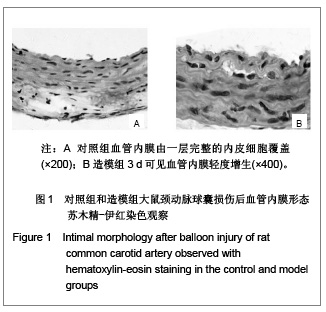
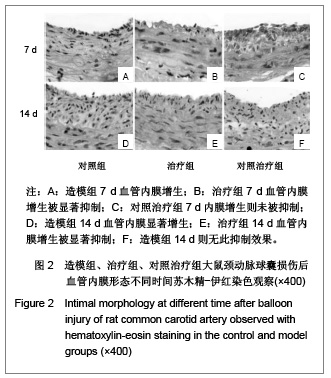
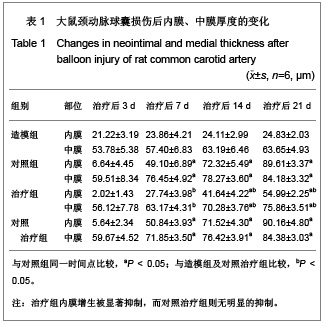
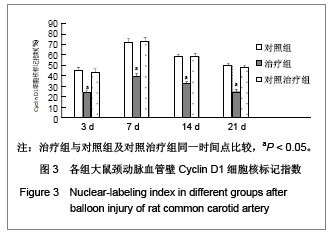
| [1] Rupp J, Hellwig-Burgel T, Wobbe V, et al. Chlamydia pneumonia infection promotes a Proliferative phenotype in the vasculature through Egr-1activation in vitro and in vivo. J Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(9):3447-3452.[2] Khachigian LM. Early growth response-1 in cardiovascular pathobiology. J Circ Res. 2006;98(2):186-191. [3] Khachigian LM. Early growth response-1: blocking angiogenesis by shooting the messenger. J Cell Cycle. 2004;3(1):10-11.[4] Wang L, Zheng J, Du Y, et al. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein maintains the contractile phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells by interacting with alpha(7)beta(1) integrin. J Circ Res. 2010;106(3):514-525. [5] Wada Y, Suzuli J, Kawauchi M, et al. Ealy growth response factor-1and basic transcriptional element-binding Protein 2 expression in cardiac allografts. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2001;20(5):590-594.[6] Tomita N, Azuma H, Kaneda Y, et al.Application of decoy oligodeoxynucleotides-based approach to renal diseases. J Curr Drug Targets. 2004;5(8):717-733.[7] Ohtani K, Egashira K, Usui M, et al. Inhibition of neointimal haperplasia after balloon injury by cis-element‘decoy’ of early growth response gene-1 in hapercholesterolemic rabbits. J Gene Therpy. 2004;11(2):126-132.[8] Tomita N, Kashihara N, Morishita R. Transcription factor decoy oligonucleotide-based therapeutic strategy for renal disease. J Clin Exp Nephrol. 2007;11(1):7-17. [9] Usui M, Egashira K, Ohtani K, et al. Anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene therapy inhibits restenotic changes(neointimal hyperplasia) after balloon injury in rat and monkeys. J FASEB J. 2002;16(13):1838-1840.[10] Bonta PI, Pols TW, van Tiel CM, et al. Nuclear receptor Nurr1 is expressed in and is associated with human restenosis and inhibits vascular lesion formation in mice involving inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation and inflammation. J Circulation. 2010;121(18):2023-2032.[11] Osherov AB, Gotha L, Cheema AN, et al. Proteins mediating collagen biosynthesis and accumulation in arterial repair: novel targets for anti-restenosis therapy. J Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(1):16-26.[12] Xiang M, Xu YJ, Liu XS, et al. Cigarette smoke extract promotes human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation through protein kinase C alpha-dependent induction of Cyclin D1. J Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(24): 3663-3670.[13] Nakagawa M, Ohno T, Maruyama R, et al. Sesquiterpene lactone suppresses vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration via inhibition of cell cycle progression. J Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(9):1754-1757.[14] Li F, Duman-Scheel M, Yang D, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling induces vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via induction of the G1 cyclin-retinoblastoma axis. J Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(9):1787-1794.[15] Kavurma MM, Khachigian LM. Sp1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells by repressing p21WAF1/Cip1 transcription and Cyclin D1-Cdk4-p21WAF1/Cip1 complex formation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(35):32537-32543.[16] Wu Y, Han W, Liu GN. A DNA enzyme targeting Egr-1 inhibits rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by down-regulation of Cyclin D1 and TGF-beta1. J Braz J Med Biol Res. 2010;43(1):17-24.[17] Zhang LS, Ma HW, Greyner HJ, et al. Inhibition of cell proliferation by CD44: Akt is inactivated and EGR-1 is down-regulated. J Cell Prolif. 2010;43(4):385-395.[18] Han W, Liu GN. EGR-1 decoy ODNs inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia of balloon- injured arteries in rat. J Life Sciences. 2010;86(7-8): 234-243. |