中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (30): 4913-4920.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1408
• 生物材料循证医学 evidence-based medicine of biomaterials • 上一篇
MOTOmed下肢功能训练器对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能影响的Meta分析
周 晶3,1,2,杨 丹3,魏 蒙3,黄彩虹3,赵 焰1,2,3
- 1湖北省中医院,湖北省武汉市 430061;2湖北省中医药研究院,湖北省武汉市 430074;3湖北中医药大学,湖北省武汉市 430070
Effects of MOTOmed lower limb function trainer on lower limb function in stroke patients with hemiplegia: a Meta-analysis
Zhou Jing3, 1, 2, Yang Dan3, Wei Meng3, Huang Caihong3, Zhao Yan1, 2, 3
- 1Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430061, Hubei Province, China; 2Hubei Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China; 3Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430070, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
成本效应分析:是通过比较医疗项目的全部成本和效益来评估医疗价值的一种方法,成本-效益分析作为一种经济决策方法,将成本费用分析法运用于医疗部门的计划决策之中,以寻求在治疗决策上如何以最小的成本获得最大的疗效,常用于评估需要量化医疗事业项目的价值。
协调训练:又称双侧对称训练,指两侧肢体独立执行同一时间和空间运动任务的运动模式,双侧上肢训练的机制可同时激活双侧大脑,减少皮质间抑制,激活同侧皮质脊髓通路并促进感觉反馈。另外,双侧训练时可对比健侧和患侧,利于治疗师观察,还可避免患者扭曲身体,长期习惯形成异常姿势。
背景:临床实践证实MOTOmed下肢功能训练器配合常规康复训练治疗脑卒中后下肢功能障碍的疗效肯定,但缺乏循证依据。
