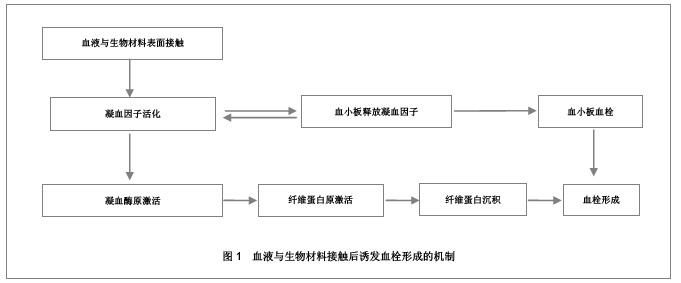
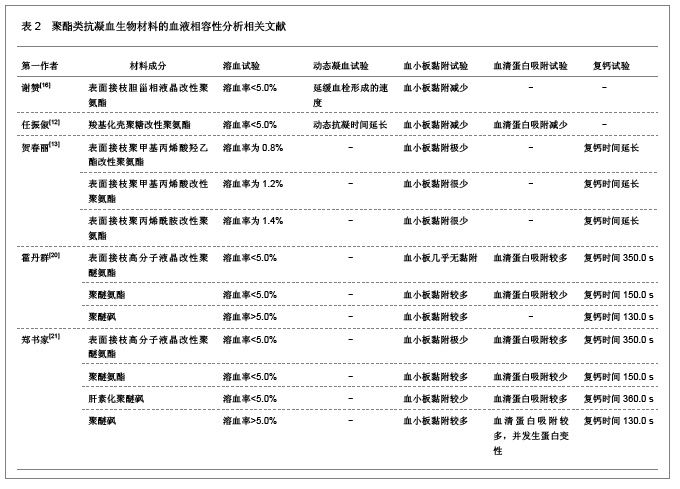
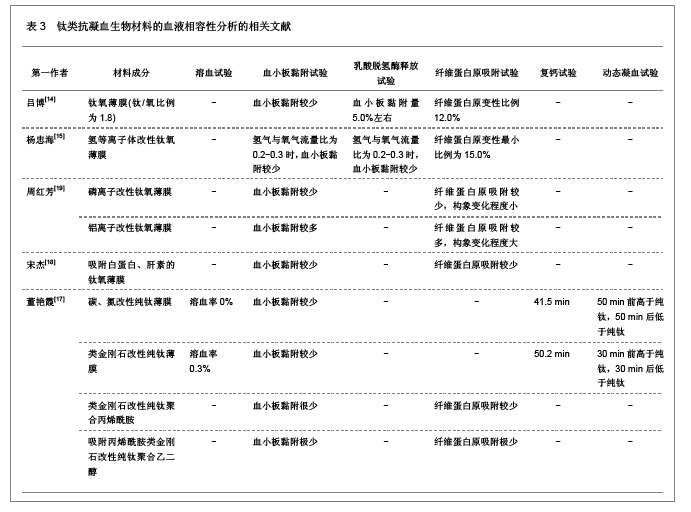
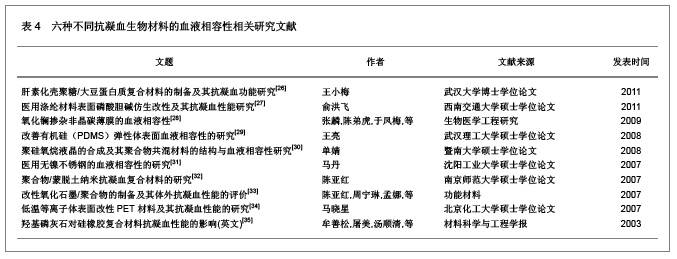
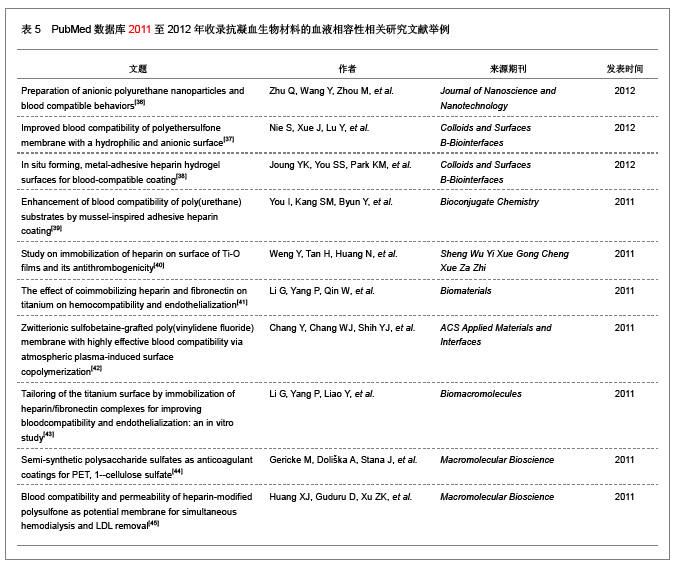
| [1] Macocinschi D, Filip D, Vlad S, et al. Segmented biopolyurethanes for medical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20(8):1659-1668. [2] Kütting M, Roggenkamp J, Urban U, et al. Polyurethane heart valves: past, present and future. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2011;8(2):227-233. [3] Gastaldello K, Melot C, Kahn RJ, et al. Comparison of cellulose diacetate and polysulfone membranes in the outcome of acute renal failure. A prospective randomized study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2000;15(2):224-230. [4] Suzuki Y, Daitoku K, Minakawa M, et al. Poly-2-methoxyethylacrylate-coated bypass circuits reduce activation of coagulation system and inflammatory response in congenital cardiac surgery. J Artif Organs. 2008;11(3): 111-116. [5] Kwok SC, Yang P, Wang J, et al. Hemocompatibility of nitrogen-doped, hydrogen-free diamond-like carbon prepared by nitrogen plasma immersion ion implantation-deposition. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;70(1):107-114. [6] Santerre JP, Woodhouse K, Laroche G, et al. Understanding the biodegradation of polyurethanes: from classical implants to tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials. 2005;26(35): 7457-7470. [7] Losi P, Lombardi S, Briganti E, et al. Luminal surface microgeometry affects platelet adhesion in small-diameter synthetic grafts. Biomaterials. 2004;25(18):4447-4455. [8] 沈健.生物医用高分子材料的研制及其基础研究[D].江苏:南京理工大学,2004:1-396.[9] 马银陈,周宁琳,陈亚红,等.新型抗凝血纳米复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J].功能材料,2007,38(10):1713-1716.[10] 程莉萍,孙树东,乐以伦,等.血液净化膜材和抗凝剂对凝血过程中接触活化的影响[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2005,36(3):411-414.[11] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-11-18. https://www.cnki.net.[12] 任振俶.羧基化壳聚糖改性聚氨酯的制备和表征[D].辽宁:大连理工大学,2012:1-67.[13] 贺春丽.不同类型亲水结构表面修饰聚氨酯的合成及其生物相容性研究[D].江苏:南京师范大学,2011:1-84.[14] 吕博.抗凝血Ti-O薄膜的电化学行为研究[D].四川:西南交通大学, 2010:1-52.[15] 杨忠海.氢等离子体改性Ti-O薄膜的血液相容性研究[D].四川:西南交通大学,2009:1-87.[16] 谢赞.表面接枝胆甾相液晶改善PU的抗凝血性能研究[D].广东:暨南大学,2007:1-59.[17] 董艳霞.钛表面改性及其血液相容性研究[D].陕西:陕西师范大学, 2007:1-68.[18] 宋杰,吴熹,黄楠,等.