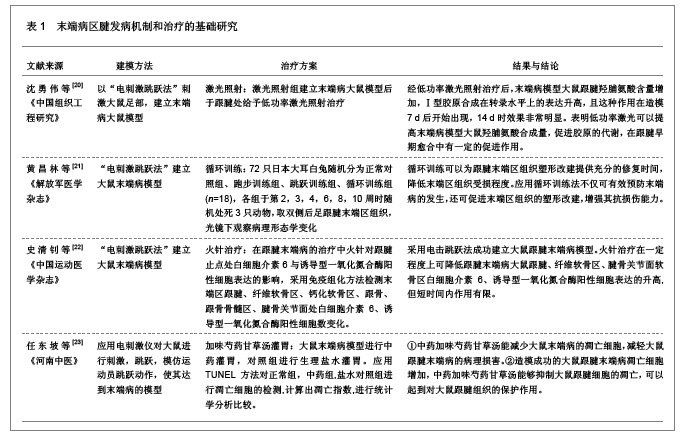
| [1] Xu Y, Murrell GA. The basic science of tendinopathy.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1528-1538. [2] Archambault JM, Jelinsky SA, Lake SP, et al. Rat supraspinatus tendon expresses cartilage markers with overuse. J Orthop Res. 2007;25(5):617-624. [3] Battery L,Maffulli N.Inflammation in overuse tendon injuries.Sports Med Arthrosc.2011;19(3):213-217.[4] Bass E. Tendinopathy: why the difference between tendinitis and tendinosis matters. Int J Ther Massage Bodywork. 2012; 5(1):14-17. [5] 方小芳,史清钊,周军.末端病发病机制的国内外研究现状[J].中国康复医学杂志,2009,24 (11):1055-1058.[6] Dirks RC, Warden SJ. Models for the study of tendinopathy. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2011;11(2):141-149. [7] J P, U F, K Q, et al. Local biochemical and morphological differences in human Achilles tendinopathy: a case control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012 Apr 5;13:53. [8] Maganaris CN,Narici MV,Maffulli N.Biomechanics of the Achilles tendon.Disabil Rehabil. 2008;30(20-22):1542-1547.[9] Thomas MV, Puleo DA. Infection, inflammation, and bone regeneration: a paradoxical relationship. J Dent Res. 2011; 90(9):1052-1061. [10] Rangaswami H, Marathe N, Zhuang S, et al. Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase mediates osteoblast mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(22):14796- 14808. [11] 林松娟,刘美娟,王蓬伟,等. L-精氨酸干预治疗对 COPD 大鼠肺动脉压的影响[J].现代预防医学.2011;38(21):4479-4480. [12] Bokhari AR, Murrell GA. The role of nitric oxide in tendon healing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(2):238-244.[13] Murrell GA. Using nitric oxide to treat tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2007;41(4):227-231.[14] Yang L, Guo A, Gu JC.c-Jun N-terminal kinase and nuclear fact or κB mediate nitric oxide-induced expression of matrix met alloproteinase-13. International Orthopedics (SICOT). 2011;35:1261–1266. [15] 扈盛,滕宇,胡亚哲,等.内皮型一氧化氮合酶在大鼠末端病中的表达[J].中国运动医学杂志,2005,24(6):689-692.[16] Benjamin M, Kaiser E, Milz S. Structure-function relationships in tendons: a review. J Anat. 2008;212(3):211-228.[17] 杨小英,梁蓓蓓,黄志平等.不同运动负荷大鼠主要器官各型 NOS 表达水平的研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2011,38(13): 2550-2553. [18] Jelinsky SA, Rodeo SA, Li J, et al. Regulation of gene expression in human tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:86.[19] Szomor ZL,Appleyard RC,Murrell GA.Overexpression of nitric oxide synthases in tendon overuse.Orthop Res.2006;24(1): 80-86. [20] 沈勇伟,史晓伟.低功率激光修复末端病大鼠跟腱胶原[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(28):5165-5169.[21] 黄昌林,高旺,黄涛,等. 循环训练模式对兔跟腱末端区组织形态学的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2012,37(5):515-518.[22] 史清钊,方小芳,周军,等. 火针治疗对跟腱末端病大鼠跟腱止点组织IL-6与iNOS表达的影响[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2011,30(7): 650-655.[23] 任东坡,唐欣荣,吕发明. 加味芍药甘草汤对大鼠跟腱末端病影响的实验研究[J]. 河南中医,2009,29(5):455-457.