目的:系统评价MOTOmed下肢功能训练器治疗脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能障碍的临床疗效。
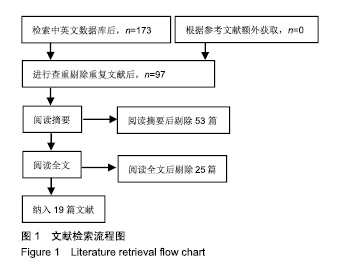
方法:检索CBM、CNKI、万方、维普、Embase、Web of Science、PubMed、OVID、Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials、Cochrane Systematic Reviews数据库,选择MOTOmed下肢功能训练器治疗脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能障碍的随机对照研究,使用Revman5.3软件进行Meta分析。
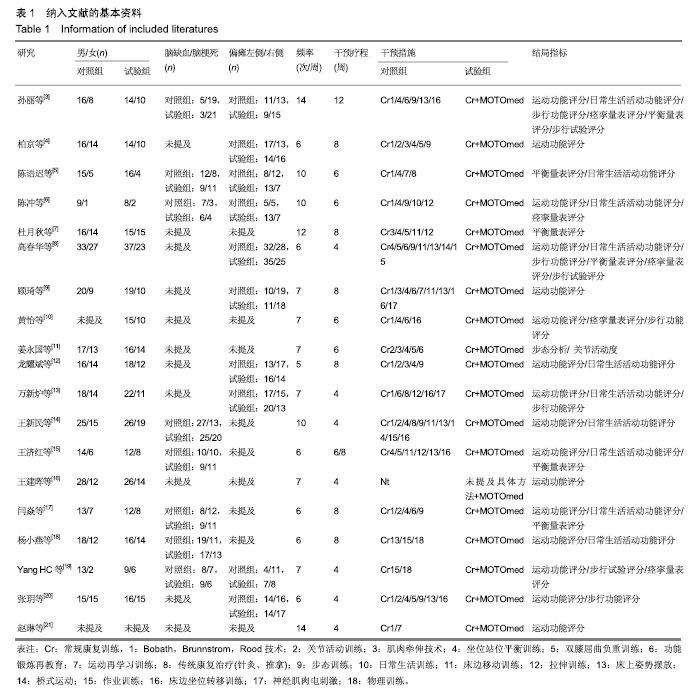
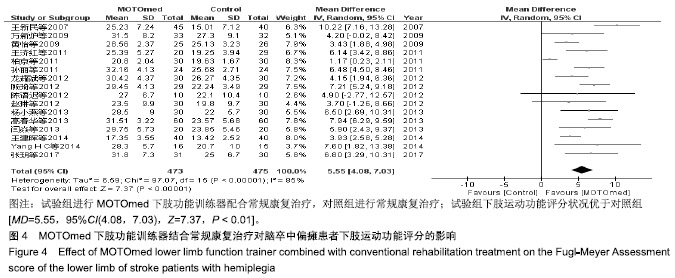
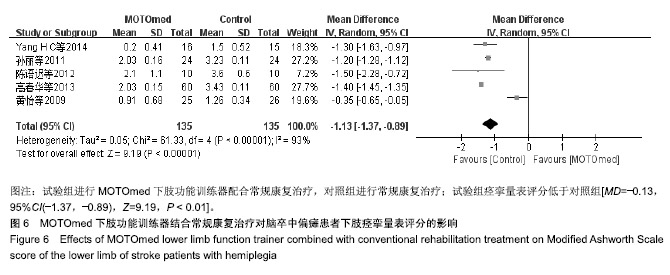
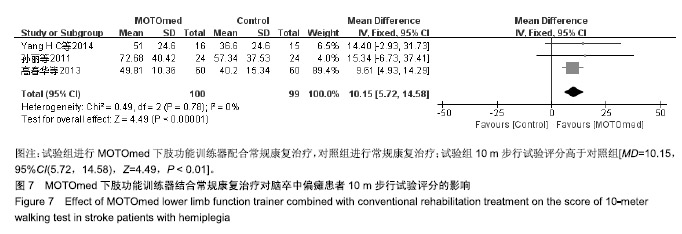
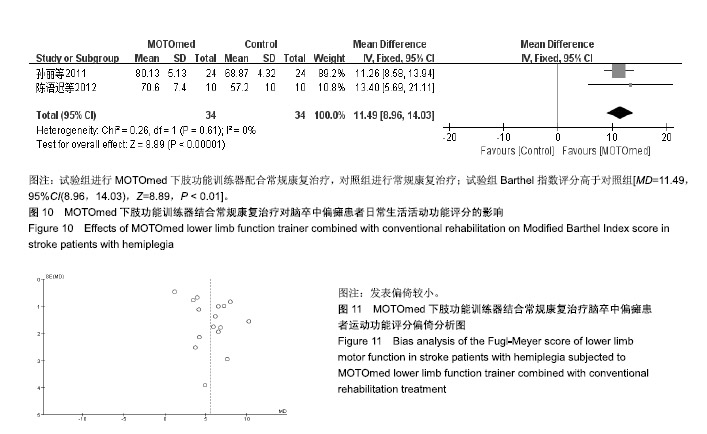
结果与结论:①共纳入19篇文献,包括1 099例脑卒中偏瘫患者,其中试验组进行MOTOmed下肢功能训练器配合常规康复治疗,对照组进行常规康复治疗;②Meta分析结果显示:试验组下肢运动功能Fugl-Meyer评分高于对照组[MD=5.55,95%CI(4.08,7.03),Z=7.37,P < 0.01],改良痉挛Ashworth评分低于对照组[MD=-0.13,95%CI(-1.37,-0.89),Z=9.19,P < 0.01],10 m步行试验评分高于对照组[MD=10.15,95%CI(5.72,14.58),Z=4.49,P < 0.01],平衡量表Berg Balance评分高于对照组[MD=13.66,95%CI(10.47,16.85),Z=8.39,P < 0.01],步行功能量表评分高于对照组[MD=0.85,95%CI(0.68,1.03),Z=9.48,P < 0.01],日常生活活动功能评分高于对照组[MD=11.49,95%CI(8.96,14.03),Z=8.89,P < 0.01];③结果说明,MOTOmed下肢功能训练器治疗脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢功能障碍具有较好的临床疗效,但仍需更多高质量的临床研究加以验证。
中图分类号:



.jpg)