纤维蛋白原与吸附白蛋白、肝素的新型血管支架材料氧化钛的血液相容性[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2007, 24(5):1097-1101.[19] 周红芳.离子注入钛氧薄膜的血液相容性研究[D].四川:西南交通大学,2006:1-66.[20] 霍丹群.肝素化高分子液晶/聚醚氨酯生物材料的研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2004:1-157.[21] 郑书家.抗凝血生物材料的血液相容性研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2004:1-62.[22] Lelah M, Pierce JA, Lambrecht LK, et al. Polyether-urethane ionomers:surface property/ex vivo blood compatibility relationships. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1985;104(2):422-439. [23] Ito Y, Sisido M, Imanishi Y. Synthesis and antithrombogenicity of anionic polyurethanes and heparin-bound polyurethanes. J Biomed Mater Res. 1986;20(8):1157-1177. [24] Goosen MF, Sefon MV. Properties of a heparin-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogelcoating. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;17: 359-361. [25] Bélanger MC, Marois Y, Roy R, et al. Selection of a polyurethane membrane for the manufacture of ventricles for a totally implantable artificial heart: blood compatibility and biocompatibility studies. Artif Organs. 2000;24(11):879-888. [26] 王小梅.肝素化壳聚糖/大豆蛋白质复合材料的制备及其抗凝血功能研究[D].湖北:武汉大学,2011:1-149.[27] 俞洪飞.医用涤纶材料表面磷酸胆碱仿生改性及其抗凝血性能研究[D].四川:西南交通大学,2011:1-63.[28] 张麟,陈弟虎,于凤梅,等.氧化镧掺杂非晶碳薄膜的血液相容性[J].生物医学工程研究,2009,28(2):96-99. [29] 王亮.改善有机硅(PDMS)弹性体表面血液相容性的研究[D].湖北:武汉理工大学,2008:1-60.[30] 单婧.聚硅氧烷液晶的合成及其聚合物共混材料的结构与血液相容性研究[D].广东:暨南大学,2008:1-90.[31] 马丹.医用无镍不锈钢的血液相容性的研究[D].辽宁:沈阳工业大学,2007:1-66.[32] 陈亚红.聚合物/蒙脱土纳米抗凝血复合材料的研究[D].江苏:南京师范大学,2007:1-75.[33] 陈亚红,周宁琳,孟娜,等.改性氧化石墨/聚合物的制备及其体外抗凝血性能的评价[J].功能材料,2007,38(3):438-440.[34] 马晓星.低温等离子体表面改性PET材料及其抗凝血性能的研究[D].北京:北京化工大学,2007:1-77.[35] 牟善松,屠美,汤顺清,等.羟基磷灰石对硅橡胶复合材料抗凝血性能的影响(英文)[J].材料科学与工程学报,2003,21(2):162-164.[36] Zhu Q, Wang Y, Zhou M, et al. Preparation of anionic polyurethane nanoparticles and blood compatible behaviors. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012;12(5):4051-4056.[37] Nie S, Xue J, Lu Y, et al. Improved blood compatibility of polyethersulfone membrane with a hydrophilic and anionic surface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;100:116-125. [38] Joung YK, You SS, Park KM, et al. In situ forming, metal-adhesive heparin hydrogel surfaces for blood-compatible coating. