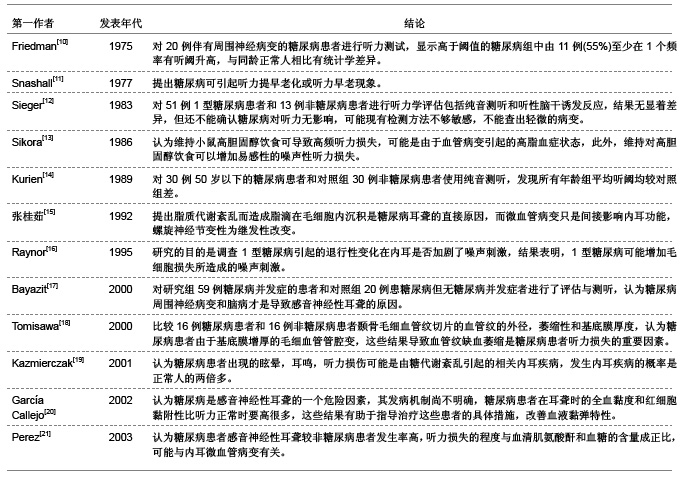
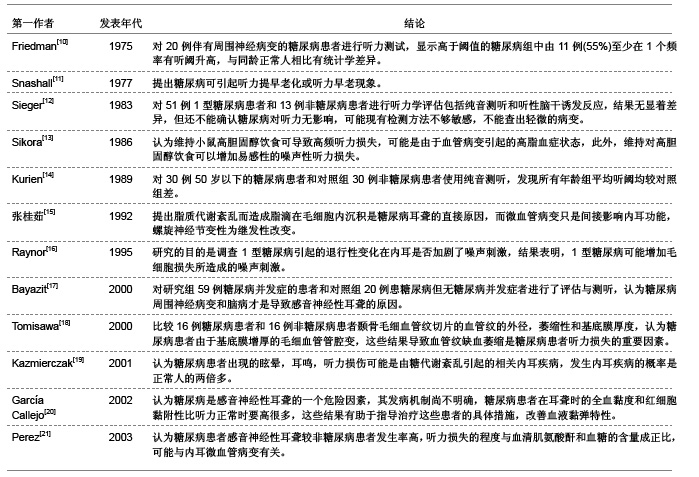
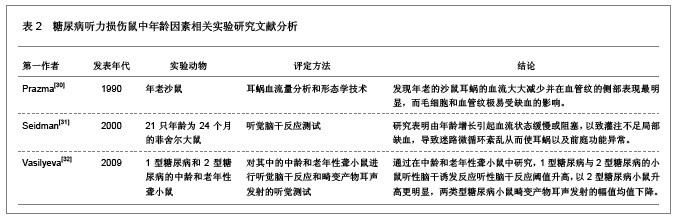
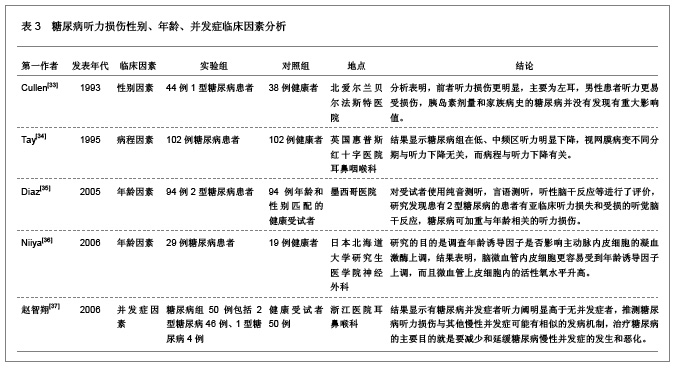
| [1] Tay HL,Ray N,Ohri R,et al.Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss.Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.1995;20(2):130-134.[2] 蒋国秀.实用糖尿病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1992:233.[3] 樊云霞,韩峰,董明,等.老年2型糖尿病患者听力损害特征及相关因素分析[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(7):707-709.[4] Orita S,Fukushima K,Orita Y,et al.Sudden hearing impairment combined with diabetes mellitus or hyperlipidemia.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2007;264(4):359-362.[5] Weng SF,Chen YS,Hsu CJ,et al.Clinical features of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients.Laryngoscope. 2005;115(9):1676-1680.[6] Fukushima H,Cureoglu S,Schachern PA,et al.Cochlear changes in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2005;133(1):100-106.[7] Ren T,Brown NJ,Zhang M,et al.A reversible ischemia model in gerbil cochlea.Hear Res.1995;92(1-2):30-37.[8] Nario K,Matsunaga T,Inui H,et al.A ABR findings, electrocochleograms and caloric tests in vertebrobasilar ischemic rats.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl.1997;528(Suppl):63-66.[9] Perlman HB,Kimura R,Fernandez C.Experiments on temporary obstruction of the internal auditory artery. Laryngoscope.1959;69(6):591-613.[10] Friedman SA,Schulman RH,Weiss S.Hearing and diabetic neuropathy.Arch Intern Med.1975;135(4):573-576.[11] Snashall SE.Békésy audiometry and tone and reflex decay tests in diabetics.Arch Otolaryngol.1977;103(6):342-343.[12] Sieger A,White NH,Skinner MW,et al.Auditory function in children with diabetes mellitus.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.1983; 92(3Pt1):237-241.[13] Sikora MA,Morizono T,Ward WD,et al.Diet-induced hyperlipidemia and auditory dysfunction.Acta Otolaryngol.1986;102(5-6):372-381.[14] Kurien M,Thomas K,Bhanu TS.Hearing threshold in patients with diabetes mellitus.J Laryngol Otol.1989;103(2):164-168.[15] 张桂茹,倪劲松.糖尿病患者内耳病变及耳聋机理的实验研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,1992,6(2):82-83.[16] Raynor EM,Carrasco VN,Prazma J,et al.An assessment of cochlear hair-cell loss in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus diabetic and noise-exposed rats.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1995;121(4):452-456.[17] Bayazit Y,Yilmaz M,Kepekçi Y,et al.Use of the auditory brainstem response testing in the clinical evaluation of the patients with diabetes mellitus.J Neurol Sci.2000;181(1-2): 29-32.