中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4828-4835.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1417
• 复合支架材料 composite scaffold materials • 上一篇 下一篇
动态冲击兔脊柱单椎体:不同冲击速率、网格数量及材料属性变化对椎体应力分布的有限元分析
韩世冰1,张绪树2,郭 媛2,杜一铭2
- 太原理工大学,1机械与运载工程学院,2生物医学工程学院,山西省太原市 030024
Dynamic impact on the rabbit spine single vertebral body: finite element analysis of the stress distribution of the vertebral body with different impact rates, mesh numbers and material properties
Han Shibing1, Zhang Xushu2, Guo Yuan2, Du Yiming2
- 1College of Mechanical and Vehicle Engineering of Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China; 2College of Biomedical Engineering of Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
单椎体:脊柱主要是通过颈椎、胸椎、腰椎、骶骨和尾骨组成,单椎体就是组成脊柱的颈椎、胸椎和腰椎。不同动物的单椎体数量不同,例如人共有7块颈椎、12块胸椎、5块腰椎,而兔子却有7块颈椎、12块胸椎、7块腰椎。
冲击:将实验样品置于冲击试验机(摆锤式和落锤式)上,对实验样品进行外力重撞,从而确定样品的力学性能。
背景:车祸和高空坠落时有发生,其中大部分造成严重的脊柱损伤,因此研究脊柱在冲击载荷作用下的损伤特性至关重要,也为脊柱的损伤防护和修复提供生物力学依据。
目的:通过有限元方法分析兔脊柱单椎体受到冲击载荷时的损伤特性及规律,分析不同冲击速率、网格数量及材料属性变化对椎体应力分布的影响。为单椎体的动态冲击实验及脊柱节段实验和模拟分析提供依据。
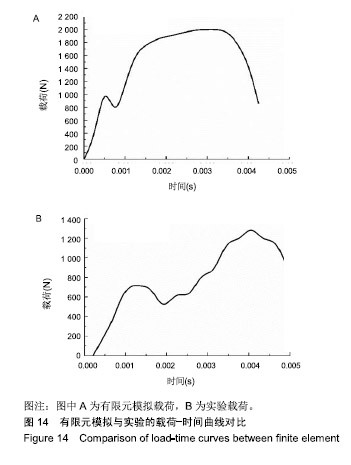
方法:利用Mimics、HyperMesh和Abaqus建立兔单椎体T12的有限元模型,首先进行网格的敏感性分析,选择合适的网格数量,然后在不同冲击速率下对椎体进行竖直方向的冲击有限元分析和模拟,并通过调节材料属性数值可模拟骨质疏松患者的椎体在受到冲击载荷下的应力分布,最后通过兔单椎体的冲击实验对模型进行验证。
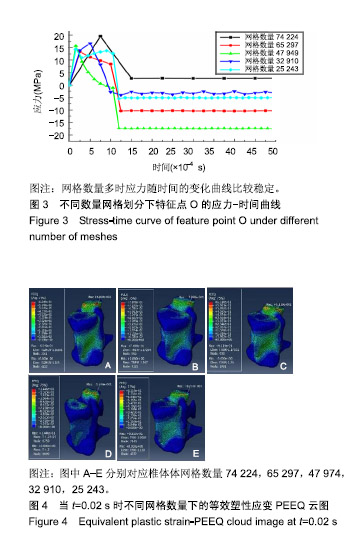
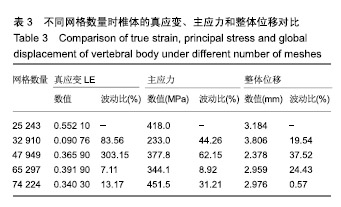
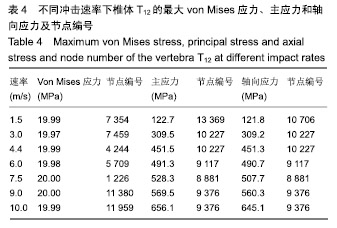
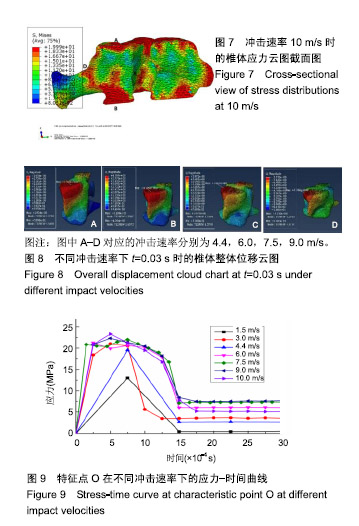
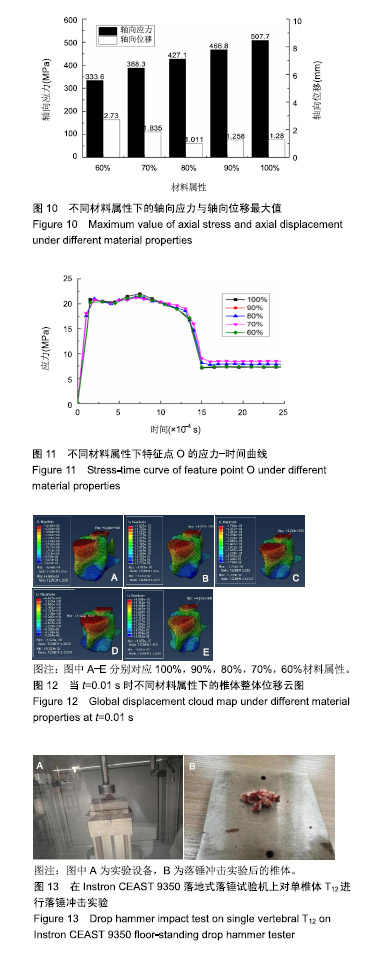
结果与结论:①通过敏感性分析发现当网格数量为74 224时,有限元分析的结果比其他网格数量下的分析结果要合理,因此实验以网格数量为74 224的前提下进行分析;椎骨材料跟大多数脆性材料一样,当受到垂直载荷作用时可发生45°角的破坏形式,并且最大应力值主要集中在椎体两端,应力传递方向与骨小梁的走向趋势一致;②结果表明,通过敏感性分析选取合适的网格数量,使有限元分析结果更加可靠;通过实验验证了该有限元模型的可靠性,有限元分析结果可在一定程度上反映椎体在不同冲击速率下和骨质疏松椎体在受到冲击下的真实情况;有限元分析方法是一种比较经济、参数易于调节和控制、适用性较强的研究方法。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)