中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3654-3659.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1307
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
基于尿液代谢组学数据评价不同刮痧方案干预腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠的效果
丁 欢1,陈丽虹1,陈宇婧1,岳容兆1,杨 敏1,徐桂华2
- (1南京中医药大学护理学院,江苏省南京市 210046;2南京中医药大学,江苏省南京市 210046)
Efficacy of different scraping protocols in the intervention of rat models of lumbar disc herniation based on urine metabolomics
Ding Huan1, Chen Lihong1, Chen Yujing1, Yue Rongzhao1, Yang Min1, Xu Guihua2
- (1School of Nursing, Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210046, Jiangsu Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
腰椎间盘突出症:主要是因为腰椎间盘各部分(髓核、纤维环及软骨板),尤其是髓核,有不同程度的退行
性改变后,在外力因素的作用下,椎间盘的纤维环破裂,髓核组织从破裂之处突出(或脱出)于后方或椎管内,导致相邻脊神经根遭受刺激或压迫,从而产生腰部疼痛,一侧下肢或双下肢麻木、疼痛等一系列临床症状。
刮痧:是以中医经络腧穴理论为指导,通过特制的刮痧器具和相应的手法,蘸取一定的介质,在体表进行反复刮动、摩擦,使皮肤局部出现红色粟粒状,或暗红色出血点等“出痧”变化,从而达到活血透痧的作用。
.jpg)
文题释义:
腰椎间盘突出症:主要是因为腰椎间盘各部分(髓核、纤维环及软骨板),尤其是髓核,有不同程度的退行
性改变后,在外力因素的作用下,椎间盘的纤维环破裂,髓核组织从破裂之处突出(或脱出)于后方或椎管内,导致相邻脊神经根遭受刺激或压迫,从而产生腰部疼痛,一侧下肢或双下肢麻木、疼痛等一系列临床症状。
刮痧:是以中医经络腧穴理论为指导,通过特制的刮痧器具和相应的手法,蘸取一定的介质,在体表进行反复刮动、摩擦,使皮肤局部出现红色粟粒状,或暗红色出血点等“出痧”变化,从而达到活血透痧的作用。
摘要
背景:刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症在临床得到广泛应用,利用代谢组学等分析技术对其作用机制进行研究。
目的:使用气相色谱-质谱联用技术的代谢组学方法,探讨刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症大鼠尿液内源性代谢物的变化与其作用机制,并分析不同刮痧方案的疗效差异,以期规范标准化刮痧疗法,为临床应用提供参考和依据。
方法:将48只雄性SD大鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、循经出痧组、穴位出痧组、循经不出痧组以及穴位不出痧组,各8只。选用自体髓核移植法复制腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型,从造模第5天始,用不同刮痧方案干预,隔日1次,共9次。实验于2017年1月获得南京中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会审理批准。
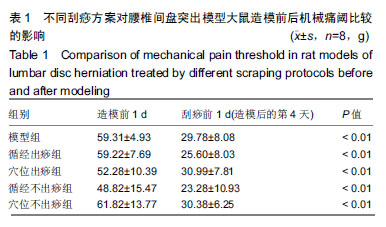
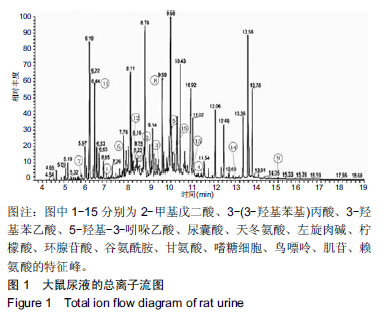
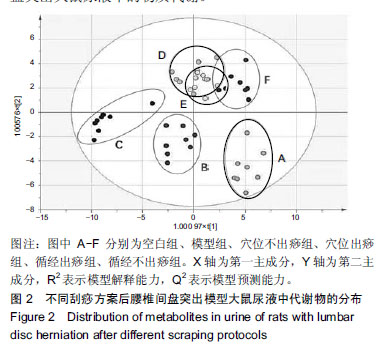
