中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (2): 291-295.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.02.019
• 组织构建细胞学实验 cytology experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
创伤性深静脉血栓形成与血液中Hmox-1基因的表达
郑燕科1,李宏坤2,汤善华1,赵 敏1,吕仁发1,陈荣剑1
- 1 解放军第184医院骨科,江西省鹰潭市 335000
2 昆明医学院第一附属医院骨科,云南省昆明市 650032
Formation of traumatic deep venous thrombosis and mRNA expression of Hmox-1 in the blood
Zheng Yan-ke1, Li Hong-kun2, Tang Shan-hua1, Zhao Min1, Lü Ren-fa1, Chen Rong-jian1
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, the 184 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Yingtan 335000, Jiangxi Province, China
2 Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
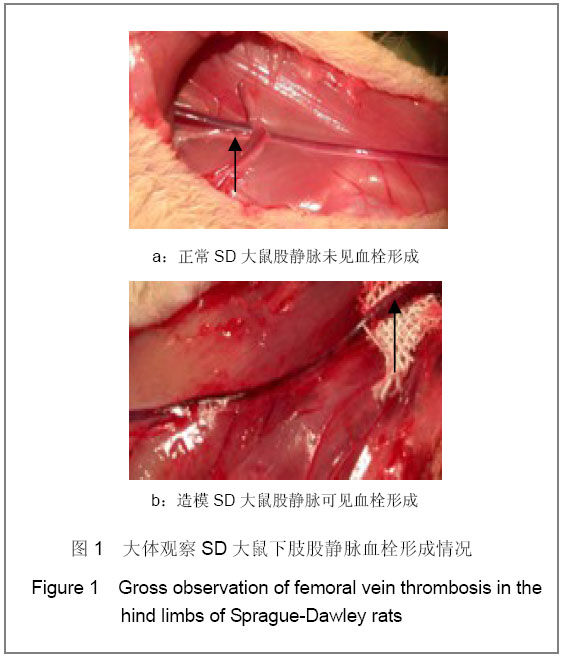
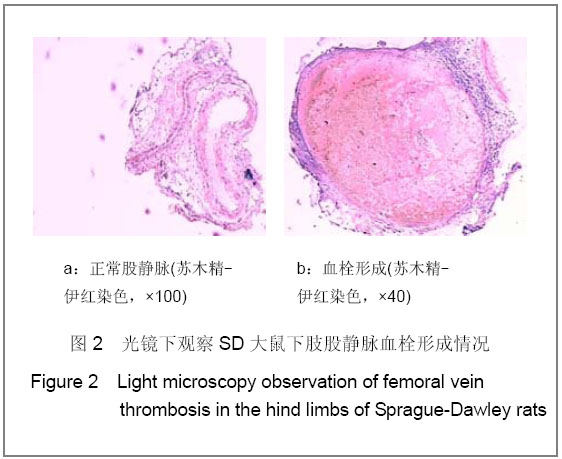
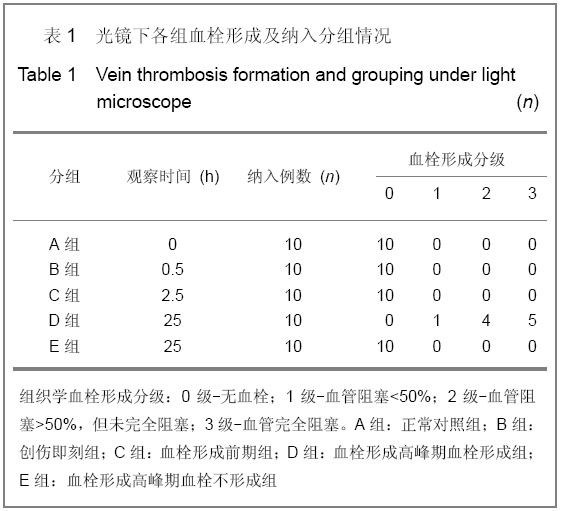
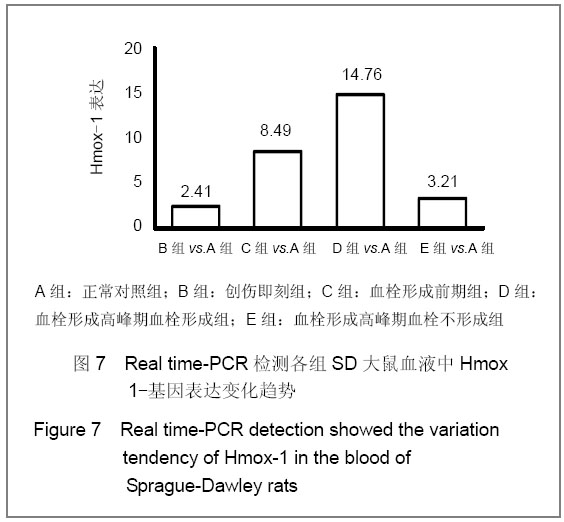
背景:目前深静脉血栓的诊断主要依赖于影像学和实验室检查,其最致命的不足是血栓已经形成方能明确诊断。因此有必要采用先进的分子技术对其进行研究,探索其发生发展的内在规律。 目的:观察Hmox-1在大鼠创伤性深静脉血栓形成过程中的变化,探讨其作为预测诊断深静脉血栓分子标记物的可行性。 方法:采用钳夹大鼠双侧股静脉和双后肢人字石膏固定的方法建立创伤性深静脉血栓形成模型。依据造模时间和血栓形成状态,将100只实验大鼠随机分为5组:正常对照组、创伤即刻组、血栓形成前期组、血栓形成高峰期血栓形成组、血栓形成高峰期血栓不形成组。Real time-PCR检测血液中Hmox-1基因表达,并切取双侧股静脉血管进行组织学观察血栓形成程度。 结果与结论:建立大鼠创伤性深静脉血栓形成模型后25 h,血栓形成率58%(38/65);血栓形成前期组、血栓形成高峰期血栓形成组Hmox-1表达高于正常对照组(P < 0.05),而血栓形成高峰期血栓不形成组与正常对照组比较差异无显著性意义。Hmox-1在血液中的表达变化趋势与血栓形成生物学过程相符,有可能作为预测大鼠深静脉血栓形成的标志物。
中图分类号: