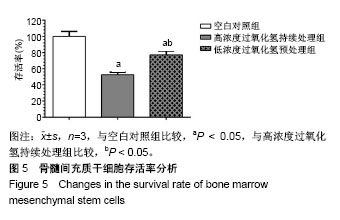
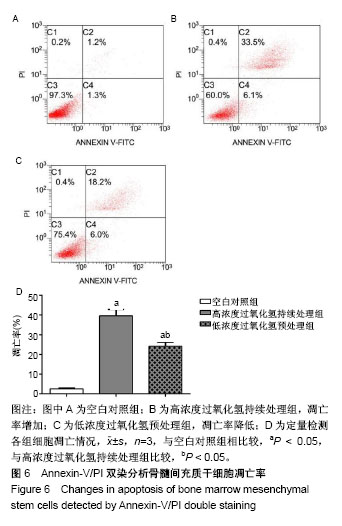
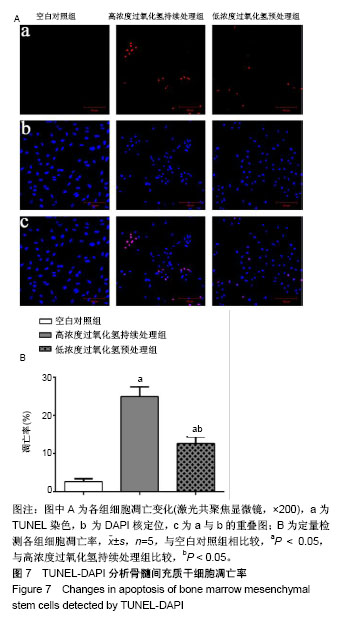
| [1] Hu W, Jing P, Wang L, et al. The positive effects of Ginsenoside Rg1 upon the hematopoietic microenvironment in a D-Galactose-induced aged rat model. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:119.[2] Thanan R, Techasen A, Hou B, et al. Development and characterization of a hydrogen peroxide-resistant cholangiocyte cell line: A novel model of oxidative stress-related cholangiocarcinoma genesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(1):182-188.[3] Ni S, Wang D, Qiu X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat by activating Nrf2 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(7): 7752-7761.[4] Ashour RH, Saad MA, Sobh MA, et al. Comparative study of allogenic and xenogeneic mesenchymal stem cells on cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):126.[5] Fan CD, Sun JY, Fu XT, et al. Astaxanthin Attenuates Homocysteine-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Vitro and in Vivo by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Damage. Front Physiol. 2017;8:1041.[6] Liu D, Zhang H, Gu W, et al. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on high glucose-induced neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79399.[7] Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang T, et al. Proteomic identification and characterization of Ctenopharyngodon idella tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1 (CiTrap1): an anti-apoptosis factor upregulated by grass carp reovirus infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015;43(2):449-459.[8] Zhang R, Zhang N, Zhang H, et al. Celastrol prevents cadmium-induced neuronal cell death by blocking reactive oxygen species-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(1):82-100.[9] Zhou Y, He W, Sun W, et al. Sulfotanshinone IIA Sodium Ameliorates Glucose Peritoneal Dialysis Solution-Induced Human Peritoneal Mesothelial Cell Injury via Suppression of ASK1-P38- mediated Oxidative Stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(6): 2434-2444.[10] He R, Cui M, Lin H, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2018;199:122-130.[11] Zhou Y, Huang S, Shen H, et al. Detection of Glutathione in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells With a Fluorescent Probe During the Course of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(1):223.e1-223.e10.[12] Bebensee DF, Can K, Müller M. Increased Mitochondrial Mass and Cytosolic Redox Imbalance in Hippocampal Astrocytes of a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome: Subcellular Changes Revealed by Ratiometric Imaging of JC-1 and roGFP1 Fluorescence. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3064016.[13] Wang LL, Yu QL, Han L, et al. Study on the effect of reactive oxygen species-mediated oxidative stress on the activation of mitochondrial apoptosis and the tenderness of yak meat. Food Chem. 2018;244: 394-402.[14] Xue T, Luo P, Zhu H, et al. Oxidative stress is involved in Dasatinib-induced apoptosis in rat primary hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2012;261(3):280-291.[15] Kapoor R, Kakkar P. Naringenin accords hepatoprotection from streptozotocin induced diabetes in vivo by modulating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptotic signaling cascade. Toxicol Rep. 2014; 1:569-581.[16] Chan S, Chan GC, Ye J, et al. Thrombopoietin Protects Cardiomyocytes from Iron-Overload Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):2063-2071.[17] Bing W, Pang X, Qu Q, et al. Simvastatin improves the homing of BMSCs via the PI3K/AKT/miR-9 pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2016; 20(5):949-961.