR, Posey KL, et al. Comparative analysis with collagen type II distinguishes cartilage oligomeric matrix protein as a primary TGFβ-responsive gene. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011; 19(10): 1246-1253..[2] Everett ET. Fluoride's effects on the formation of teeth and bones,and the influence of genetics. Dent Res. 2011;90(5): 552-560.[3] Tachi K,Takami M,Sato H,et al.Enhancement of bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced ectopic bone formation bytransforming growth factor-β1[J]. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(5-6):597-606.[4] 尹君,高传芳. 浅议TGF-β与原发性骨质疏松[J]. 临床医学, 2011, 26:86-87.[5] 王惠娟,董进. 转化生长因子 β 对成骨细胞增殖、BMP- 2及 Cbfal 基因表达的影响[J]. 中国当代医药,2011,18(22):21-23.[6] Wakefield LM, Stuehcn C. Keeping order in the neighborhood: newroles forTGF beta in maintaining epithelial homeostasis. CancerCel,l 2007;4: 293-295.[7] Sila Asna M,Bunyaratvej A,Maeda S,et al.Osteoblast differentiation and bone formation gene expression in stron-tium inducing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell.Kobe J Med Sci.2007;53(12):25 -35.[8] 王维刚,王志刚,李大鹏,等. 骨肽对骨髓间充质干细胞TGF-β1表达的影响[J].中国实验诊断学,2012,16(4): 607-608.[9] 樊志强,庞炜,杨连甲,等. 白介素 1 受体拮抗剂及转化生长因子 β1 对兔膝关节骨性关节炎(OA)的治疗研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(13):2447-2450[10] 陈宁杰. 血管内皮细胞生长因子和转化生长因子β1在骨关节炎滑膜组织中的表达及相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(2):288-291.[11] 田峰,崔学生,张帅,等.转化生长因子β1及白介素-1β对终板软骨细胞的作用[J]. 重庆医学,2012,41(1): 36-37,39.[12] 顾海伦,刘莉,王欢,等. d-BMP-2和Ad-TGF-β1共转染人退变椎间盘髓核细胞对细胞外基质代谢的影响[J]. 生物医学工程与临床,2009,13(1):58-61.[13] 俞猛,于方,付胜良,等.TGF-β1和bFGF对骨髓基质干细胞增殖、分化的影响[J]. 中国骨肿瘤骨病,2006,5(6): 321-325.[14] 郑丽芳,张小乔,张红,等.Snail基因沉默对转化生长因子- β1促进骨髓间充质干细胞迁移的抑制作用[J]. 解剖学报,2008,39(5): 717-722.[15] Couchourel D, Aubry I, Delalandre A,et al. Altered mineralization of human osteoarthritic osteoblasts is attributable to abnormal type I collagen production. Arthritis Rheum.2009;60(5):1438-1450.[16] 郭静,李琪佳. TGF-β1在骨性关节炎中的表达及与关节软骨和滑膜细胞凋亡的关系[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2008,11(4): 462-465.[17] 孔祥英,万蓉,李莉,等.不同治法方药对激素性股骨头坏死鸡成骨相关因子的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2011,36(5):614-617. [18] 王磊磊,金格勒,任龙龙,等. 不同植骨材料在腰椎融合过程中的应用及转化生长因子β的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(16):2885-2888.[19] 鲁茂森,夏亚一,袁凌伟,等. 转化生长因子β1与软骨源性形态发生蛋白1修复关节软骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(50):9824-9826[20] 易成清,曹云,马成辉,等.pAD- TGF-β1骨组织工程种子细胞转归的转基因保护[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(2):127-135.[21] 胡振宇. TGF-β1促进rhBMP-2对成骨前体细胞增殖分化的观察[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,22(1):24-26.[22] 杨冠,杨晓.TGF-β超家族在软骨发生、发育和维持中的作用[J].遗传,2008,30(8):953 -959.[23] Cabiling DS, Kim E, Yan D, et al. Differentialeffects of TGF-beta isoforms on murine fetal dural cells and calvarialosteoblasts.Plast Reconstr Surg.2007;120(3): 614-624.[24] 郑纪伟,高玉光,胡温庭,等.骨涎蛋白、骨桥蛋白在小鼠骨组织和牙胚组织发育中的表达[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2009,6(12): 123-128.[25] 尹琳,谢静,蒋稼欢,等. TGF-β1刺激下损伤的前交叉韧带和内侧副韧带中 BMP-1基因的表达[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2012, 34(7): 647-650.[26] 吴剑.转化生长因子β与骨关节炎的研究进展[J].医学综述,2009,15(13):1929-1931.[27] Qureshi HY,Ahmad R,Sylvester J,et al. Re-quirement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signalingpathway for regulation of tissue inhibitor of metallopro-teinases-3 gene expression by TGF-beta in human chon-drocytes.Cell Signal.2007;19(8): 1643 1651.[28] 郭静,张文丽,李琪佳,等. 基质金属蛋白酶 9 及 TGF-β1mRNA 和蛋白在骨关节炎中的表达[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2011, 25(8): 992-997. [29] 张平,蔡道章,刘斌. 