| [1] Greenland P,Blaha MJ,Budoff MJ, et al.Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk.J Am Coll Cardiol.2018;72(4):434-447.[2] González-Montero J,Brito R, Gajardo AI, et al. Myocardial reperfusion injury and oxidative stress: Therapeutic opportunities. World J Cardiol.2018;10(9):74-86.[3] Frangogiannis NG. Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction. Compr Physiol.2015;5(4):1841-1875.[4] Guo Y, Luo F, Liu Q, et al. Regulatory non-coding RNAs in acute myocardial infarction.J Cell Mol Med.2017;21(5):1013-1023.[5] Roberts RE.The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway: a potential therapeutic target in hypertension.J Exp Pharmacol.2012;4:77-83.[6] Pei HX,Hua R,Guan CX,et al.Ginkgolide B Reduces the Degradation of Membrane Phospholipids to Prevent Ischemia/ Reperfusion Myocardial Injury in Rats.Pharmacology. 2015; 96(5-6):233-239.[7] Li MY,Chang CT,Han YT,et al.Ginkgolide B promotes neuronal differentiation through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in neural stem cells of the postnatal mammalian subventricular zone.Sci Rep 2018;8(1):14947.[8] Januzzi JL,Filippatos G,Nieminen M,et al.Troponin elevation in patients with heart failure: on behalf of the third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction Global Task Force: Heart Failure Section. Eur Heart J.2012;33(18):2265-2271.[9] Martin LM,Januzzi JL,Thompson RW,et al.Clinical Profile of Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients Included in the Hospital Readmissions Reduction Program.J Am Heart Assoc.2018; 7(16):e009339.[10] Durak I,Kudaiberdieva G,Gorenek B.Prognostic implications of arrhythmias during primary percutaneous coronary interventions for ST-elevation myocardial infraction.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;13(1):85-94.[11] Pan J, Alimujiang M, Chen Q, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-146a-modified adipose-derived stem cells attenuate acute myocardial infarction-induced myocardial damage via downregulation of early growth response factor 1.J Cell Biochem. 2018;[12] Wang A,Zhang H,Liang Z,et al.U0126 attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy in myocardium through MEK/ERK/EGR-1 pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;788:280-285.[13] Traister A,Li M,Aafaqi S,et al.Integrin-linked kinase mediates force transduction in cardiomyocytes by modulating SERCA2a/PLN function.Nat Commun.2014;5:4533.[14] Xu Z,Sun J,Tong Q,et al.The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(12).[15] Liu P,Zhong TP.MAPK/ERK signalling is required for zebrafish cardiac regeneration.Biotechnol Lett.2017;39(7):1069-1077.[16] Filippone SM,Samidurai A,Roh SK,et al.Reperfusion Therapy with Rapamycin Attenuates Myocardial Infarction through Activation of AKT and ERK.Oxid Med Cell Longev.2017;2017:4619720.[17] Hausenloy DJ,Yellon DM.New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway.Cardiovasc Res.2004;61(3): 448-460.