中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (24): 3924-3930.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1226
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
锁定钢板与顺行髓内钉治疗成人肱骨干骨折临床效果的Meta分析
王 磊,李子龙,袁斌斌,吴庆伟,唐烽明
- 武警后勤学院,天津市 300162
Clinical effect of locking plate versus anterograde intramedullary nail in the treatment of adult humeral shaft fractures: a meta-analysis
Wang Lei, Li Zilong, Yuan Binbin, Wu Qingwei, Tang Fengming
- Logistic University of Chinese People’s Armed Police Force, Tianjin 300162, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
锁定钢板:带有锁定孔的钢板,可以和锁定螺钉形成机械连接,锁定加压钢板具有结合孔,既可以使用传统螺钉,也可以使用锁定螺钉。
带锁髓内钉:亦称交锁髓内钉,在髓内钉的近端及远端斜形或横行穿入交锁螺钉,以增加抗扭力。
摘要
背景:目前发表的Meta分析文献,多数没有区分所采用的钢板类型,也没有区分是顺行还是逆行置入髓内钉,临床指导意义不强,需要进一步研究。
目的:通过对近年所发表的有关肱骨干骨折治疗的相关文献进行Meta分析,比较锁定钢板和顺行髓内钉治疗成人肱骨干骨折的临床效果,以更好的指导临床工作。
