| [1]Spang MT,Christman KL.Extracellular matrix hydrogel therapies: In vivo applications and development. Acta Biomaterialia.2018;68:1-14.[2]Gibbs DMR,Black CRM,Dawson JI,et al.A review of hydrogel use in fracture healing and bone regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(3):187-198.[3]Saldin LT,Cramer MC,Velankar SS,et al.Extracellular matrix hydrogels from decellularized tissues: Structure and function. Acta Biomaterialia. 2017;49:1-15.[4]Badylak S,Freytes D,Gilbert T.Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function.Acta Biomaterialia.2009; 5(1):1-13.[5]Zhang Y,He Y,Bharadwaj S,et al.Tissue-specific extracellular matrix coatings for the promotion of cell proliferation and maintenance of cell phenotype.Biomaterials. 2009; 30(23-24): 4021-4028.[6]Freytes DO,Martin J,Velankar SS,et al.Preparation and rheological characterization of a gel form of the porcine urinary bladder matrix. Biomaterials.2008;29(11):1630-1637.[7]Lewis PL,Su J,Yan M,et al.Complex bile duct network formation within liver decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1): 12220.[8]Agarwal T,Narayan R,Maji S,et al.Decellularized Caprine liver extracellular matrix as a 2D substrate coating and 3D hydrogel platform for vascularized liver tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3):e1678-e1690.[9]Loneker AE,Faulk DM,Hussey GS,et al.Solubilized liver extracellular matrix maintains primary rat hepatocyte phenotype in-vitro.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(7): 1846-1847.[10]Sellaro TL,Ranade A,Faulk DM,et al.Maintenance of human hepatocyte function in vitro by liver-derived extracellular matrix gels.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(3):1075-1082.[11]Keane TJ,Londono R,Carey RM,et al. Preparation and characterization of a biologic scaffold from esophageal mucosa. Biomaterials. 2013;34(28): 6729-6737.[12]Meng F,Modo M,Badylak SF.Biologic scaffold for CNS repair. Regen Med.2014;9(3):367-383.[13]Lee JS, Shin J, Park H,et al. Liver extracellular matrix providing dual functions of two-dimensional substrate coating and three-dimensional injectable hydrogel platform for liver tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules.2013;15(1):206-218.[14]Wolf MT,Daly KA,Brennan-Pierce EP,et al.A hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2012; 33(29): 7028-7038.[15]Gilbert TW,Sellaro TL,Badylak SF.Decellularization of tissues and organs.Biomaterials.2006; 27(19): 3675-3683.[16]Ng SL,Narayanan K,Gao S,et al.Lineage restricted progenitors for the repopulation of decellularized heart. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30): 7571-7580.[17]马金辉,于洁,乔叶薷,等.两种去污剂在制备脱细胞肺支架中的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2): 248-253.[18]郑方平,毛凯丽,赵应征.脑去细胞生物支架的制备与鉴定[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2018,37(2):202-207.[19]Crapo PM,Gilbert TW,Badylak SF.An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(12): 3233-3243.[20]Mazza G,Al-Akkad W,Rombouts K,et al.Liver tissue engineering: From implantable tissue to whole organ engineering.Hepatol Commun. 2018; 2(2):131-141.[21]Zhang X,Dong J.Direct comparison of different coating matrix on the hepatic differentiation from adipose-derived stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2015;456(4):938-944.[22]Aamodt JM,Grainger DW.Extracellular matrix-based biomaterial scaffolds and the host response. Biomaterials. 2016;86:68-82.[23]Lin P,Chan WC,Badylak SF,et al.Assessing porcine liver-derived biomatrix for hepatic tissue engineering.Tissue Eng. 2004;10(7-8): 1046-1053.[24]Gilbert TW,Wognum S,Joyce EM,et al.Collagen fiber alignment and biaxial mechanical behavior of porcine urinary bladder derived extracellular matrix. Biomaterials. 2008; 29(36):4775-4782.[25]Singelyn JM,Dequach JA,Seif-Naraghi SB,et al.Naturally derived myocardial matrix as an injectable scaffold for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials.2009;30(29):5409-5416.[26]Agmon G,Christman KL.Controlling stem cell behavior with decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds.Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci.2016;20(4): 193-201.[27]Faulk DM,Wildemann JD,Badylak SF.Decellularization and cell seeding of whole liver biologic scaffolds composed of extracellular matrix.J Clin Exp Hepatol.2015;5(1):69-80.[28]Ji R,Zhang N,You N,et al.The differentiation of MSCs into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a liver biomatrix scaffold and their transplantation into liver-fibrotic mice.Biomaterials.2012; 33(35): 8995-9008.[29]Londono R,Gorantla VS,Badylak SF.Emerging Implications for Extracellular Matrix-Based Technologies in Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016: 1541823.[30]O'Neill JD, Freytes DO,Anandappa AJ, et al.The regulation of growth and metabolism of kidney stem cells with regional specificity using extracellular matrix derived from kidney. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(38): 9830-9841. |
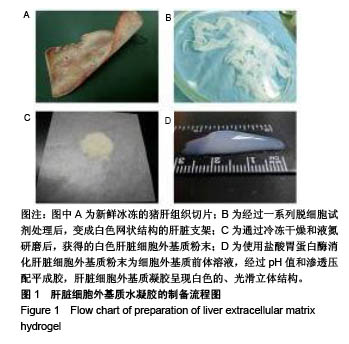
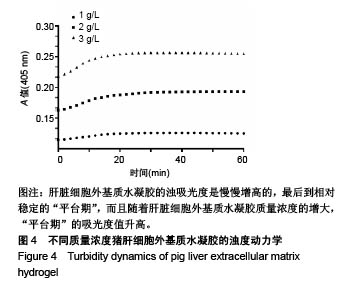
.jpg)
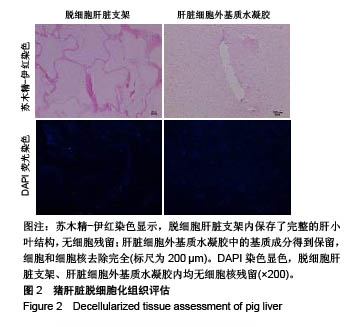
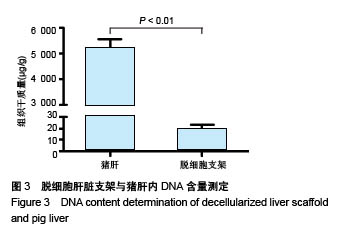
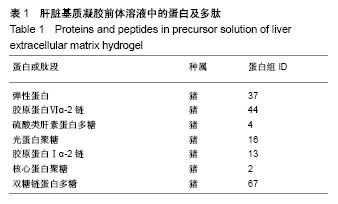
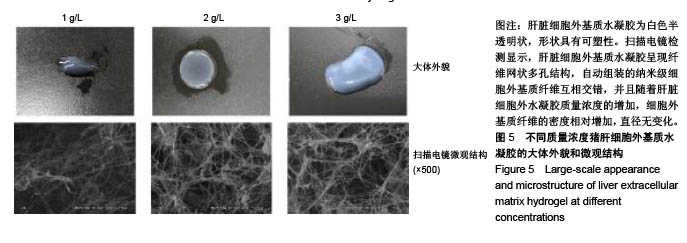
.jpg)