[18] Tomisawa H.Diabetic changes in the stria vascularis in humans--a study of PAS-stained temporal bone sections. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho.2000;103(11):1227-1237.[19] Ka?mierczak H, Doroszewska G.Metabolic disorders in vertigo,tinnitus,and hearing loss.Int Tinnitus J.2001;7(1): 54-58.[20] García Callejo FJ,Orts Alborch MH,Morant Ventura A,et al.Neurosensory sudden deafness, blood hyperviscosity syndrome, and diabetes mellitu.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp. 2002;53(3):221-224.[21] Perez R,Freeman S,Cohen D,et al.The differential vulnerability of the inner ear end-organs to several external factors.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.2003;14(2):85-93.[22] 樊云霞.老年2型糖尿病患者听力损害特征及相关因素分析[D].山东:山东大学,2007:1-40.[23] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2012-08-10. https://www.cnki.net.[24] SCI数据库.Web of Sciencevia ISI Web of Knowledge[DB/OL]. 2012-08-10. http://ip-science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl[25] Lisowska G,Namys?owski G,Morawski K,et al.Cochlear dysfunction and diabetic microangiopathy.Scand Audiol Suppl.2001;(52):199-203.[26] 陈彦华,蒋连强,李玲,等.2型糖尿病并发血管病变的临床实验研究[J].柳州医学,2002,15(2):61-64.[27] Kakarlapudi V,Sawyer R,Staecker H.The effect of diabetes on sensorineural hearing loss.Otol Neurotol.2003;24(3):382-386.[28] Fukushima H,Cureoglu S,Schachern PA,et al.Effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on cochlear structure in humans.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2006;132(9):934-938.[29] Loader B,Stokic D,Riedl M,et al.Combined analysis of audiologic performance and the plasma biomarker stromal cell-derived factor 1a in type 2 diabetic patients.Otol Neurotol. 2008;29(6):739-744.[30] Prazma J,Carrasco VN,Butler B,et al.Cochlear microcirculation in young and old gerbils.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1990;116(8):932-936.[31] Seidman MD,Khan MJ,Bai U,et al.Biologic activity of mitochondrial metabolites on aging and age-related hearing loss.Am J Otol.2000;21(2):161-167.[32] Vasilyeva ON,Frisina ST,Zhu X,et al.Interactions of hearing loss and diabetes mellitus in the middle age CBA/CaJ mouse model of presbycusis.Hear Res.2009;249(1-2):44-53.[33] Cullen JR,Cinnamond MJ.Hearing loss in diabetics.J Laryngol Otol.1993;107(3):179-182.[34] Tay HL,Ray N,Ohri R,et al.Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss.Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.1995;20(2):130-134.