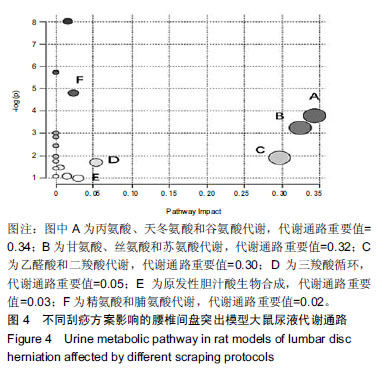
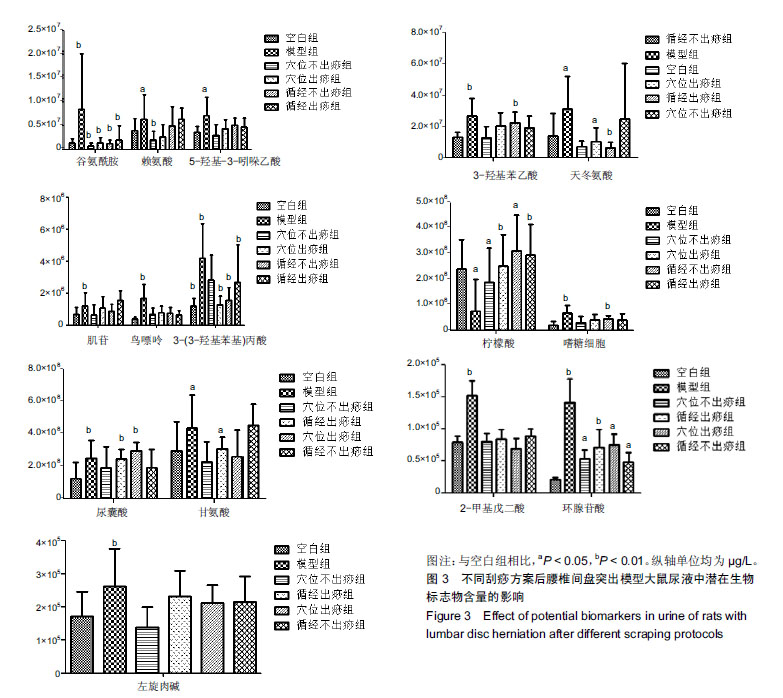
结果与结论:①同造模前相比,刮痧组及造模后的模型组机械痛阈值下降(P < 0.01);②筛选后共得出15种潜在生物标志物和6条代谢通路。刮痧后3-(3-羟基苯基)丙酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酰含量降低,甘氨酸、柠檬酸、环腺苷酸含量上升,通过调节丙氨酸,天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢通路以镇痛,甘氨酸,丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢和三羧酸循环以抗炎;③循经出痧组调节代谢物效果优于其他3组,推测其为治疗最佳刮痧方案。
背景:刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症在临床得到广泛应用,利用代谢组学等分析技术对其作用机制进行研究。
目的:使用气相色谱-质谱联用技术的代谢组学方法,探讨刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症大鼠尿液内源性代谢物的变化与其作用机制,并分析不同刮痧方案的疗效差异,以期规范标准化刮痧疗法,为临床应用提供参考和依据。
方法:将48只雄性SD大鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、循经出痧组、穴位出痧组、循经不出痧组以及穴位不出痧组,各8只。选用自体髓核移植法复制腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型,从造模第5天始,用不同刮痧方案干预,隔日1次,共9次。实验于2017年1月获得南京中医药大学实验动物伦理委员会审理批准。
结果与结论:①同造模前相比,刮痧组及造模后的模型组机械痛阈值下降(P < 0.01);②筛选后共得出15种潜在生物标志物和6条代谢通路。刮痧后3-(3-羟基苯基)丙酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酰含量降低,甘氨酸、柠檬酸、环腺苷酸含量上升,通过调节丙氨酸,天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢通路以镇痛,甘氨酸,丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢和三羧酸循环以抗炎;③循经出痧组调节代谢物效果优于其他3组,推测其为治疗最佳刮痧方案。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
腰椎间盘突出症:主要是因为腰椎间盘各部分(髓核、纤维环及软骨板),尤其是髓核,有不同程度的退行#br#
性改变后,在外力因素的作用下,椎间盘的纤维环破裂,髓核组织从破裂之处突出(或脱出)于后方或椎管内,导致相邻脊神经根遭受刺激或压迫,从而产生腰部疼痛,一侧下肢或双下肢麻木、疼痛等一系列临床症状。#br#
刮痧:是以中医经络腧穴理论为指导,通过特制的刮痧器具和相应的手法,蘸取一定的介质,在体表进行反复刮动、摩擦,使皮肤局部出现红色粟粒状,或暗红色出血点等“出痧”变化,从而达到活血透痧的作用。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
腰椎间盘突出症:主要是因为腰椎间盘各部分(髓核、纤维环及软骨板),尤其是髓核,有不同程度的退行#br#
性改变后,在外力因素的作用下,椎间盘的纤维环破裂,髓核组织从破裂之处突出(或脱出)于后方或椎管内,导致相邻脊神经根遭受刺激或压迫,从而产生腰部疼痛,一侧下肢或双下肢麻木、疼痛等一系列临床症状。#br#
刮痧:是以中医经络腧穴理论为指导,通过特制的刮痧器具和相应的手法,蘸取一定的介质,在体表进行反复刮动、摩擦,使皮肤局部出现红色粟粒状,或暗红色出血点等“出痧”变化,从而达到活血透痧的作用。#br#
#br#