[18] Duan J, Yang Y, Liu H, et al. Osthole ameliorates acute myocardial infarction in rats by decreasing the expression of inflammatory- related cytokines, diminishing MMP-2 expression and activating p-ERK.Int J Mol Med.2016;37(1):207-216.[19] Liu Z,Chen JM,Huang H,et al.The protective effect of trimetazidine on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating AMPK and ERK signaling pathway.Metabolism, 2016;65(3):122-130.[20] Thomas CJ,Lim NR,Kedikaetswe A,et al.Evidence that the MEK/ERK but not the PI3K/Akt pathway is required for protection from myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by 3',4'-dihydroxyflavonol. Eur J Pharmacol.2015;758:53-59.[21] Zheng PD,Mungur R,Zhou HJ,et al.Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro. Neural Regen Res.2018;13(7):1204-1211.[22] 杨鹏飞, 陈卫东. 银杏内酯B药理作用研究进展[J]. 安徽中医学院学报, 2012,31(5):86-90.[23] Fang W,Deng Y,Li Y,et al.Blood brain barrier permeability and therapeutic time window of Ginkgolide B in ischemia-reperfusion injury.Eur J Pharm Sci.2010;39(1-3):8-14.[24] Gu JH,Ge JB,Li M,et al.Inhibition of NF-κB activation is associated with anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Ginkgolide B in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharm Sci.2012;47(4):652-660.[25] Shu ZM, Shu XD, Li HQ, et al. Ginkgolide B Protects Against Ischemic Stroke Via Modulating Microglia Polarization in Mice. CNS Neurosci Ther 2016;22(9):729-739.[26] Hao Y,Sun Y,Xu C,et al.Improvement of contractile function in isolated cardiomyocytes from ischemia-reperfusion rats by ginkgolide B pretreatment. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009;54(1): 3-9.[27] 姜秀新,管斯斯,鲍利,等.银杏内酯B对胶原或二磷酸腺苷刺激血小板活化后一氧化氮含量及血管舒张因子刺激磷酸蛋白磷酸化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(11):2066-2070. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
ERK(extracellular signal-regulated kinase):是一种丝裂原活化蛋白激酶,有许多亚族,其中ERK1、ERK2具有高度同源性,也是目前研究最多的两个亚族,研究发现磷酸化的ERK1/2可以显著降低心肌细胞凋亡,对心肌缺血再灌注损伤具有非常重要的保护作用。
银杏内酯B(Ginkgolide B,GB):是银杏叶提取物银杏内酯中生理活性最强的成分,具有抑制细胞凋亡、抗炎、抗氧化、血管保护、抗血小板聚集、神经元保护等多种作用,被广泛用于急性缺血性脑卒中、心血管疾病、转移性癌症等疾病的治疗。
文题释义:
ERK(extracellular signal-regulated kinase):是一种丝裂原活化蛋白激酶,有许多亚族,其中ERK1、ERK2具有高度同源性,也是目前研究最多的两个亚族,研究发现磷酸化的ERK1/2可以显著降低心肌细胞凋亡,对心肌缺血再灌注损伤具有非常重要的保护作用。
银杏内酯B(Ginkgolide B,GB):是银杏叶提取物银杏内酯中生理活性最强的成分,具有抑制细胞凋亡、抗炎、抗氧化、血管保护、抗血小板聚集、神经元保护等多种作用,被广泛用于急性缺血性脑卒中、心血管疾病、转移性癌症等疾病的治疗。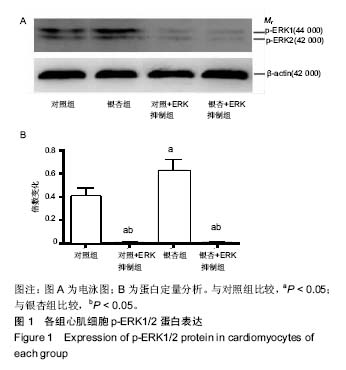
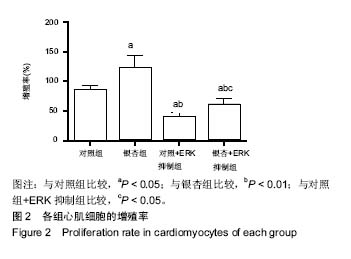
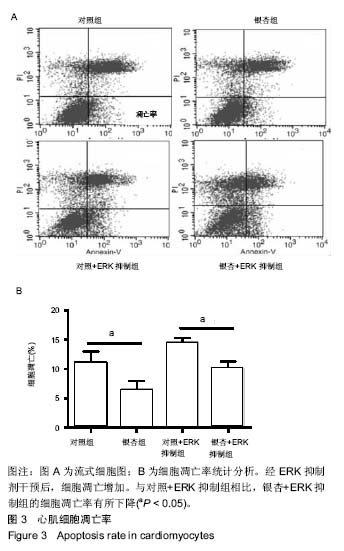
.jpg) 文题释义:
ERK(extracellular signal-regulated kinase):是一种丝裂原活化蛋白激酶,有许多亚族,其中ERK1、ERK2具有高度同源性,也是目前研究最多的两个亚族,研究发现磷酸化的ERK1/2可以显著降低心肌细胞凋亡,对心肌缺血再灌注损伤具有非常重要的保护作用。
银杏内酯B(Ginkgolide B,GB):是银杏叶提取物银杏内酯中生理活性最强的成分,具有抑制细胞凋亡、抗炎、抗氧化、血管保护、抗血小板聚集、神经元保护等多种作用,被广泛用于急性缺血性脑卒中、心血管疾病、转移性癌症等疾病的治疗。
文题释义:
ERK(extracellular signal-regulated kinase):是一种丝裂原活化蛋白激酶,有许多亚族,其中ERK1、ERK2具有高度同源性,也是目前研究最多的两个亚族,研究发现磷酸化的ERK1/2可以显著降低心肌细胞凋亡,对心肌缺血再灌注损伤具有非常重要的保护作用。
银杏内酯B(Ginkgolide B,GB):是银杏叶提取物银杏内酯中生理活性最强的成分,具有抑制细胞凋亡、抗炎、抗氧化、血管保护、抗血小板聚集、神经元保护等多种作用,被广泛用于急性缺血性脑卒中、心血管疾病、转移性癌症等疾病的治疗。