| [1] Olschewski P, Hunold G, Eipel C, et al. Improved microcirculation by low-viscosity histidine- tryptophan-ketoglutarate graft flush and subsequent cold storage in University of Wisconsin solution: results of an orthotopic rat liver transplantation model. Transpl Int. 2008; 21(12):1175-1180.[2] Feng L, Zhao N, Yao X, et al. tidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate solution vs. University of Wisconsin solution for liver transplantation: a systematic review. Liver Transpl. 2007; 13(8): 1125-1136.[3] Spiegel HU, Schleimer K, Kranz D, et al. gan preservation with EC, HTK, and UW solutions in orthotopic liver transplantation in syngeneic rats. Part I: Functional parameters. J Invest Surg. 1998;11(1):49-56.[4] Zuluaga GL, Agudelo RE, Tobón JJ. Preservation Solutions for Liver Transplantation in Adults: Celsior versus Custodiol: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis With an Indirect Comparison of Randomized Trials. Transplant Proc. 2012 Sep 15. [5] Juang SE, Huang HW, Kao CW, et al. Effect of university of wisconsin and histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate preservation solutions on blood potassium levels of patients undergoing living-donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(2): 366-368.[6] Salahudeen AK, Haider N, May W. Cold ischemia and the reduced long-term survival of cadaveric renal allografts. Kidney Int. 2004;65(2):713-718.[7] Luo G,Luo DL,Li XZ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(18):3235-3238.罗刚,罗地来,李晓征,等.自制PV液与大鼠肝脏低温保存:与UW液的对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(18): 3235-3238.[8] Wu J, Zheng SS. Liver transplantation in China: problems and their solutions. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004;3(2): 170-174.[9] Zhou ZH,Cui XG,Han QC,et al,Dier Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2007; 28(2):122-126.周智华,崔心刚,韩秋成,等.上海多器官保存液保存离体大鼠肝脏的实验研究[J].第二军医大学学报,2007,28(2):122-126.[10] Jiang XQ.Diyi Junyi Daxue,2006.蒋晓青.肝移植术中还原型谷胱甘肽对机体氧自由基代谢水平影响的研究[D].第一军医大学,2006.[11] Montalvo-Jave EE, Escalante-Tattersfield T, Ortega-Salgado JA, et al. Factors in the pathophysiology of the liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 2008;147(1): 153-159.[12] Fernandez-Checa JC, Yi JR, Garcia Ruiz C, et al.Plasma membrane and mitochondrial transport of hepatic reduced glutathione.Semin Liver Dis. 1996;16(2):147-158.[13] Yuan WY,Jiang WQ,Jian WL,et al,Zhongguo Yishi Zazhi. 2004; 6(5):638-640.元文勇,姜文泉,姜惟龙,等.大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤早期肝亚细胞成份中氧自由基的变化[J].中国医师杂志,2004,6(5):638-640. [14] Geng ZL, Lu HM, Cao H, et al. Jiefangjun Yixue Zazhi. 2011; 36(3):221-224.耿智隆,陆化梅,曹虹,等. 己酮可可碱对重度失血性休克大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注后氧自由基的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志,2011, 36(3):221-224.[15] Deree J, Martins JO, Leedom A, et al. Hypertonic saline and pen toxifylline educes hemorrhagic shock resuscitation-induced pulmonary inflammation through attenuation of neutrophil degranulation and pro-inflammatory mediator synthesis. Trauma.2007;62(2):104-111.[16] Zhao K. Zhongyuan Yikan. 2007;34(3):5-6.赵珂.银杏叶提取物对大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中原医刊,2007,34(3):5-6. [17] Nair N, Bedwal S, Prasad S, et al.Short-term zinc deficiency in diet induces increased oxidative stress in testes and epididymis of rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 2005;43(9):786-794.[18] Chen SJ,Sun YM,Meng YJ,et al. Huan Jing Yu Jian Kang Za Zhi. 2007;24(8):627-629.陈树君,孙玉敏,孟羽俊,等.慢性氟中毒大鼠睾丸组织总抗氧化能力与一氧化氮合酶和一氧化氮的变化[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2007, 24(8):627.[19] Tang ZZ,Dai CL,Shen Y,et al,Zhongguo Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2002;31(4):270-272.唐志宇,戴朝六,沈勇,等.SOD在缺血预处理保护大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J].