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;99:102-107. [39] You I, Kang SM, Byun Y, et al. Enhancement of blood compatibility of poly(urethane) substrates by mussel-inspired adhesive heparin coating. Bioconjug Chem. 2011;22(7):1264-1269.[40] Weng Y, Tan H, Huang N, et al. Study on immobilization of heparin on surface of Ti-O films and its antithrombogenicity. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2011;28(1):86-89.[41] Li G, Yang P, Qin W, et al. The effect of coimmobilizing heparin and fibronectin on titanium on hemocompatibility and endothelialization. Biomaterials. 2011;32(21):4691-4703. [42] Chang Y, Chang WJ, Shih YJ, et al. Zwitterionic sulfobetaine-grafted poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane with highly effective blood compatibility via atmospheric plasma-induced surface copolymerization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2011;3(4):1228-1237. [43] Li G, Yang P, Liao Y, et al. Tailoring of the titanium surface by immobilization of heparin/fibronectin complexes for improving bloodcompatibility and endothelialization: an in vitro study. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(4):1155-1168. [44] Gericke M, Doliška A, Stana J, et al. Semi-synthetic polysaccharide sulfates as anticoagulant coatings for PET, 1--cellulose sulfate. Macromol Biosci. 2011;11(4):549-556.[45] Huang XJ, Guduru D, Xu ZK, et al. Blood compatibility and permeability of heparin-modified polysulfone as potential membrane for simultaneous hemodialysis and LDL removal. Macromol Biosci. 2011;11(1):131-140. [46] Wagner WR, Johnson PC, Thompson KA, et al. Heparin-coated cardiopulmonary bypass circuits: hemostatic alterations and postoperative blood loss. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(3):734-740; discussion 741.[47] Bozdayi M, Borowiec J, Nilsson L, et al. Effects of heparin coating of cardiopulmonary bypass circuits on in vitro oxygen free radical production during coronary bypass surgery. Artif Organs. 1996;20(9):1008-1016. [48] Høgevold HE, Moen O, Fosse E, et al. Effects of heparin coating on the expression of CD11b, CD11c and CD62L by leucocytes in extracorporeal circulation in vitro. Perfusion. 1997;12(1):9-20. [49] Moen O, Fosse E, Brockmeier V, et al. Disparity in blood activation by two different heparin-coated cardiopulmonary bypass systems. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995;60(5):1317-1323. |