| [1] Chi YL. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2005;15(3):133-134. 池永龙.脊柱外科的微创意识,微创观念与微创技术[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,15(3):133-134.[2] Gejo R, Matsui H, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Serial changes in trunk muscle performance after posterior lumbar surgery. Spine. 1999;24(10):1023-1028.[3] Pavlov PW, Meijers H, van Limbeek J, et al. Good outcome and restoration of lordosis after anterior lumbar interbody fusion with additional posterior fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(17):1893-1900.[4] Aepli M, Mannion AF, Grob D. Translaminar screw fixation of the lumbar spine: long-term outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(14):1492-1498.[5] Suk SI, Lee CK, Kim WJ, et al. Adding posterior lumbar interbody fusion to pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral fusion after decompression in spondylolytic spondylolisthesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(2):210-220.[6] Japanese Orthopaedic Association. Assessment of surgical treatment of low back pain. Jpn Orthop Assoc. 1984; 58:1183-1187.[7] Chu JZ, Cui ZM, Xu GH, et al. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Zazhi. 2012;1(1):41-45. 储惊蛰,崔志明,徐冠华.改良PLIF术治疗原位复发性腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012,1(1):41-45.[8] DiPaola CP, Molinari RW. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(3):130-139.[9] Brantigan JW, Neidre A, Toohey JS. The Lumbar I/F Cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the variable screw placement system: 10-year results of a Food and Drug Administration clinical trial. Spine J. 2004;4(6):681-688.[10] Uzi EA, Dabby D, Tolessa E, et al. Early retropulsion of titanium-threaded cages after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a report of two cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26(9):1073-1075. [11] Ebara S, Harada T, Hosono N, et al. Intraoperative measurement of lumbar spinal instability. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(3 Suppl):S44-50.[12] Lowe TG, Coe JD. Bioresorbable polymer implants in the unilateral transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion procedure. Orthopedics. 2002;25(10 Suppl):s1179-1183.[13] Rosenberg WS, Mummaneni PV. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: technique, complications, and early results. Neurosurgery. 2001;48(3):569-575.[14] Suk KS, Lee HM, Kim NH, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in lumbar spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(14):1843-1847.[15] Chen HH, Cheung HH, Wang WK, et al. Biomechanical analysis of unilateral fixation with interbody cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(4):E92-96.[16] Chen ZM. Shanghai: Dier Junyi Daxue. 2012. 陈志明.腰椎单侧椎弓根螺钉固定的生物力学研究及临床应用[D].上海:第二军医大学,2012.[17] Liu YS, Chen QX, Liao SH, et al. Guoji Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng Zazhi. 2006;31(5):260-266. 刘耀升,陈其昕,廖胜辉,等.小关节角矢状化、椎间盘退变对退变性腰椎滑移作用的有限元研究[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2006, 31(5):260-266.[18] Little JS, Ianuzzi A, Chiu JB, et al. Human lumbar facet joint capsule strains: II. Alteration of strains subsequent to anterior interbody fixation. Spine J. 2004;4(2):153-162.[19] Kandziora F, Schleicher P, Scholz M, et al. Biomechanical testing of the lumbar facet interference screw. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(2):E34-39.[20] Burton D, McIff T, Fox T, et al. Biomechanical analysis of posterior fixation techniques in a 360 degrees arthrodesis model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(24):2765-2771.[21] Schmid R, Lindtner RA, Lill M, et al. Combined posteroanterior fusion versus transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) in thoracolumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2012; 43(4):475-479.[22] Rodgers WB, Gerber EJ, Patterson J. Intraoperative and early postoperative complications in extreme lateral interbody fusion: an analysis of 600 cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(1):26-32.[23] Motosuneya T, Asazuma T, Tsuji T, et al. Postoperative change of the cross-sectional area of back musculature after 5 surgical procedures as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(5):318-322.[24] Moskowitz A. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002;33(2):359-366. |
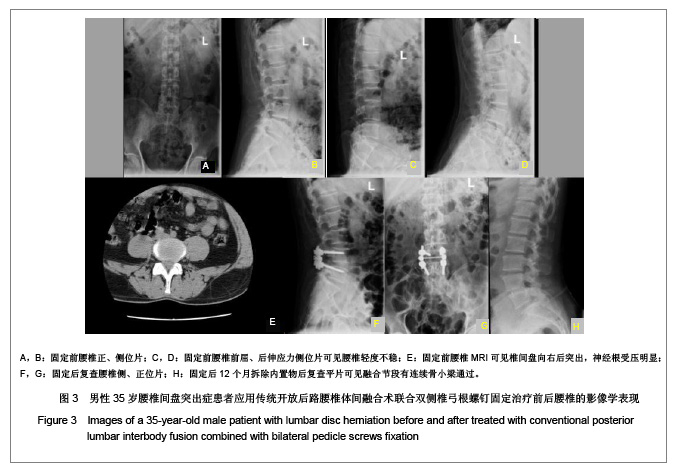
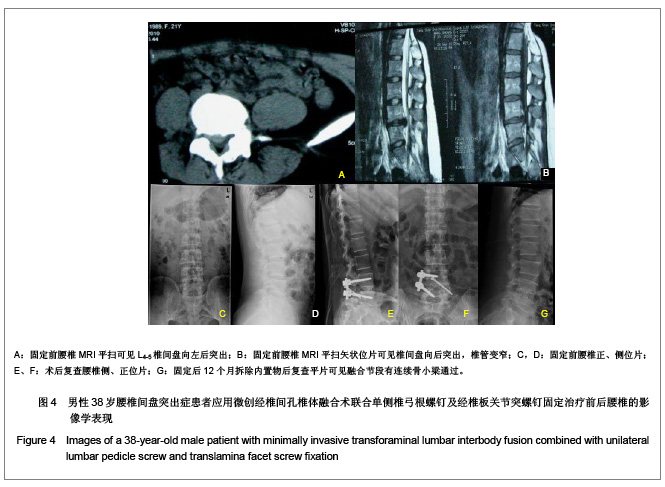
.jpg)
.jpg)