中国医科大学学报,2002,31(4): 270-272.[20] Li K, Chen XP, Xue HZ, et al. Zhonghua Putong Waike Zazhi. 2009;9:744-747.李珂,陈晚平,薛焕洲,等. 去铁胺对自体肝移植大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2009,9:744-747.[21] Zhao ZL, Zhang YS, Yu JL, et al. SHijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2001;9(1):77-79.赵子粼,张云生, 俞金龙,等. 肝移植用保存液[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2001,9(1):77-79.[22] Shen XD, Ke B, Uchida Y, et al. Native macrophages genetically modified to express heme oxygenase 1 protect rat liver transplants from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Liver Transpl. 2011;17(2):201-210.[23] Ghafaripour S, Sahmeddini MA, Lahsaee SM, et al. Hypotension after reperfusion in liver transplantation: histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate versus University of Wisconsin solution. Prog Transplant. 2010;20(3):256-261.[24] Garcia JH, Barros MA, Gonçalves BP, et al. Evaluation of hepatic function after orthotopic liver transplantation: a comparative study using Belzer and Collins solutions. Transplant Proc. 2006;38(5):1236-1237.[25] Liu DM, Piao YR, Dong XZ, et al. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2012;29(1):147-147.刘东明,朴勇瑞,董秀哲,等. 自制多器官保存液对兔肾脏低温保存期间线粒体功能的保护作用[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2012, 29(1):147-147.[26] Chen L,Yan WX, Tang LL, et al. Gandanyi Waike Zazhi, 2010, 22(3):200-202.陈亮,颜王鑫,唐兰兰,等.L-精氨酸对兔缺血再灌注损伤肝脏能量代谢的影响[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2010,22(3):200-202.[27] Zhao WY. Dier Junyi Daxue. 2009. 赵闻雨.新型SMO多器官保存液在大鼠肝脏保存中的实验研究[D].第二军医大学,2009.[28] Wang H,Chen ZZ,Zhonghua Ganzangbing Zazhi, 2000,8(2): 98.王红,陈在忠.川芎嗪对大鼠肝纤维化脂质过氧化的影响[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2000,8(2):98.[29] Wang WT,Xu ZJ.Lin LN. et al. Zhonghuo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Jijiu Zazhi, 2002,9(4):216-218.王万铁,徐正衸,林丽娜,等.川芎嗪抗肝缺血-再灌注损伤作用机制的实验研究[J].中华中西医结合急救杂志,2002,9(4):216-218.[30] Zhang B,Qian HX,Q L,et al. Suzhou Daxue Xuebao yixueban. 2006;26(3):396-399.张伯,钱海鑫,秦磊,等.川芎嗪对大鼠供肝冷保存再灌注损伤中肝细胞凋亡及调控基因表达的影响[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2006, 26(3):396-399.[31] Zhai YR,Yu XF,Qu SC,et al. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2010; 26(2):276-277.翟玉荣,于小风,曲绍春,等.苦碟子总黄酮对大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中国药理学通报,2010,26(2):276-277.[32] Sun W,Zhang JP,Jie F,et al,Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu Yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(31):5813-5816.孙雯,张金萍,揭芳,等.自制多脏器保存液对大鼠睾丸一氧化氮合酶的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(31): 5813-5816.[33] Ko JS, Kim GS, Gwak MS, et al. Greater hemodynamic instability with histidine-tryptophan-ketoglutarate solution than University of Wisconsin solution during the reperfusion period in living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2008; 40(10):3308-3310.[34] Muñoz-Bonet JI, López-Santamaria M, Ruza-Tarrio F, et al. Oxygen consumption, lactate metabolism, and gastric intramucosal pH in an experimental liver transplantation model. Crit Care Med. 1998 ;26(11):1850-1856. |
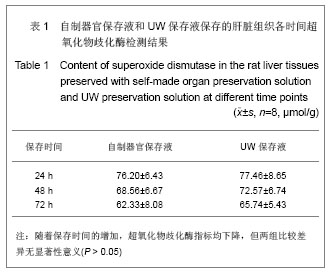
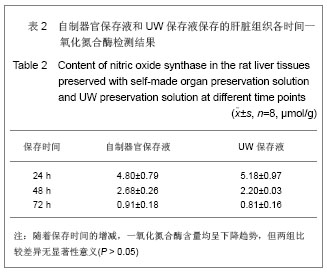
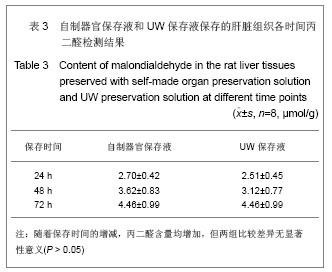
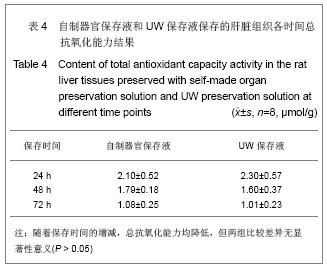

 实验结果显示,随着低温保存肝脏时间的延长,实验组和对照组肝组织丙二醛、一氧化氮合酶、TAO-C均逐渐下降,实验组下降幅度较对照组缓慢;实验组同时间点丙二醛含量均高于对照组;实验组对低温保存大鼠肝脏同时点超氧化物歧化酶、一氧化氮合酶和总抗氧化能力活性及丙二醛含量与对照组比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05) ,上述指标均表明自制器官保存液的川芎嗪和苦碟子能够协同作用,共同发挥对抗氧自由基的作用减轻肝脏缺血再灌注的损伤[33-34],对低温保存大鼠肝脏具有较好的保护作用,与UW液相当。
实验结果显示,随着低温保存肝脏时间的延长,实验组和对照组肝组织丙二醛、一氧化氮合酶、TAO-C均逐渐下降,实验组下降幅度较对照组缓慢;实验组同时间点丙二醛含量均高于对照组;实验组对低温保存大鼠肝脏同时点超氧化物歧化酶、一氧化氮合酶和总抗氧化能力活性及丙二醛含量与对照组比较,差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05) ,上述指标均表明自制器官保存液的川芎嗪和苦碟子能够协同作用,共同发挥对抗氧自由基的作用减轻肝脏缺血再灌注的损伤[33-34],对低温保存大鼠肝脏具有较好的保护作用,与UW液相当。