| [1] Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C. The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet. 2007;370(9597):S1508-1519.[2] Del Buono A, Denaro V, Maffulli N. Genetic susceptibility to aseptic loosening following total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review. Br Med Bull. 2012;101:39-55.[3] Gudena R, Kuna S, Pradhan N. Aseptic loosening of total hip replacement presenting as an anterior thigh mass. Musculoskelet Surg. 2013;97(3):247-249.[4] Landgraeber S, Wegner A, Canbay A, et al. Serum levels of adiponectin in patients with aseptic loosening after total hip replacement. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(2):748-752.[5] Ollivere B, Darrah C, Brankin RC, et al. The continued value of clinical and radiological surveillance: the Charnley Elite Plus hip replacement system at 12 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91(6): 720-724.[6] Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1): 128-133.[7] Jiang Y, Jia T, Wooley PH, et al. Current research in the pathogenesis of aseptic implant loosening associated with particulate wear debris. Acta Orthop Belg. 2013;79(1):1-9.[8] Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, et al. Effects of Ti, PMMA, UHMWPE, and Co-Cr wear particles on differentiation and functions of bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(10): 2817-2825.[9] Ingham E, Fisher J. Biological reactions to wear debris in total joint replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2000;214(1):21-37.[10] Zhang K, Yang SY, Yang S, et al. Different influence of Ti, PMMA, UHMWPE, and Co-Cr particles on peripheral blood monocytes during periprosthetic inflammation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 103(1):358-364.[11] Lin TH, Tamaki Y, Pajarinen J, et al. Chronic inflammation in biomaterial-induced periprosthetic osteolysis: NF-κB as a therapeutic target. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(1):1-10.[12] Catelas I, Jacobs JJ. Biologic activity of wear particles. Instr Course Lect. 2010;59:3-16.[13] Lübbeke A, Garavaglia G, Barea C, et al. Influence of patient activity on femoral osteolysis at five and ten years following hybrid total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(4):456-463.[14] Chiba J, Rubash HE, Kim KJ, et al. The characterization of cytokines in the interface tissue obtained from failed cementless total hip arthroplasty with and without femoral osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(300):304-312.[15] Shanbhag AS, Kaufman AM, Agarwal S, et al. Critical insights into osteolysis using protein microarrays: The importance of IL-6 and T-cell Activation. Trans Orthop Res Soc. 2005; 30:148.[16] Kaufman AM, Alabre CI, Rubash HE, et al. Human macrophage response to UHMWPE, TiAlV, CoCr, and alumina particles: analysis of multiple cytokines using protein arrays. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(2):464-474.[17] Atkins GJ, Haynes DR, Howie DW, et al. Role of polyethylene particles in peri-prosthetic osteolysis: A review. World J Orthop. 2011;2(10):93-101.[18] Matthews JB, Besong AA, Green TR, et al. Evaluation of the response of primary human peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes to challenge with in vitro generated clinically relevant UHMWPE particles of known size and dose. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;52(2):296-307.[19] Shanbhag AS, Jacobs JJ, Black J, et al. Human monocyte response to particulate biomaterials generated in vivo and in vitro. J Orthop Res. 1995;13(5):792-801.[20] Shanbhag AS, Jacobs JJ, Black J, et al. Effects of particles on fibroblast proliferation and bone resorption in vitro. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (342):205-217.[21] Haynes DR, Rogers SD, Hay S, et al. The differences in toxicity and release of bone-resorbing mediators induced by titanium and cobalt- chromium-alloy wear particles.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1993;75(6): 825-834.[22] Sethi RK, Neavyn MJ, Rubash HE, et al. Macrophage response to cross-linked and conventional UHMWPE. Biomaterials. 2003; 24(15):2561-2573.[23] Yamanaka Y, Karuppaiah K, Abu-Amer Y. Polyubiquitination events mediate polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) particle activation of NF-kappaB pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(27):23735-23741.[24] González O, Smith RL, Goodman SB. Effect of size, concentration, surface area, and volume of polymethylmethacrylate particles on human macrophages in vitro. J Biomed Mater Res.1996;30(4): 463-473.[25] Sabbatini M, Piffanelli V, Boccafoschi F, et al. Different apoptosis modalities in periprosthetic membranes. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(1):175-184.[26] Catelas I, Petit A, Zukor DJ, et al. TNF-alpha secretion and macrophage mortality induced by cobalt and chromium ions in vitro-qualitative analysis of apoptosis. Biomaterials. 2003; 24(3): 383-391.[27] Schalock PC, Menné T, Johansen JD, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to metallic implants - diagnostic algorithm and suggested patch test series for clinical use. Contact Dermatitis. 2012;66(1):4-19.[28] Tsaousi A, Jones E, Case CP. The in vitro genotoxicity of orthopaedic ceramic (Al2O3) and metal (CoCr alloy) particles. Mutat Res. 2010; 697(1-2):1-9.[29] VanOs R, Lildhar LL, Lehoux EA, et al. In vitro macrophage response to nanometer-size chromium oxide particles. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(1):149-159. |
.jpg)
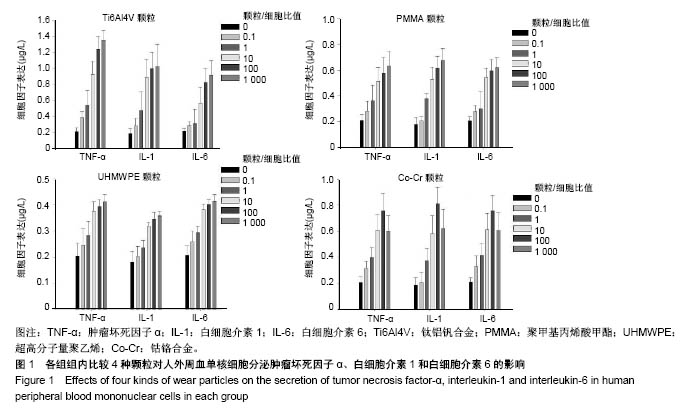
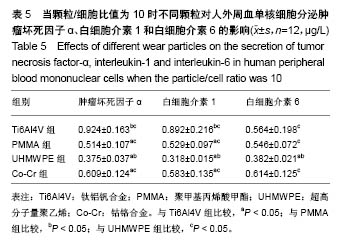
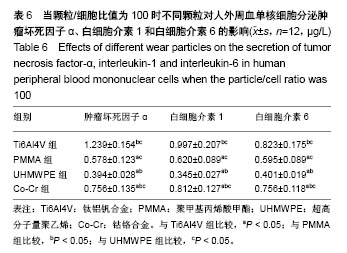
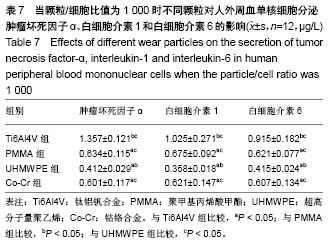
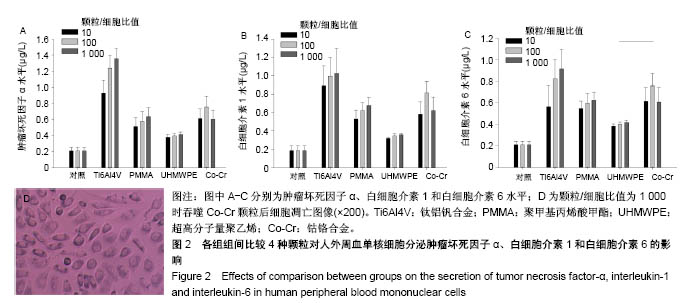
.jpg)