[18] Ren M, Yang S, Li J, et al. Ginkgo biloba L. extract enhances the effectiveness of syngeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in lowering blood glucose levels and reversing oxidative stress. Endocrine. 2013;43(2):360-369.[19] Tao SC, Yuan T, Rui BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):733-750.[20] Chen R, Liu S, Piao F, et al. 2,5-hexanedione induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells from rat bone marrow via mitochondria-dependent caspase-3 pathway. Ind Health. 2015; 53(3):222-235.[21] Amiri F, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, Roudkenar MH. In vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability in stressful microenvironments : In vitro augmentation of mesenchymal stem cells viability. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2015;20(2):237-251.[22] Mahrouf-Yorgov M, Augeul L, Da Silva CC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells sense mitochondria released from damaged cells as danger signals to activate their rescue properties. Cell Death Differ. 2017;24(7):1224-1238.[23] Wang Y, Ma J, Du Y, et al. Human Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells against Oxidative Stress-Mediated Dysfunction via ERK1/2 MAPK Signaling. Mol Cells. 2016;39(3):186-194.[24] Kavanagh DP, Suresh S, Newsome PN, et al. Pretreatment of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Manipulates Their Vasculoprotective Potential While Not Altering Their Homing Within the Injured Gut. Stem Cells. 2015;33(9):2785-2797.[25] Liu GY, Jiang XX, Zhu X, et al. ROS activates JNK-mediated autophagy to counteract apoptosis in mouse mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015;36(12):1473-1479.[26] Yu HH, Xu Q, Chen HP, et al. Stable overexpression of DJ-1 protects H9c2 cells against oxidative stress under a hypoxia condition. Cell Biochem Funct. 2013;31(8):643-651.[27] Román F, Urra C, Porras O, et al. Real-Time H2O2 Measurements in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Show Increased Antioxidant Capacity in Cells From Osteoporotic Women. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(3):585-593.[28] Lv C, Hao Y, Han Y, et al. Role and mechanism of microRNA-21 in H2O2-induced apoptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;27:154-160.[29] Liu H, Yang X, Zhang Y, et al. Fullerol antagonizes dexamethasone-induced oxidative stress and adipogenesis while enhancing osteogenesis in a cloned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(7):1051-1057. [30] Sun ZB, Wang JW, Xiao H, et al. Icariin may benefit the mesenchymal stem cells of patients with steroid-associated osteonecrosis by ABCB1-promoter demethylation: a preliminary study. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(1):187-197.[31] Fan L, Zhang C, Yu Z, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and osteogenesis in rabbit femoral head osteonecrosis. Bone. 2015;81:544-553.[32] Li J, Huang Z, Chen L, et al. Restoration of bone defects using modified heterogeneous deproteinized bone seeded with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(7): 3200-3211.[33] Kim JY, Lee JS, Han YS, et al. Pretreatment with Lycopene Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2015;23(6): 517-524.[34] Jeong HJ, Kim DW, Kim MJ, et al. Protective effects of transduced Tat-DJ-1 protein against oxidative stress and ischemic brain injury. Exp Mol Med. 2012;44(10):586-593.[35] Shen ZY, Sun Q, Xia ZY, et al. Overexpression of DJ-1 reduces oxidative stress and attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in NRK-52E cells exposed to high glucose. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(3): 729-736. |
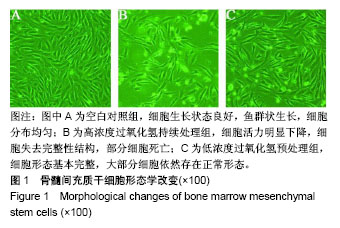
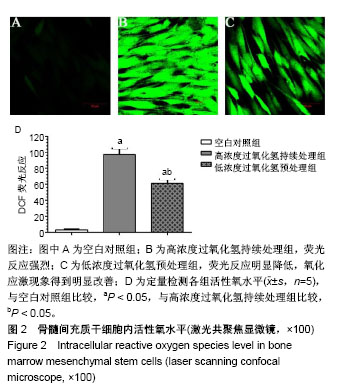
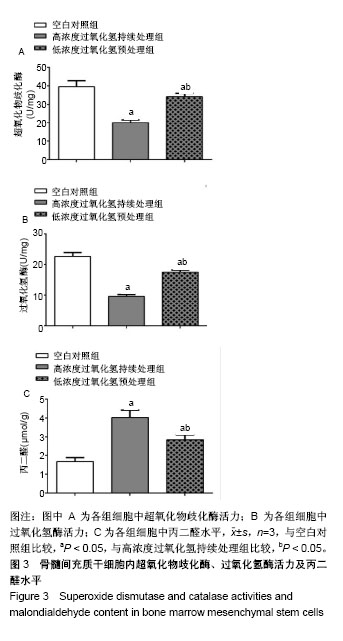
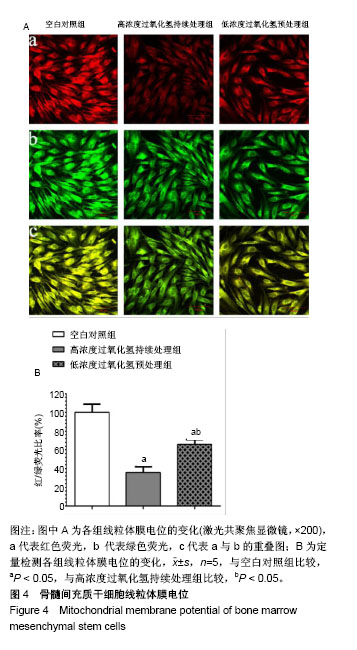
.jpg)
.jpg)