[35] Díaz de León-Morales LV,Jáuregui-Renaud K,Garay-Sevilla ME,et al.Auditory impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Med Res.2005;36(5):507-510.[36] Niiya Y,Abumiya T,Shichinohe H,et al.Susceptibility of brain microvascular endothelial cells to advanced glycation end products-induced tissue factor upregulation is associated with intracellular reactive oxygen species.Brain Res.2006;1108(1): 179-187.[37] 赵智翔,许敏达,陈松岳,等.糖尿病影响听力的相关因素分析[J].浙江临床医学,2006,8(8):817.[38] Parving A,Elberling C,Balle V,et al.Hearing disorders in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Audiology. 1990;29(3):113-121.[39] 王洪田,钟乃川.畸变产物耳声发射选择注意效应测试对糖尿病人听力的评价[J].临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,1998,12(11):483-486.[40] Orts Alborch M,Morant Ventura A,García Callejo J,et al.The study of otoacoustic emissions in diabetes mellitus.Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp.1998;49(1):25-28.[41] Ottaviani F,Dozio N,Neglia CB,et al.Absence of otoacoustic emissions in insulin-dependent diabetic patients: is there evidence for diabetic cochleopathy?J Diabetes Complications. 2002;16(5):338-343.[42] Lasisi OA,Nwaorgu OGB,Bella AF.Cochlear vestibular complications of diabetes mellitus in Ibadan,Nigeria.Int Congress Series.2003;12(40):1325-1328.[43] 张曼华,张丽.脑干听觉诱发电位对糖尿病耳聋诊断价值的探讨[J].临床内科杂志,2005,22(8):563.[44] Raynor EM,Carrasco VN,Prazma J,et al.An assessment of cochlear hair-cell loss in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus diabetic and noise-exposed rats.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1995;121(4):452-456.[45] Perez R,Ziv E,Freeman S,et al.Vestibular end-organ impairment in an animal model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Laryngoscope.2001;111(1):110-113.[46] 王士礼,陈学明,毕道周,等.实验性糖尿病大鼠内耳毛细血管超微结构变化[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2006,14(4):278-279.[47] 张永胜,张玉海.糖尿病大鼠耳蜗病变的形态学观察[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2008,22(1):64-66.[48] 雒富基,陈小婉,罗维民.糖尿病早期内耳损伤听力学改变的实验研究[J].听力学及言语疾病杂志,2009,17(3):265-267.[49] Masutani H,Takahashi H,Sando I.Stria vascularis in Ménière's disease: a quantitative histopathological study.Auris Nasus Larynx.1992;19(3):145-152.[50] Gutmann R,Wollenberg B,Krampert B,et al.Incidence of Doppler ultrasound detectable stenoses of cervical arteries in patients with cochlear-vestibular symptoms. Laryngorhinootologie.1993;72(10):502-505.[51] 董民声,董明敏,娄卫华.内耳疾病研究进展[M].郑州:河南医科大学出版社,1999:109-110.[52] 罗志强,孔维佳.耳蜗微循环的自身调节机制[J].国外医学:耳鼻咽喉科学分册,2001,25(4):216-219.[53] Aird WC.Endothelium as an organ system.Crit Care Med.2004;32(5Suppl):271-279. |