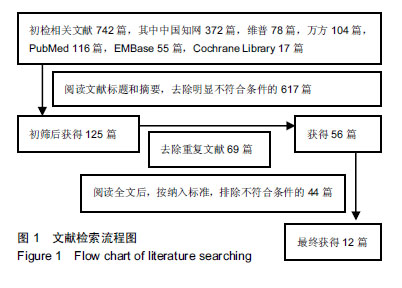
方法:通过检索中文数据库CNKI、维普、万方和外文数据库PubMed、EMBase、Cochrane Library所收录的相关文献,用RevMan 5.3软件对文献中锁定钢板和顺行髓内钉治疗成人肱骨干骨折的手术时间、术中出血量、术后上肢功能和术后不良反应进行比较分析。
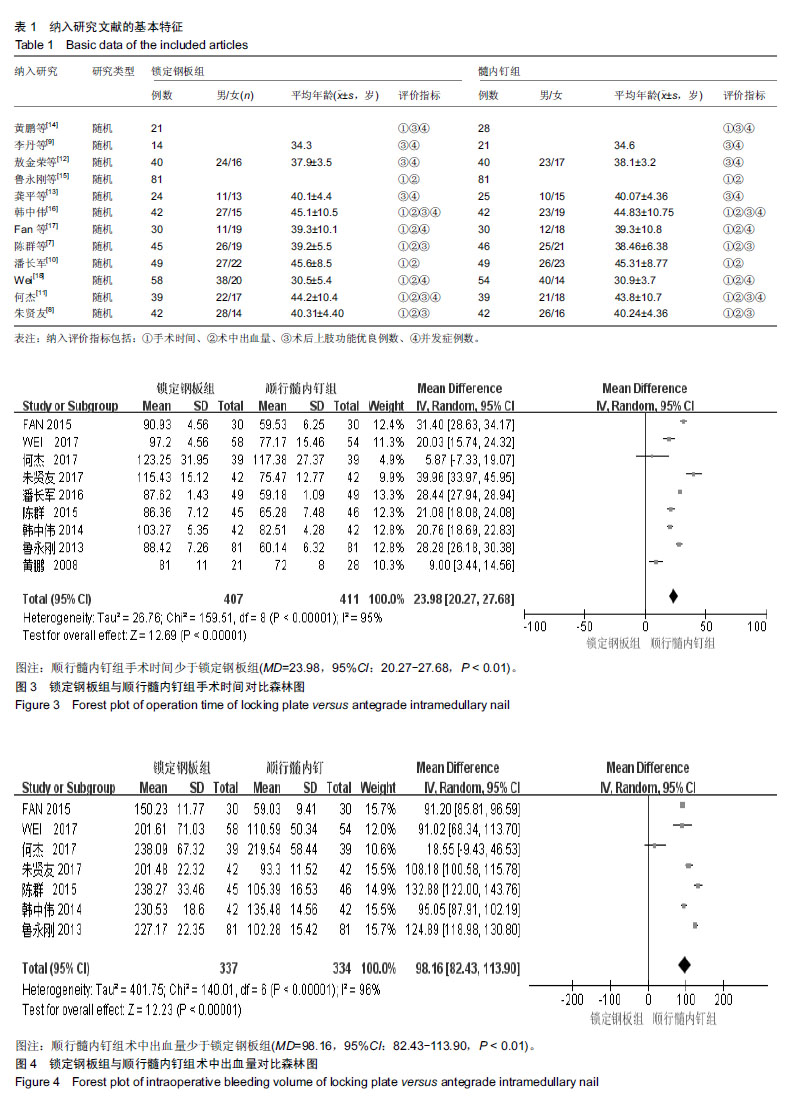
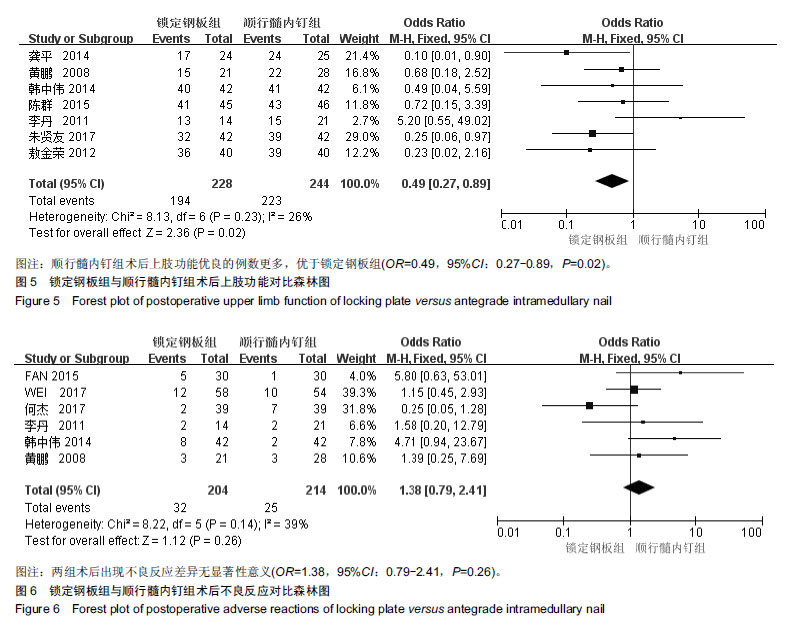
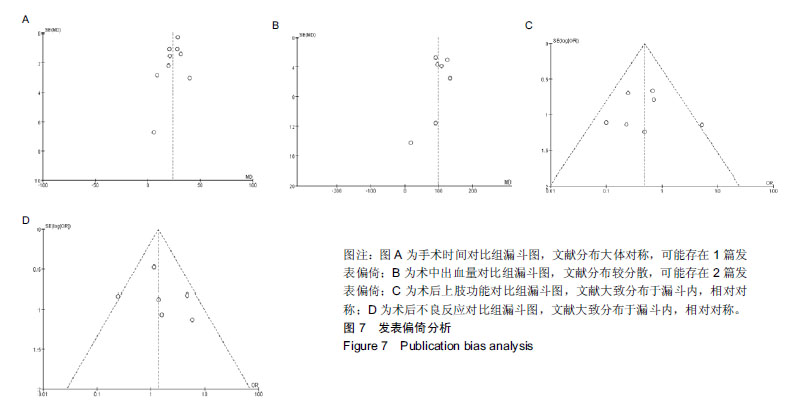
结果与结论:共有12篇文献纳入研究,全部为临床随机对照试验,共982例患者(锁定钢板组共485例,髓内钉组共497)。Meta分析结果:9篇文献进行了手术时间的统计分析,7篇文献进行了术中出血量的统计分析,7篇文献进行了术后上肢功能的统计分析,6篇文献进行了术后不良反应的统计分析。所纳入的研究显示,顺行髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗成人肱骨干骨折在手术时间(MD=23.98,95%CI:20.27-27.68,P < 0.01)、术中出血量(MD=98.16,95%CI:82.43-113.90,P < 0.01)和术后上肢功能(OR=0.49,95%CI:0.27-0.89,P=0.02)方面差异有显著性意义,顺行髓内钉比锁定钢板更有优势,在术后不良反应上,顺行髓内钉组与锁定钢板组无显著性意义(OR=1.38,95%CI:0.79-2.41,P=0.26)。结果证实,髓内钉治疗肱骨干骨折相较于钢板螺钉内固定的临床效果并不处于劣势。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7366-1788(王磊)
中图分类号:
R459.9|R615

.jpg)