[24] Abramson SB. Nitric oxide in inflammation and pain associated with osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10 Suppl 2:S2.[25] 田学忠,刘越, 陈华.白细胞介素1和诱导型一氧化氮合酶在兔肢体缺血再灌注后关节软骨中的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2007;11(45):9021-9025.[26] Forterre S, Zurbriggen A, Spreng D. Nitric oxide induces cell death in canine cruciate ligament cells by activation of tyrosine kinase and reactive oxygen species. [27] Nichols SP, Storm WL, Koh A, et al. Local delivery of nitric oxide: targeted delivery of therapeutics to bone and connective tissues. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1177- 1188.[28] Khosla S. Is nitroglycerin a novel and inexpensive treatment for osteoporosis? JAMA. 2011;305(8):826-827.[29] Murrell GA, Tang G, Appleyard RC, et al. Addition of nitric oxide through nitric oxide-paracetamol enhances healing rat achilles tendon. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1618- 1624.[30] Ryu B, Qian ZJ, Kim SK. SHP-1, a novel peptide isolated from seahorse inhibits collagen release through the suppression of collagenases 1 and 3, nitric oxide products regulated by NF-kappaB/p38 kinase. Peptides. 2010;31(1):79-87.[31] Saito Y, Sawa T, Yoshitake J, et al. Nitric oxide promotes recycling of 8-nitro-cGMP, a cytoprotective mediator, into intact cGMP in cells. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8(11):2909-2915.[32] Molloy TJ, de Bock CE, Wang Y, et al. Gene expression changes in SNAP-stimulated and iNOS-transfected tenocytes--expression of extracellular matrix genes and its implications for tendon-healing. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(9): 1869-1882.[33] McCarrel TM, Minas T, Fortier LA. Optimization of leukocyte concentration in platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of tendinopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(19):e1431- 1438.[34] McCallum SD, Paoloni JA, Murrell GA. Five-year prospective comparison study of topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic lateral epicondylosis at the elbow. Br J Sports Med. 2011;45(5):416-420.[35] 赵晓芳, 王刚, 孙先润,等.体外震波仪治疗肌腱末端病的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(19):1806-1808.[36] 雷鸣鸣,张璐. 体外冲击波治疗国家队运动员髌腱末端病的疗效分析[J]. 华西医学,2012,27(01):37-39.[37] 魏军成, 纪益魁. 微型骨锚在治疗跟腱末端病的应用[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2010,15(03):326-327.[38] 王国祥, 严永军,岳春林. 髌腱末端病运动员膝关节等速向心和离心运动时股四头肌表面肌电的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(46):9105-9108.[39] 郭佳佳,史清钊,张玉芹.末端病基础研究和临床治疗的国内外研究现状[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2009,9(22):4397-4400.[40] 方小芳,史清钊,周军.末端病发病机制的国内外研究现状[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2009,24(11):1055-1058. [41] 扈盛,滕宇,胡亚哲.内皮型一氧化氮合酶在大鼠末端病中表达的研究[G]. 全国软组织疼痛微创技术专题研讨会论文汇编,2004.[42] 王和平,滕宇,胡亚哲,等. 诱导型一氧化氮合酶在末端病大鼠跟腱末端区表达及分布的规律[J]. 中国临床康复,2005,9(24): 159-161.[43] 黎明,韩红,滕宇,等.跟腱末端病的发病和保护修复机制[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,4:10-12. |