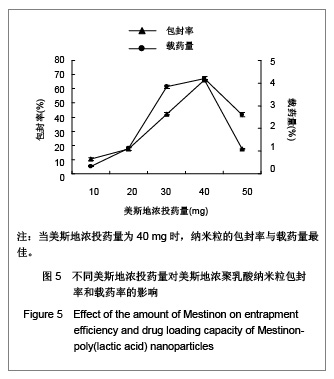
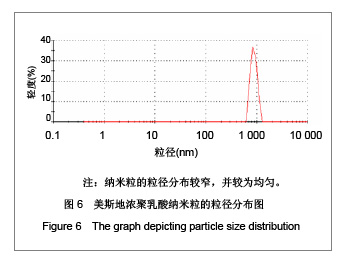
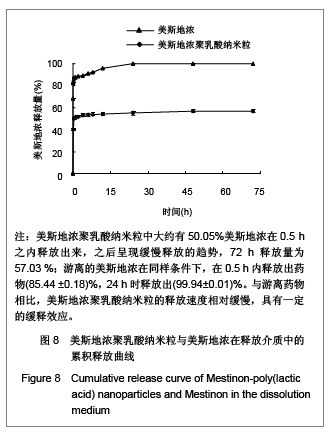
| [1] Adair JH,Parette MP,Altino?lu EI,et al. Nanoparticulate alternatives for drug delivery. ACS Nano. 2010;4(9): 4967-4970.[2] Ishihara T,Takahashi M,Higaki M,et al.Preparation and characterization of a nanoparticulate formulation composed of PEG-PLA and PLA as anti-inflammatory agents. Int J Pharm. 2010;385(1-2):170-175.[3] Chen CC,Chueh JY,Tseng H,et al.Preparation and characterization of biodegradable PLA polymeric blends. Biomaterials.2003;24(7):1167-1173.[4] Xiong XY,Guo L,Gong YC,et al.In vitro &in vivo targeting behaviors of biotinylated Pluronic F127/poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles through biotin-avidin interaction. Eur J Pharm Sci.2012; 46(5):537-544. [5] Lasprilla AJ,Martinez GA,Lunelli BH,et al. Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices.Biotechnol Adv.2012;30(1):321-328. [6] Andersen JB,Engeland A,Owe JF,et al.Myasthenia gravis requiring pyridostigmine treatment in a national population cohort. Eur J Neurol.2010; 17(12): 1445-1450.[7] Barak D,Ordentlich A,Stein D,et al.Accommodation of physostigmine and its analogues by acetylcholinesterase is dominated by hydrophobic interactions. Biochem J.2009; 417(1): 213-222.[8] Liu J,Qiu Z,Wang S,et al.A modified double-emulsion method for the preparation of daunorubicin-loaded polymeric nanoparticle with enhanced in vitro anti-tumor activity.Biomed Mater. 2010;5(6):065002.[9] Costa HM,Ramos VD,Visconte LLY,et al. Design and analysis of single-factor experiments: Analysis of variance of the effect of rice husk ash and commercial fillers in NR compounds. Polymer Bulletin.2007;58:597-610.[10] Danhier F,Ansorena E,Silva JM,et al. PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications.J Control Release.2012;161(2):505-522.[11] Wu ZM,Zhou L,Guo XD,et al.HP55-coated capsule containing PLGA/RS nanoparticles for oral delivery of insulin.Int J Pharm. 2012;425(1-2):1-8.[12] Li X,Chang S,Du G,et al.Encapsulation of azithromycin into polymeric microspheres by reduced pressure-solvent evaporation method.Int J Pharm.2012;433(1-2):79-88.[13] Liu R,Ma GH,Wan YH,et al.Influence of process parameters on the size distribution of PLA microcapsules prepared by combining membrane emulsification technique and double emulsion-solvent evaporation method.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2005;45(3-4):144-153.[14] Chognot D,Léonard M,Six JL,et al. Surfactive water-soluble copolymers for the preparation of controlled surface nanoparticles by double emulsion/solvent evaporation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2006;51(1):86-92. [15] Zhang JQ,Zhang ZR,Yang H,et al.Lyophilized paclitaxel magnetoliposomes as a potential drug delivery system for breast carcinoma via parenteral administration: in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharm Res.2005;22: 573-583.[16] Tan QY,Wang N,Yang H,et al. Characterization, stabilization and activity of uricase loaded in lipid vesicles.Int J Pharm. 2010;384(1-2):165-172.[17] Markovic B,Vladimirov S,Cudina O,et al.An application of second-order UV-derivative spectrophotometry for study of solvolysis of a novel fluocinolone acetonide ester. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectros.2010;75(2):930-935.[18] Xia SH,Lu J,Cao LY,et al.Zhongguo Yiyuan Yaoxue Zazhi. 2007; 27(4):564-565. 夏曙辉,陆鉴,曹凌燕,等.二阶导数光谱法测定盐酸利多卡因胶浆中盐酸利多卡因的含量[J].中国医院药学杂志,2007, 27(4): 564-565.[19] Wang Y,Zhang Y.Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi. 2007;27(1):139. 王彦,张燕.二阶导数光谱法测定硫酸阿托品胶浆剂的含量[J].药物分析杂志,2007,27(1):139.[20] Luan X,Skupin M,Siepmann J,et al.Key parameters affecting the initial release (burst) and encapsulation efficiency of peptide-containing poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microparticles.Int J Pharm.2006;324(2):168-175. |
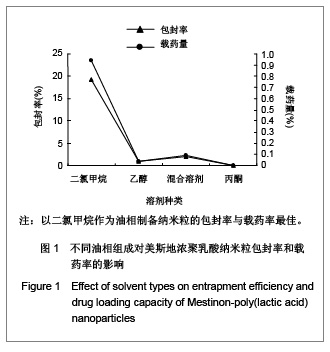
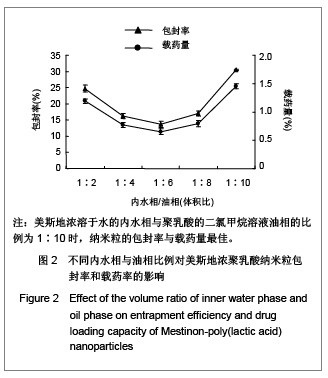
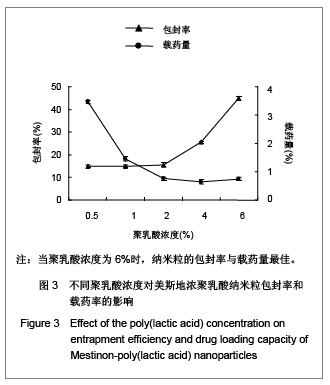
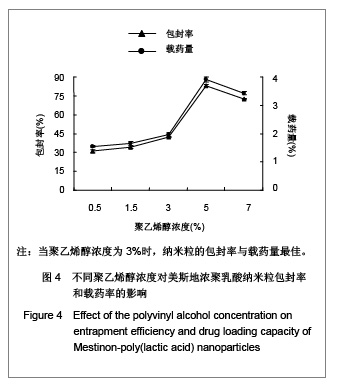


.jpg)
.jpg)