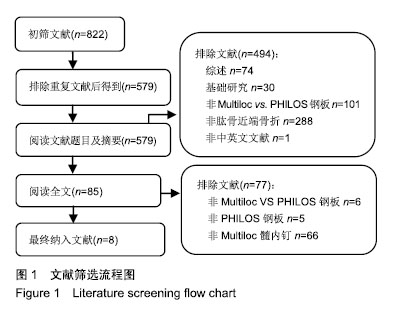
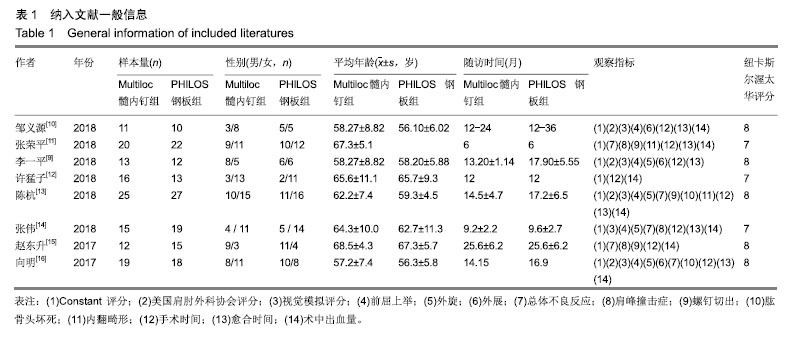
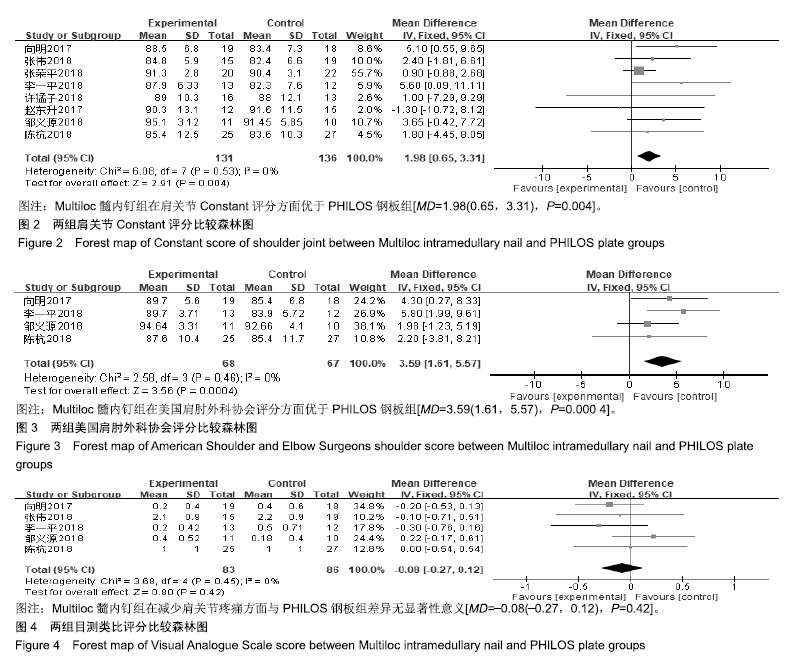
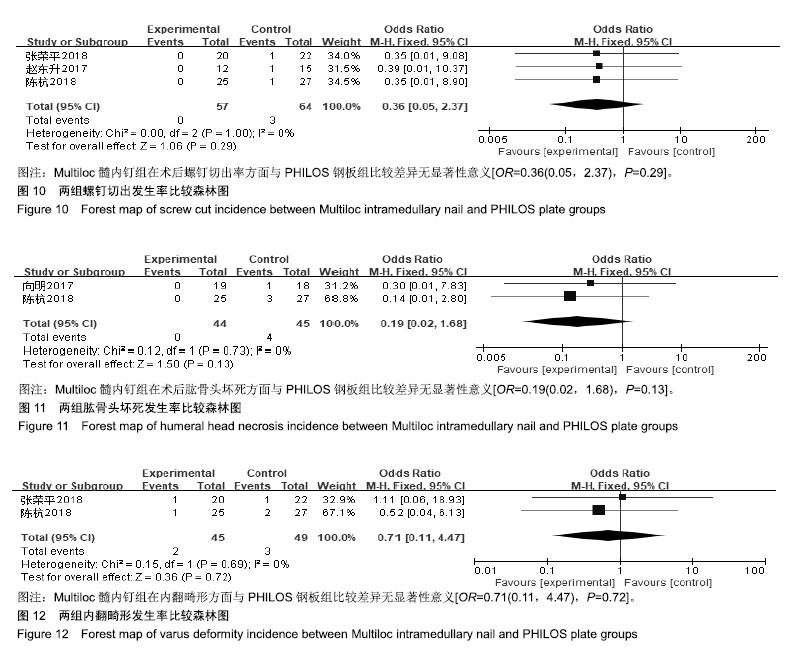
| [1]Bell JE, Leung BC, Spratt KF, et al. Trends and variation in incidence, surgical treatment, and repeat surgery of proximal humeral fractures in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;2: 121-131.[2]Palvanen M, Kannus P, Niemi S, et al. Update in the epidemiology of proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442:87-92.[3]Gracitelli M, Malavolta EA, Assuncao JH, et al. Locking intramedullary nails versus locking plates for the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Expert Rev Med Dev. 2017;9: 733-739.[4]Hessmann MH, Nijs S, Mittlmeier T, et al. Internal fixation of fractures of the proximal humerus with the multiloc nail. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;4-5:418-431.[5]Gupta AK, Harris JD, Erickson BJ, et al. Surgical management of complex proximal humerus fractures-a systematic review of 92 studies including 4500 patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;1: 54-59.[6]Sun JC, Li YL, Ning GZ, et al. Treatment of Three- and Four-Part Proximal Humeral Fractures with Locking Proximal Humerus Plate. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;6:699-704.[7]Handoll H, Brorson S. Interventions for treating proximal humeral fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(11):CD000434.[8]Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;9:603-605.[9]李一平,向明,杨国勇,等.内翻型肱骨近端骨折的治疗:锁定钢板与髓内钉的临床效果[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2018,37(11): 945-950.[10]邹义源,向明,陈杭,等.Neer二部分肱骨外科颈骨折微创治疗: Phlios钢板与Multiloc髓内钉对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(19):2981-2987.[11]张荣平. Multiloc髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的早期疗效[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2018,3(20):54-56.[12]许猛子,周君琳,宋华伟,等.Multiloc髓内钉与Philos锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折疗效对比研究[J]. 国际外科学杂志, 2018,45(3): 168-172.[13]陈杭,向明,胡晓川,等.Philos钢板与Multiloc髓内钉治疗中老年肱骨近端三?四部分骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34 (12):1067-1074.[14]张伟,范建波,崔志明,等.MultiLoc髓内钉与 PHILOS 钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2018,7(11): 811-815.[15]赵东升,郑晓勇,余清文,等.Multiloc髓内针治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的临床疗效[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(5):453-455.[16]向明,杨国勇,邹义源,等.锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(21):1333-1341.[17]丁国庆,李晓林.老年肱骨近端骨折治疗进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2011,32(6):372-374, 383.[18]Konrad G, Audige L, Lambert S, et al. Similar outcomes for nail versus plate fixation of three-part proximal humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;2:602-609.[19]林浩东,周军.老年肱骨近端骨折的最佳治疗方案选择[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2018,7(11):801-803.[20]Li M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Intramedullary nail versus locking plate for treatment of proximal humeral fractures: a meta-analysis based on 1384 individuals. J Int Med Res. 2018; 11:4363-4376.[21]Yoon RS, Dziadosz D, Porter DA, et al. A comprehensive update on current fixation options for two-part proximal humerus fractures. Injury. 2014;45(3):510-514.[22]Sun Q, Ge W, Li G, et al. Locking plates versus intramedullary nails in the management of displaced proximal humeral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2018;3:641-650.[23]Maier D, Jaeger M, Izadpanah K, et al. Proximal humeral fracture treatment in adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 3: 251-261.[24]Burkhart KJ, Dietz SO, Bastian L, et al. The treatment of proximal humeral fracture in adults. Deutsch Arztebl Int. 2013; 35-36:591-597.[25]Wang G, Mao Z, Zhang L, et al. Meta-analysis of locking plate versus intramedullary nail for treatment of proximal humeral fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:122.[26]王伟,陈永佳,沈磊,等.微创钢板内固定与传统手术治疗成人肱骨干骨折的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(35): 5715-5723.[27]罗世彤,高宏,刘峰瑞,等.髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端两部分骨折疗效的Meta分析[J].中华创伤杂志, 2016,32(12): 1073-1079.[28]焦庆丰,白鹏程,张媺,等.Philos钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折疗效分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志,2016,19(3):336-337.[29]Lowe JB, Monazzam S, Walton B, et al. How to use fluoroscopic imaging to prevent intraarticular screw perforation during locked plating of proximal humerus fractures: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;10:e401-e407.[30]王富强,孙斌,孔凡强.分叉交锁髓内钉与锁定钢板对肱骨骨折患者生物力学比较研究[J]. 中华保健医学杂志, 2018,20(3):203-205.[31]高峰,王秀会,夏胜利,等.锁定钢板与髓内钉治疗肱骨近端骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2018,26(12):1068-1073.[32]余德涛,王雷,邢帧全.锁定钢板与弹性髓内钉对桡神经损伤性肱骨骨折临床疗效比较研究[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2018,15(11): 1640-1643. |
.jpg)

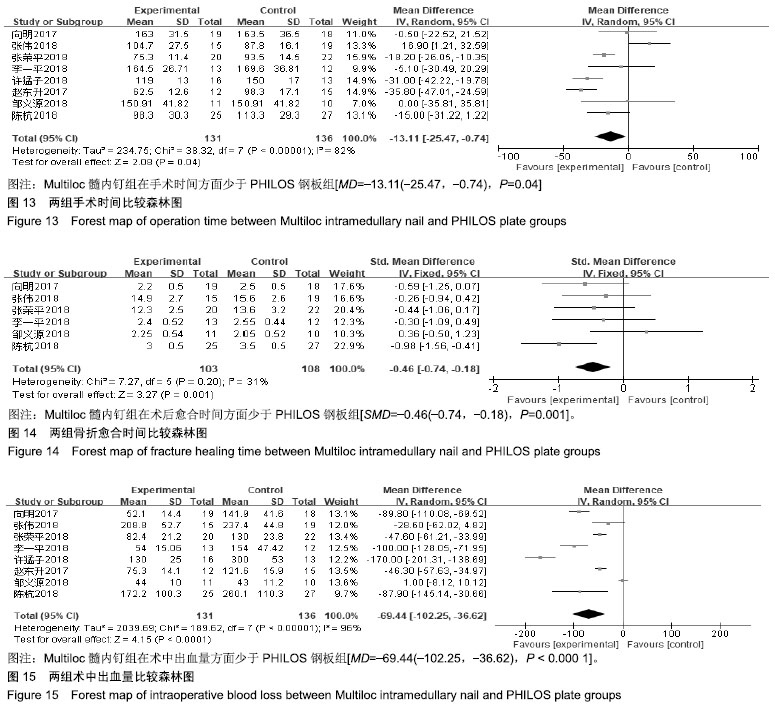
.jpg)