| [1] Feng W,Jin AM,Zhang H,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(41):8025-8028. 冯伟,靳安民,张辉,等. 纳米羟基磷灰石-聚羟基丁酸戊酯/聚乙二醇人工骨对骨缺损修复的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(41):8025-8028.[2] Yoshikawa M,Toda T. Reconstruction of alveolar bone defect by calcium phosphate compounds. J Biomed Mater Res.2000; 53(4):430-437.[3] Hideki A,Masataka O.Effect of adracin-adsorbing HAP-sol on Ca-9 cell growth. Reports Institute Meal Dental Eng.1993; 27: 39-44.[4] Itokazu M,Kumazawa S,Wada E,et al.Sustained release of adriamycin from implanted hydroxyapatite blocks for the treatment of experimental osteogenic sarcoma in mice. Cancer Lett.1996;107(1):11-18.[5] Savic R,Luo L,Eisenberg A,et al.Micellar nanocontainers distribute to defined cytoplasmic organelles. Science. 2003; 300(25):615-618.[6] Kubo M,Kuwayama N,Hirashima Y,et al.Hydroxyapatite ceramics as a particulate embolic material: l report of the clinical experience.A JNR Am J Neuroradiol.2003; 24(8): 1545-1547.[7] Xia QH,Chen DD,Lin H.Wuhan Gongye Daxue Xuebao. 1999; 21(2):5-6. 夏清华,陈道达,林华.HASM对W-256细胞系DNA含量及细胞周期的影响[J].武汉工业大学学报,1999,21(2):5-6.[8] Chen J,Cao XY,Han YC,et al.Wuhan Ligong Daxue Xuebao. 2005;27(9):29-31. 陈筠,曹献英,韩颖超,等.纳米磷灰石对肝癌癌基因表达的影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报,2005,27(9):29-31.[9] Qi ZT,Cao XY,Han YH,et al.The effect of nanoapatite on the expression of telom erase gene of human hepatocarcinoma. Wuhan Ligong Daxue Xuebao.2004;26(7): 46-48.[10] Deng Y,Lin X,Zheng Z,et al. Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co- hydroxyhexanoate) promoted production of extracellular matrix of articular cartilage chondrocytes in vitro. Biomaterials. 2003;24(23):4273-4281.[11] Zhao K,Deng Y,Chen JC,et al.Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds with good mechanical properties and biocompatibility.Biomaterilas.2003;24(6):1041-1045.[12] Gangrade N,Price JC. Poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate) microspheres containing progesterone: preparation, morphology and release properties. J Microencapsul. 1991; 8(2):185.[13] Yagmurlu MF,Korkusuz F,Gursel I,et al. Sulbactam-cefoperazone polyhydroxybutyrate-co- hydroxyvalerate (PHBV) local antibiotic delivery system: in vivo effectiveness and biocompatibility in the treatment of implant-related experimental osteomyelitis. J Biomed Mater Res.1999;46(4):494.[14] Luscher TF. Endothelin: Systemic arterial and pulmonary effects of a new peptide with potent biological properties. Am Rev Respir Dis.1992;146 (5 Pt 2):56-60.[15] Yang ZQ,Gu YQ.Zhongguo Xueye Liubianxue Zazhi. 2001; 11(1): 83-84. 杨志强,顾月清.慢性肺心病患者血浆内皮素和心钠素变化[J].中国血液流变学杂志, 2001,11(1):83-84.[16] Kwon GS.Polymeric Micelles for Delivery of Poorly Water-Soluble Compounds.Crit Rev The Drug Carrier Syst. 2003;20(5):357-403.[17] Yang ZL,Yang KW,Li XR,et al.Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi. 2007; 42(7):519-523. 杨卓理,杨可伟,李馨儒,等.两性霉素B的聚乙二醇-聚乳酸胶束的制备及其体外释放动力学[J].中国药学杂志,2007,42(7):519- 523.[18] Yu DS,Huang HZ,Pan CB,et al.Zhongguo Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi. 2007;5(2):122-126. 余东升,黄洪章,潘朝斌,等.聚乙二醇-聚谷氨酸纳米微球介导双自杀基因治疗金黄地鼠颊癌的实验研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2007,5(2):122-126. |
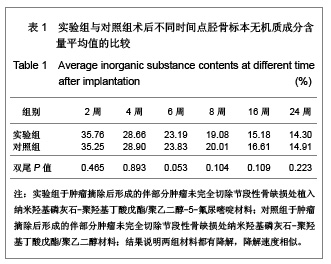
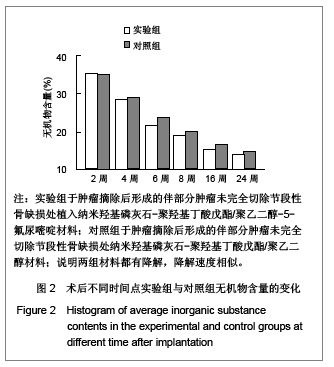


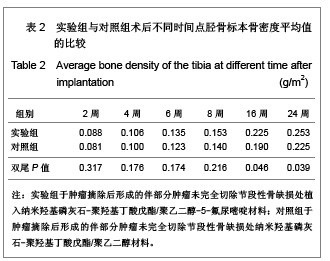
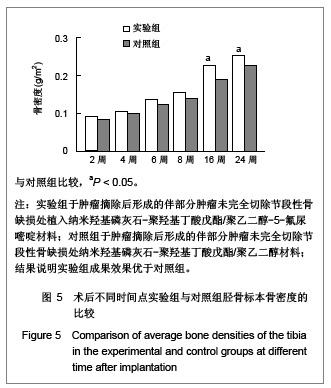
.jpg)