| [1] Weiss DJ. Stem cells, cell therapies, and bioengineering in lung biology and diseases. Comprehensive review of the recent literature 2010-2012. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10(5):S45-97.[2] Rodrigo SF, van Ramshorst J, Hoogslag GE, et al. Intramyocardial injection of autologous bone marrow-derived ex vivo expanded mesenchymal stem cells in acute myocardial infarction patients is feasible and safe up to 5 years of follow-up. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013;6(5):816-825.[3] Zhou Z, You Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice by MiR-142a-5p-Controlled Pulmonary Endothelial Cell Autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1): 258-266.[4] Gupta N, Su X, Popov B, et al. Intrapulmonary delivery of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves survival and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. J Immunol. 2007;179(3):1855-1863.[5] Li D, Pan X, Zhao J, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Acute Lung Injury Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Through Inhibiting the TLR2, 4/NF-κB Pathway in Rats with Multiple Trauma. Shock. 2016;45(6):641-646.[6] Rojas M, Xu J, Woods CR, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in repair of the injured lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005;33(2):145-152.[7] Zhen G, Liu H, Gu N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells transplantation protects against rat pulmonary emphysema. Front Biosci. 2008; 13:3415-3422.[8] Liu HM, Liu YT, Zhang J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate lung injury through anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect in COPD mice. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017;37(4):496-504.[9] Ambalavanan N, Novak ZE. Peptide growth factors in tracheal aspirates of mechanically ventilated preterm neonates. Pediatr Res. 2003;53(2):240-244.[10] Morino S, Nakamura T, Toba T, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 induces recovery of pulmonary blood flow in canine emphysema models. Chest. 2005;128(2):920-926.[11] Morino S, Toba T, Tao H, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes recovery of pulmonary function in a canine models of elastase-induced emphysema. Exp Lung Res. 2007;33(1):15-26.[12] Tanni SE, Pelegrino NR, Angeleli AY, et al. Smoking status and tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediated systemic inflammation in COPD patients. J Inflamm (Lond). 2010;7:29.[13] Gu W, Song L, Li XM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate airway inflammation and emphysema in COPD through down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 via p38 and ERK MAPK pathways. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8733.[14] Srivastava PK, Dastidar SG, Ray A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: role of matrix metalloproteases and future challenges of drug therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16(7):1069-1078.[15] Tzouvelekis A, Laurent G, Bouros D. Stem cell therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Seeking the Prometheus effect. Curr Drug Targets. 2013;14(2):246-252.[16] Badri L, Walker NM, Ohtsuka T, et al. Epithelial interactions and local engraftment of lung-resident mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45(4):809-816.[17] Robinson AB, Stogsdill JA, Lewis JB, et al. RAGE and tobacco smoke: insights into modeling chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Physiol. 2012;3:301.[18] Gupta V, Banyard A, Mullan A, et al. Characterization of the inflammatory response to inhaled lipopolysaccharide in mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79(5):767-776.[19] Parasuramalu BG, Huliraj N, Prashanth Kumar SP, et al. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its association with tobacco smoking and environmental tobacco smoke exposure among rural population. Indian J Public Health. 2014;58(1):45-49.[20] Kobayashi S, Fujinawa R, Ota F, et al. A single dose of lipopolysaccharide into mice with emphysema mimics human chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation as assessed by micro-computed tomography. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013; 49(6):971-977.[21] Matsui R, Brody JS, Yu Q. FGF-2 induces surfactant protein gene expression in foetal rat lung epithelial cells through a MAPK-independent pathway. Cell Signal. 1999;11(3):221-228.[22] Guzy RD, Stoilov I, Elton TJ, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 is required for epithelial recovery, but not for pulmonary fibrosis, in response to bleomycin. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;52(1): 116-128.[23] Zhao YF, Luo YM, Xiong W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based FGF2 gene therapy for acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(5):857-865.[24] 赵悦,马琳,彭珊珊,等.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的基因表达[J].医学研究生学报, 2015,28(12):1246-1251.[25] Ding X, Li M, Cao Y, et al. Effects of Plasmid Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Magnetic Chitosan Gelatin Microspheres on Proliferation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2015;32(5):1083-1089.[26] Tong L, Zhou J, Rong L, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor-10 (FGF-10) Mobilizes Lung-resident Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Protects Against Acute Lung Injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21642.[27] 宋燕峰,曹洁.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子转染骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗肺动脉高压[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(6):918-922.[28] 崔利德,李铁民.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复急性肾损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(28):4169-4175.[29] 田雪品,刘海英.碱性成纤维细胞生长因子基因真核表达载体转染骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(36): 5385-5391.[30] 张琳,居士明,王敢,等.成纤维细胞生长因子修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞移植对颅脑损伤模型大鼠神经功能的改善机制分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2016,15(12):1137-1140.[31] Papi A, Bellettato CM, Braccioni F, et al. Infections and airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severe exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173(10):1114-1121.[32] Vitenberga Z, Pilmane M, Babjoniševa A. The evaluation of inflammatory, anti-inflammatory and regulatory factors contributing to the pathogenesis of COPD in airways. Pathol Res Pract. 2019; 215(1):97-105.[33] Silva BSA, Lira FS, Ramos D, et al. Severity of COPD and its relationship with IL-10. Cytokine. 2018;106:95-100.[34] Saxena A, Khosraviani S, Noel S, et al. Interleukin-10 paradox: A potent immunoregulatory cytokine that has been difficult to harness for immunotherapy. Cytokine. 2015;74(1):27-34.[35] Huang AX, Lu LW, Liu WJ, et al. Plasma Inflammatory Cytokine IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-α Levels Correlate with Pulmonary Function in Patients with Asthma-Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Overlap Syndrome. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:2800-2808.[36] Zobel K, Martus P, Pletz MW, et al. Interleukin 6, lipopolysaccharide- binding protein and interleukin 10 in the prediction of risk and etiologic patterns in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: results from the German competence network CAPNETZ. BMC Pulm Med. 2012;12:6.[37] Sapan HB, Paturusi I, Jusuf I, et al. Pattern of cytokine (IL-6 and IL-10) level as inflammation and anti-inflammation mediator of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) in polytrauma. Int J Burns Trauma. 2016;6(2):37-43.[38] Barnes PJ. Cytokine modulators as novel therapies for airway disease. Eur Respir J Suppl. 2001;34:67s-77s.[39] Barnes PJ. Targeting cytokines to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(7): 454-466.[40] Zhu J, Qiu Y, Valobra M, et al. Plasma cells and IL-4 in chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175(11):1125-1133.[41] Luzina IG, Lockatell V, Lavania S, et al. Natural production and functional effects of alternatively spliced interleukin-4 protein in asthma. Cytokine. 2012;58(1):20-26.[42] Liu Y, Zhuo A, Liu W, et al. The -33C/T polymorphism in the interleukin 4 gene is associated with asthma risk: a meta-analysis. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2014;24(2):114-121. |
.jpg)
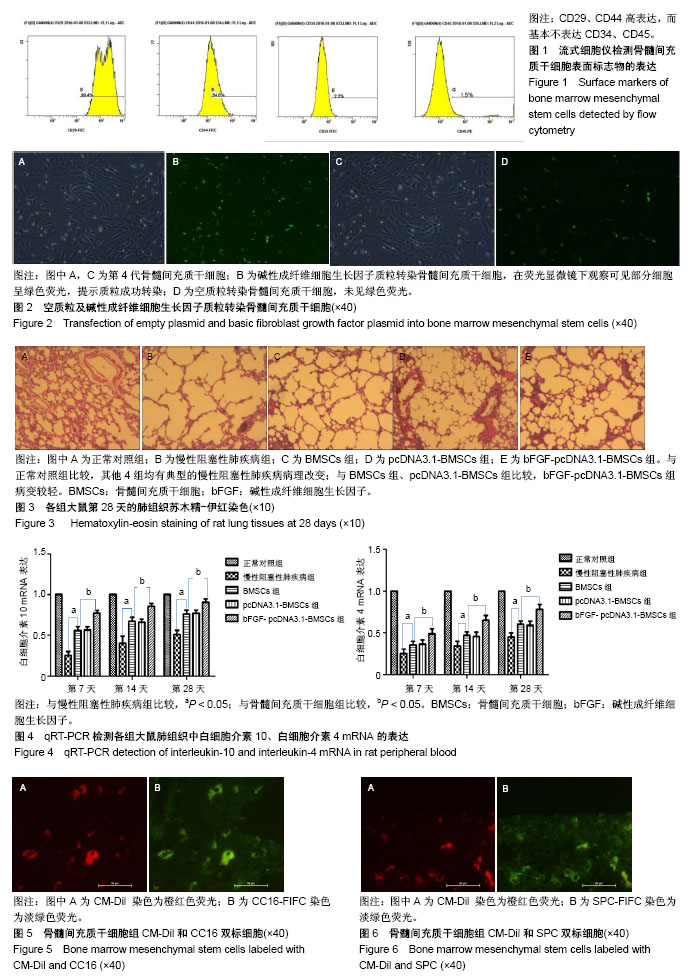

.jpg)
.jpg)