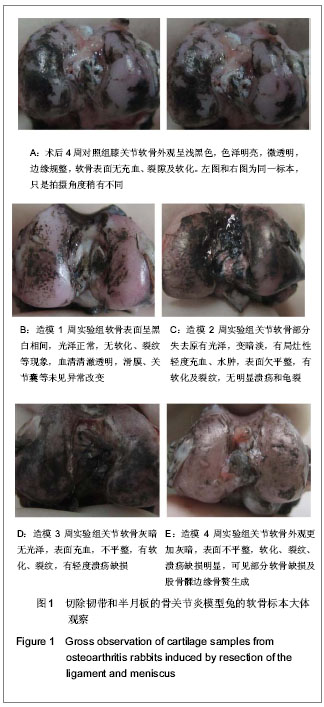
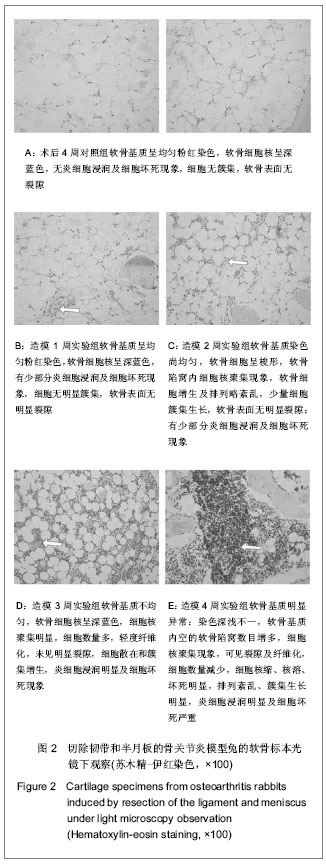
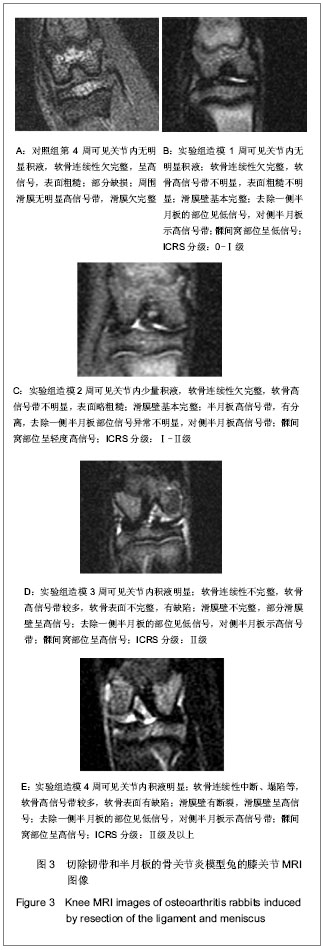
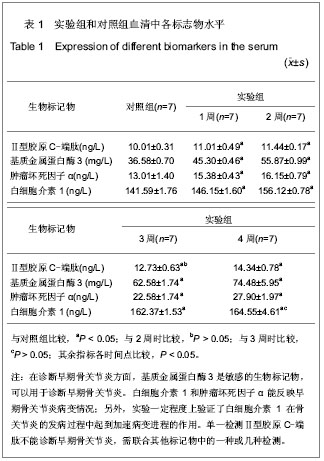
| [1] Zhang R, Fang H, Chen Y,et al. Gene expression analyses of subchondral bone in early experimental osteoarthritis by microarray. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32356.[2] Blaney Davidson EN, Vitters EL, van Beuningen HM, et al. Resemblance of osteophytes in experimental osteoarthritis to transforming growth factor beta-induced osteophytes: limited role of bone morphogenetic protein in early osteoarthritic osteophyte formation. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(12): 4065-4073.[3] Huebner JL, Williams JM, Deberg M,et al. Collagen fibril disruption occurs early in primary guinea pig knee osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(3):397-405.[4] Gregory JS, Waarsing JH, Day J,et al. Early identification of radiographic osteoarthritis of the hip using an active shape model to quantify changes in bone morphometric features: can hip shape tell us anything about the progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11):3634-3643.[5] Ling SM, Patel DD, Garnero P,et al. Serum protein signatures detect early radiographic osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(1):43-48. [6] Dam EB, Byrjalsen I, Karsdal MA,et al. Increased urinary excretion of C-telopeptides of type II collagen (CTX-II) predicts cartilage loss over 21 months by MRI.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(3):384-389.[7] Hatta T, Sugita T, Aizawa T,et al. Bony island within the articular cartilage of the knee in a child: a rare condition for early osteoarthritis.Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2011;3(1):e7.[8] Rhee J, Ryu JH, Kim JH,et al. α-Catenin inhibits β-catenin-T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor transcriptional activity and collagen type II expression in articular chondrocytes through formation of Gli3R.α-catenin.β-catenin ternary complex. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(15):11751-11760.[9] Alam MR, Ji JR, Kim MS,et al. Biomarkers for identifying the early phases of osteoarthritis secondary to medial patellar luxation in dogs. J Vet Sci. 2011;12(3):273-280.[10] Urso ML, Wang R, Zambraski EJ,et al. Adenosine A3 receptor stimulation reduces muscle injury following physical trauma and is associated with alterations in the MMP/TIMP response. J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(4):658-670.[11] Steenport M, Khan KM, Du B,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 induce macrophage MMP-9: evidence for the role of TNF-alpha and cyclooxygenase-2. J Immunol. 2009;183(12):8119-8127.[12] Braza-Boïls A, Ferrándiz ML, Terencio MC,et al. Analysis of early biochemical markers and regulation by tin protoporphyrin IX in a model of spontaneous osteoarthritis. Exp Gerontol. 2012;47(5):406-409.[13] Zhou PH, Liu SQ, Peng H.The effect of hyaluronic acid on IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat model of osteoarthritis.J Orthop Res. 2008;26(12):1643-1648.[14] Cohen SB, Proudman S, Kivitz AJ,et al. A randomized, double-blind study of AMG 108 (a fully human monoclonal antibody to IL-1R1) in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):R125.[15] Chevalier X, Conrozier T, Richette P. Desperately looking for the right target in osteoarthritis: the anti-IL-1 strategy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):124.[16] Eda H, Shimada H, Beidler DR,et al. Proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α, induce expression of interleukin-34 mRNA via JNK- and p44/42 MAPK-NF-κB pathway but not p38 pathway in osteoblasts.Rheumatol Int. 2011;31(11):1525-1530.[17] Bowen CJ, Edwards CJ, Hooper L,et al. Improvement in symptoms and signs in the forefoot of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF therapy.J Foot Ankle Res. 2010;3:10.[18] Stannus O, Jones G, Cicuttini F, et al. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(11):1441-1447.[19] Aktas E, Sener E, Zengin O, et al. Serum TNF-alpha levels: potential use to indicate osteoarthritis progression in a mechanically induced model. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22(2):119-122 |