转 IL-1Ra 和 TGF-β1 基因治疗兔骨性关节炎[J]. 中华关节外科杂志,2011,5(3):335-422.[30] 张清林,吕惠成,吴一民. 转化生长因子β1联合骨形态发生蛋白2诱导骨髓间充质干细胞体外向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(24):4371-4375.[31] 林成,刘宝林,刘彦普,等. VEGF和TGF-β1促进非血管化骨移植同期种植骨结合的实验研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(1): 12-16.[32] Hajishengallis G, Wang M, Liang S. Induction of distinct TLR2- mediated proinflammatory and proadhesive signalingpathways in response to Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae. J Immunol.2009;182(1): 6690- 6696. [33] 陈波,谢西梅,李佳霖,等.艾灸治疗对兔 KOA 软骨损伤及 TNF- α、TGF- β1和IGF- 1 表达调节作用的实验研究[J].江苏中医药,2009,41(6):69-71.[34] 蒋滔,程祥荣,夏海滨,等. rhBMP-2/rhTGF-β1联合应用对兔成骨样细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2005,6(1): 1-3.[35] 袁百胜,陈晓亮,栾军伟. 转化生长因子β1基因29T >C单核苷酸多态性与脊柱融合的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(24):4686-4689.[36] 马进峰,周东生,马学晓,等. TGF-β1基因29T>C单核苷酸多态性与骨肉瘤的关联研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(18): 1510-1513.[37] 曲攀,高秀秋. 2型糖尿病伴牙周病大鼠牙槽骨中转化生长因子β1 mRNA的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(46):8576-8580.[38] Yang X, Chen L, Xu X,et al.TGF-beta/Smad3 signals repress chondrocyte hypertro-phic differentiation and are required for maintaining ar-ticular cartilage. J Cell Biol.2001;153(1): 35-46.[39] Andrew WT.Review of the actvation of TGF-β1 in immunity. LeukoeBiol.2009;85:29-33.[40] Yang X,Chen L,Xu X, ,et al.TGF-beta/ Smad3 signalsrepress chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation and are required for maintaining articular cartilage.J Cell Biol.2001;153(1):35-46.[41] Blaney Davidson EN,Scharstuhl A,Vitters EL,et al.Reduced transforming growth factor—beta signaling in cartilage of old mice:role in impaired repair capacity.Arthritis ResTher. 2005; 7(6): R1338 -1347.[42] 万晓晨,刘翠平,陈海啸,等.TGF-β/骨形态发生蛋白、Wnt 和 MAPK 信号通路在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中的作用[J]. 细胞生物学杂志,2010,30:697-700.[43] 阎新龙,刘兵,毛宁.间充质干细胞迁移特性的研究进展.[J].中国实验血液学杂志2009,17(4):1101-1105.[44] 武鹏宇,戴立里,唐静,等. 骨形态发生蛋白-7对人肝星状细胞转化生长因子β信号转导的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2010, 32(13): 1433-1437.[45] 孙啸.骨关节炎进程中软骨细胞膜受体 ALK1在软骨 TGFβ 信号通路中的作用及调控[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2012,5(1): 88-92.[46] 杨晓. Smad4 介导转化生长因子β 信号调节骨骼发育和稳态维持的功能[J]. 生命科学,2008,20(2):165-169.[47] KaleVP. Differential activation of MAPK signaling pathways by TGF-beta1 forms the molecular mechanism behind its dose-dependent bidirectional effects on hematopoiesis. Stem Cells and Development .2004;13(l):27-38.[48] Janssens,tenDijkeP,JanssensS,et al.Transforming growth faetor-betal to the bone.EndocrReV.2005;26(6):743-774.[49] Quinn JM, Itoh K, Udagawa N,et al.Transforminggrowth factor b affects osteoclast differentiation via direct and indirect actions.Bone Miner Res.2001; 10:1787-1794.[50] 周名亮,李谧,余希杰. 微小RNA对成骨细胞分化成熟的调控及临床意义[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(6):761-765.[51] Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, et al. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in dif-ferentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1responses. Arthritis Rheum, 2009, 60(9): 2723-2730.[52] 苏金梅,金晔,曲强,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化过程中miR130a的表达[J]. 基础医学与床,2010,30(5):520-523.[53] Miyaki S, Sato T, Inoue A, et al. MicroRNA-140 plays dual roles inboth cartilage development and homeostasis. Genes Dev, 2010, 24(11):1173-1185[54] 张秀梅,崔亚洲,周小艳,等. microRNAs 参与韧带成纤维细胞成骨分化相关分子表达的调节[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2011,27(6):540-547 |