中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4387-4391.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1390
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
小鼠腹部心脏移植模型的建立及技术改进
李军良1,2,张 东3,郭天康1,2,田宏伟1,王 涛1
- (甘肃省人民医院,1普通外科,3医疗质量控制科,甘肃省兰州市 730030;2兰州大学第一临床学院,甘肃省兰州市 730030)
Establishment of abdominal cardiac transplant model in mice and technical modifications
Li Junliang1, 2, Zhang Dong3, Guo Tiankang1, 2, Tian Hongwei1, Wang Tao1
- (1Department of General Surgery, 3Department of Medical Quality Control, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2the First School of Clinical Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。
文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。
.jpg) 文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。
文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。摘要
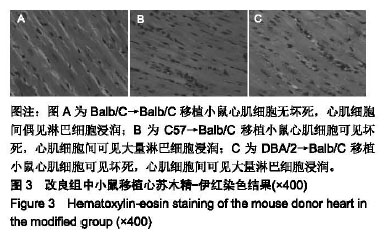
背景:小鼠腹部心脏移植模型是研究免疫耐受的重要平台,虽然有各种改良方法的报道,但是最终均要行显微外科血管吻合。作者针对小鼠腹部心脏移植血管端侧吻合技术的一系列改良方法做了报道,改良的技术方法同样也适用于其他微血管端侧吻合。
目的:建立稳定、可靠、易于掌握的小鼠腹部心脏移植模型。
方法:实验动物供体为C57/BL6J(H-2b),DBA/2(H-2d),Balb/C(H-2d)小鼠共144只,每种各48只;受体为Balb/C(H-2d)共144只;由北京维通利华公司提供,实验方案经甘肃省人民医院动物实验伦理委员会批准(批准号为2017-011)。实验分为改良组和传统方法组,各施行心脏移植72对。改良组采用改良方法摘取供心;自制弧形血管夹阻断受体血管,11-0缝合针法切开血管前壁,170°双定点法吻合肺动脉与下腔静脉等方法施行小鼠腹部心脏移植;传统方法摘取供心采用游离升主动脉至头臂干处,游离肺动脉至左右分叉处,并分别离断的方法。比较2组血管吻合时间和移植成功率。
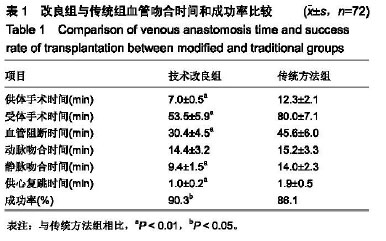
结果与结论:①应用改良方法心脏移植成功率90.3%,供体手术时间(7.0±0.5) min,受体手术时间(53.5±5.9)min,血管阻断时间(30.4±4.5)min,静脉吻合时间(9.4±1.5)min;传统方法心脏移植成功率86.1%,供体手术时间(12.3±2.1) min,受体手术时间(80.0±7.1) min,血管阻断时间(45.6±6.0) min,静脉吻合时间(14.0±2.3) min,改良组心脏移植的时间及成功率显著优于传统方法组(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);②结果说明,改良方法提高了小鼠腹部心脏移植的速度,降低了手术难度,成功的建立了稳定,可靠的小鼠腹部心脏移植模型。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。
文题释义:
170°双定点吻合法:微血管端侧吻合时下角和上角偏后壁10°处双定点固定,两血管前壁由于弹性回缩,后壁暴露充分,依次连续缝合后壁和前壁,此方法既克服了单定点法吻合口易狭窄的缺点,又克服了双定点法后壁暴露不充分的缺点。
组织相容性复合体:引起排斥反应的抗原称为组织相容性抗原。此抗原存在于细胞表面,无器官特异性,不同个体间其抗原特异性互不相同,凡能引起快而强的排斥反应者称为主要组织相容性抗原系统(MHC),引起慢而弱的排斥反应者称为次要组织相容性抗原系统(mHC)。