| [1]Lladó L, Figueras J. Techniques of orthotopic liver transplantation. HPB (Oxford). 2004;6(2):69-75.[2]Zagoura DS, Roubelakis MG, Bitsika V, et al. Therapeutic potential of a distinct population of human amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells and their secreted molecules in mice with acute hepatic failure. Gut. 2012;61(6):894-906.[3]Vosough M, Moslem M, Pournasr B, et al. Cell-based therapeutics for liver disorders. Br Med Bull. 2011;100:157-172.[4]Muraca M. Evolving concepts in cell therapy of liver disease and current clinical perspectives. Dig Liver Dis. 2011;43(3):180-187.[5]Gramignoli R, Vosough M, Kannisto K, et al. Clinical hepatocyte transplantation: practical limits and possible solutions. Eur Surg Res. 2015;54(3-4):162-177.[6]Chen X, Zhang S, Liu T, et al. Maintenance of rat hepatocytes under inflammation by coculture with human orbital fat-derived stem cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012;17(2):182-195.[7]Jeong D, Han C, Kang I, et al. Effect of Concentrated Fibroblast-Conditioned Media on In Vitro Maintenance of Rat Primary Hepatocyte. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0148846.[8]Tomasoni S, Longaretti L, Rota C, et al. Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(5):772-780.[9]Agarwal N, Popovic B, Martucci NJ, et al. Biofabrication of Autologous Human Hepatocytes for Transplantation: How do we get there. Gene Expr. 2018 Aug 24. doi: 10.3727/105221618X15350366478989. [Epub ahead of print] [10]Zhilai Z, Biling M, Sujun Q, et al. Preconditioning in lowered oxygen enhances the therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2016;1642:426-435.[11]Liu WH, Song FQ, Ren LN, et al. The multiple functional roles of mesenchymal stem cells in participating in treating liver diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):511-520.[12]Yu Y, Fisher JE, Lillegard JB, et al. Cell therapies for liver diseases. Liver Transpl. 2012;18(1):9-21.[13]Galipeau J, Sensébé L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018; 22(6):824-833. [14]Guo ZY, Sun X, Xu XL, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote peripheral nerve repair via paracrine mechanisms. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(4):651-658.[15]Ahn SY, Chang YS, Sung DK, et al. Cell type-dependent variation in paracrine potency determines therapeutic efficacy against neonatal hyperoxic lung injury. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(8): 1025-1035.[16]Fiore EJ, Domínguez LM, Bayo J, et al. Taking advantage of the potential of mesenchymal stromal cells in liver regeneration: Cells and extracellular vesicles as therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(23):2427-2440.[17]杨记农,姜亦瑶,袁超,等.不同氧体积分数下脂肪间充质干细胞和脐带间充质干细胞的旁分泌能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(21): 3322-3327.[18]Li J, Mao Q, He J, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve the reserve function of perimenopausal ovary via a paracrine mechanism. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):55.[19]Xiong N, Zhang Z, Huang J, et al. VEGF-expressing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, an improved therapy strategy for Parkinson's disease. Gene Ther. 2011;18(4):394-402.[20]Le Blanc K, Frassoni F, Ball L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579-1586.[21]Wang YH, Wu DB, Chen B, et al. Progress in mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):227.[22]Chen L, Zhang J, Yang L, et al. The Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cocultured with Hepatocytes on Damaged Hepatocytes and Acute Liver Failure in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:9156560.[23]Shen C, Lie P, Miao T, et al. Conditioned medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells induces migration and angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(1):20-30.[24]Liu Z, Meng F, Li C, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells rescue mice from acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(9):1207-1219.[25]Chen X, Zhang S, Liu T, et al. Maintenance of rat hepatocytes under inflammation by coculture with human orbital fat-derived stem cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2012;17(2):182-195.[26]Jin S, Li H, Han M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Enhanced Bcl-2 Expression Promote Liver Recovery in a Rat Model of Hepatic Cirrhosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(5):1117-1128.[27]Azhdari Tafti Z, Mahmoodi M, Hajizadeh MR, et al. Conditioned Media Derived from Human Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Improves Primary Hepatocyte Maintenance. Cell J. 2018;20(3):377-387.[28]Li F, Liu Y, Cai Y, et al. Ultrasound Irradiation Combined with Hepatocyte Growth Factor Accelerate the Hepatic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2018;44(5):1044-1052.[29]Teshima T, Matsumoto H, Michishita M, et al. Allogenic Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Acute Hepatic Injury in Dogs. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:3892514.Tang WP, Akahoshi T, Piao JS, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor-treated adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell infusion to ameliorate liver cirrhosis via paracrine hepatocyte growth factor. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;30(6):1065-1074. |
.jpg)

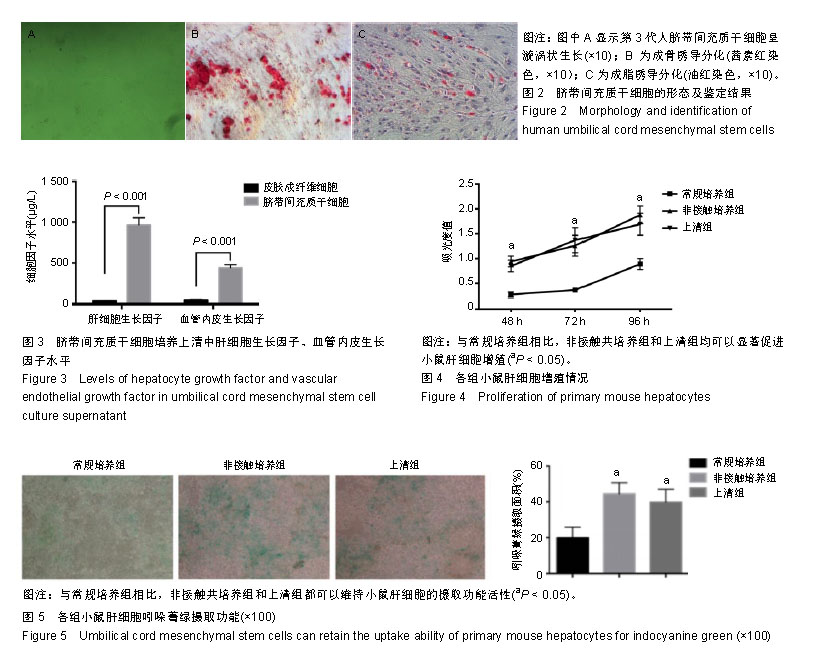
.jpg)
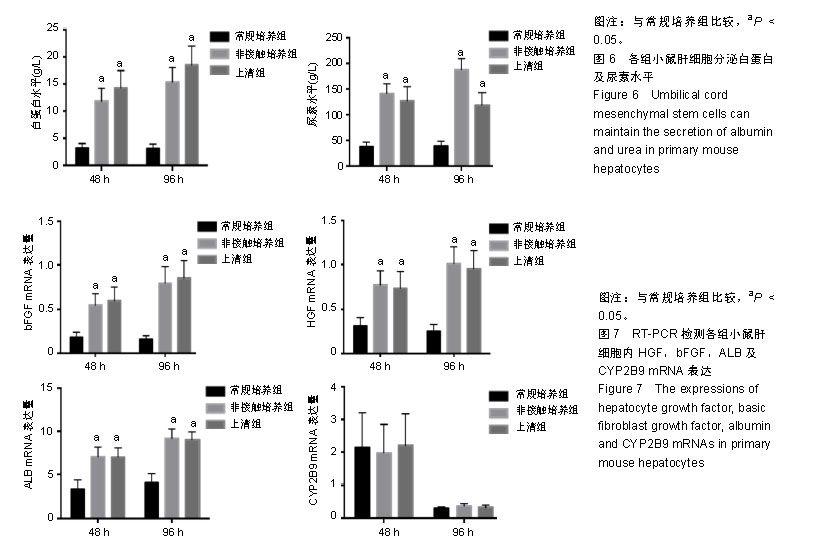
.jpg)
.jpg)