| [1] Dayan AD.Quantitative histological studies on the aged human brain. II. Senile plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia (with an appendix on their occurrence in cases of carcinoma). Acta Neuropathol. 1970;16(2):95-102.[2] Grundke-Iqbal I,Iqbal K,Tung YC, et al. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1986;83:4913-4917.[3] Kowall NW, Beal MF, Busciglio J, et al.An in vivo modelfor the neurodegenerative effects of beta amyloid and protection by substance P.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1991;88:7247-7251.[4] Hardy J, Selkoe DJ.The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science.2002;297:353-356.[5] Lue LF, Kuo YM, Roher AE,et al. Soluble amyloid beta peptide concentration as a predictor of synaptic change in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol.1999;155:853-862.[6] McLean CA, Cherny RA, Fraser FW, et al. Soluble pool of Abeta amyloid as a determinant of severity of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1999;46(6):860-866.[7] Mucke L, Masliah E, Yu GQ, et al. High-level neuronal expression of abeta 1–42 in wild-type human amyloid protein precursor transgenic mice: synaptotoxicity without plaque formation. J. Neurosci.2000;20:4050-4058.[8] Koistinaho M,Ort M,Cimadevilla JM, et al.Specific spatial learning deficits become severe with age in beta-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice that harbor diffuse beta-amyloid deposits but do not form plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:14675–14680.[9] Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, et al. Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction.Neuron.2003; 39:409-421.[10] Billings LM,Oddo S,Green KN, et al. IntraneuronalAbeta causes the onset of early Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deficits in transgenic mice. Neuron 2005;45: 675–688.[11] Zhang L, Xie JW, Yang J, et al. Tyrosine Phosphatase STEP 61 Negatively Regulates Amyloid b-Mediated ERK/CREB Signaling Pathways Via a7 NicotinicAcetylcholine Receptors. J Neurosci Res.2013;91:1581-1590.[12] Abdoulaye IA, Guo YJ. A Review of Recent Advances in Neuroprotective Potential of 3-N-Butylphthalide and Its Derivatives. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5012341.[13] Xu HL, Feng YP. Inhibitory effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on inflamma-tion following focal ischemic brain injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2000;21:433-438.[14] Liu RZ, Fan CX, Zhang ZL, et al. Effects of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide on Cerebral Ischemia Infarction in Rat Model by Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(11): 2451. [15] Li F, Ma Q, Zhao H, et al. L-3-n-Butylphthalide reduces ischemic stroke injury and increases M2 microglial polarization. Metab Brain Dis. 2018; 33(6): 1995-2003. [16] Peng Y, Zeng X, Feng Y, et al. Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activity of L-3-n-butylphthalide in rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004;43:876-881.[17] Peng Y, Xu S, Chen G, et al. l-3-n-Butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007;321: 902-910.[18] Zhang C, Zhao S, Zang Y, et al.The efficacy and safety of Dl-3n-butylphthalide on progressive cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled STROBE study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(30):e7257. [19] Lei H, Zhang Y, Huang L, et al.L-3-n-Butylphthalide Regulates Proliferation, Migration, and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cell In Vitro and Promotes Neurogenesis in APP/PS1 Mouse Model by Regulating BDNF/TrkB/CREB/Akt Pathway. Neurotox Res. 2018;34(3):477-488. [20] Bi MJ, Sun XN, Zou Y, et al.Front Pharmacol. N-Butylphthalide Improves Cognitive Function in Rats after Carbon Monoxide Poisoning . Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:64. [21] Zhao Y, Lee JH, Chen D, et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalide Induced Neuroprotection, Regenerative Repair, Functional Recovery and Psychological Benefits following Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice.Neurochem Int. Neurochem Int. 2017;111:82-92. [22] Liu CY, Zhao ZH, Chen ZT, et al.DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects endothelial cells against advanced glycation end product-induced injury by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation responses.Exp Ther Med. 2017; 14(3): 2241–2248. [23] Chang Q, Wang XL.Effects of chiral 3-n-butylphthalide on apoptosis induced by transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2003;24:796–804.[24] Wang CY, Xu Y, Wang X, et al. Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome and Mitigates Alzheimer's-Like Pathology via Nrf2-TXNIP-TrX Axis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Apr 25. [25] Diao XX, Zhong K, Li XL, et al. Isomer-selective distribution of 3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) hydroxylated metabolites, 3-hydroxy-NBP and 10-hydroxy-NBP, across the rat blood-brain barrier. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015; 36(12): 1520-1527. [26] Lv C, Ma Q, Han B, et al.Long-Term DL-3-n-Butylphthalide Treatment Alleviates Cognitive Impairment Correlate With Improving Synaptic Plasticity in SAMP8 Mice. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:200. [27] González-Reyes RE, Nava-Mesa MO, Vargas-Sánchez K, et al.Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:427.[28] Maurice T, Hippert C, Serratrice N, et al. Cystine accumulation in the CNS results in severe age-related memory deficits. Neurobiol Aging. 2009;30(6):987-1000.[29] Frank AW, Randy JA, Fengju BA. Proteomic survey of rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Proteomics. 2005; 5(8): 2177-2201.[30] Ruan L, Kang Z, Pei G, et al. Amyloid deposition and in-flammation in APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alz-heimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009; 6(6):531-540.[31] Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Fadeeva JV, et al. Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid b protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo.Nature 2002;416:535-539.[32] Kamenetz F,Tomita T,Hsieh H,et al. APP processing and synaptic function.Neuron.2003;37:925-937.[33] Snyder EM, Nong Y,Almeida CG, et al. Regu-lation of NMDA receptor trafficking by amyloid-beta. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8: 1051-1058.[34] Yan CH, Feng YP, Zhang JT.Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on regional cerebral blood flow in right middle cerebral artery occlusion rats. Zhongguo Yao Li XueBao.1998;19:117–120.[35] Xiang J, Pan J, Chen F, et al.L-3-n-butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment of APP/PS1 mice by BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/ AKT pathway.Int J ClinExp Med.2014;7(7):1706-1713.[36] Barr AJ, Knapp S. MAPK-specific tyrosine phosphatases: new tar-gets for drug discovery? