| [1]Hayes JS,Richards RG.The use of titanium and stainless steel in fracture fixation.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2010;7(6):843-853.
[2]Brown SA,Mayor MB.The biocompatibility of materials for internal fixation of fractures.J Biomed Mater Res. 1978;12(1):67-82.
[3]周耀,王佳,竺智雄.不同内固定材料治疗三踝骨折效果分析[J].中国医药导报,2014,35(17):61-64.
[4]Uhthoff HK, Bardos DI, Liskova-Kiar M.The advantages of titanium alloy over stainless steel plates for the internal fixation of fractures. An experimental study in dogs.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1981;63-B(3): 427-484.
[5]Brown SA,Simpson JP.Crevice and fretting corrosion of stainless- steel plates and screws.J Biomed Mater Res. 1981;15(6): 867-878.
[6]Disegi JA,Eschbach L.Stainless steel in bone surgery. Injury. 2000; 31: D2-D6.
[7]Ganesh VK, Ramakrishna K, Ghista DN.Biomechanics of bone-fracture fixation by stiffness-graded plates in comparison with stainless-steel plates.Biomed Eng Online. 2005;4:46.
[8]Martola M,Lindqvist C,Hänninen H,et al.Fracture of titanium plates used for mandibular reconstruction following ablative tumor surgery.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007;80(2):345-352.
[9]Cho JH.Percutaneous cannulated screws with tension band wiring technique in patella fractures.Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013;25(4): 215-219.
[10]Carpenter JE, Kasman RA, Patel N, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of current patella fracture fixation techniques.J Orthop Trauma. 1997;11(5): 351-356.
[11]Leung PC,Mak KH,Lee SY.Percutaneous tension band wiring: a new method of internal fixation for mildly displaced patella fracture.J Trauma. 1983;23(1):62-64.
[12]Lhotka C, Szekeres T, Steffan I,et al.Four-year study of cobalt and chromium blood levels in patients managed with two different metal-on-metal total hip replacements.J Orthop Res.2003;21(2): 189-195.
[13]李铁军,丁中伟,何强.钛合金内固定材料严重电解反应1例[J].河北北方学院学报(医学版),2010,27(3): 49-50.
[14]胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].3版.北京:人民军医出版社, 2005: 356-357.
[15]Rüedi Th,Perren SM,Pohler O,et al.[Titanium, steel and their combination in bone surgery].Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1975; Suppl: 395-398.
[16]Wächter R,Stoll P.[Can steel screws be combined with titanium plates? Hard polishing technique and SEM in animal experiments].Dtsch Z Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir. 1991;15(4): 275-284.
[17]Richard M,Einhorn TA.The biology of fracture healing. Injury. 2011; 42(6): 551-555.
[18]郭庆勇,张毅,买买提•黑牙斯丁,等.小动物骨折的诊断与治疗[J].新疆畜牧业, 2010,26(5):50-53.
[19]John D.Wrought 18% chromium-14% nickel-2.5% molybdenum stainless steel implant material. AO ASIF Materials Technical Commission,1998.
[20]Barbosa MA.Corrosion mechanisms of metallic biomaterials. Barbosa,MA Porto: Elsevier Science Publishers BV,1991:227-258.
[21]Griffin CD,Buchanan RA,Lemons JE.In vitro electrochemical corrosion study of coupled surgical implant materials.J Biomed Mater Res. 1983; 17(3):489-500.
[22]Brown SA,Merritt K.Fretting corrosion of plates and screws: an in vitro test method. Corrosion and Degradation of Implant Materials: Second Symposium.ASTM International,1985.
[23]Serhan H, Slivka M, Albert T,et al.Is galvanic corrosion between titanium alloy and stainless steel spinal implants a clinical concern? Spine J. 2004; 4(4):379-387.
[24]Venugopalan R,Lucas LC.Evaluation of restorative and implant alloys galvanically coupled to titanium.Dent Mater. 1998;14(3): 165-172.
[25]Høl PJ,Mølster A,Gjerdet NR.Should the galvanic combination of titanium and stainless steel surgical implants be avoided?Injury. 2008;39(2):161-169.
[26]Acevedo D,Loy BN,Lee B,et al.Mixing implants of differing metallic composition in the treatment of upper-extremity fractures. Orthopedics.2013;36(9):e1175-1179.
[27]陈欣,黄亚娟,田谦,等.钛合金与不锈钢内固定材料置入修复脊柱结核的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(30):4860-4864.
[28]Textor M,Caroline Sittig C,Frauchiger V,et al.Properties and biological significance of natural oxide films on titanium and its alloys.Titanium in medicine.Springer,Berlin,Heidelberg, 2001: 171-230.
[29]侯金健,高强强,安晓婷.国内外高温钛合金研究及应用的最新发展[J].热加工工艺,2014,43(10):11-15.
[30]Ghaith el-S, Hodgson S, Sharp M.Laser surface alloying of 316L stainless steel coated with a bioactive hydroxyapatite-titanium oxide composite.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):83.
[31]Banaszkiewicz PA.Metallic wear in failed titanium-alloy total hip replacements: A histological and quantitative analysis.Classic Papers in Orthopaedics.Springer,London, 2014:97-100.
[32]Leopold SS, Berger RA, Patterson L, et al.Serum titanium level for diagnosis of a failed, metal-backed patellar component.J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(7):938-943. |
.jpg)
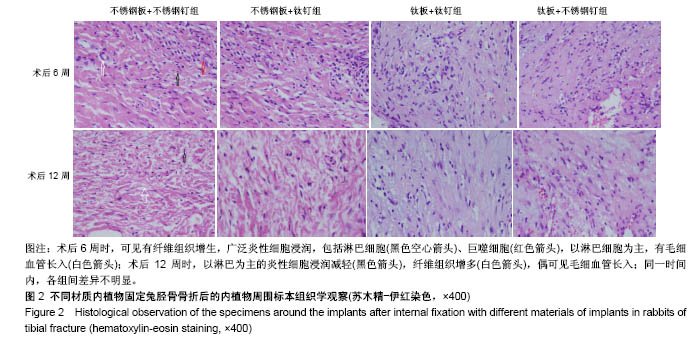
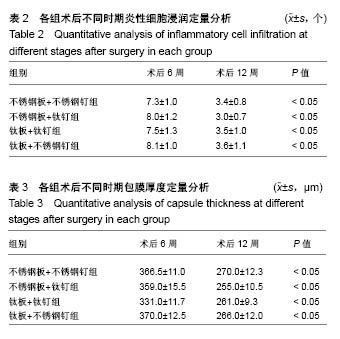

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)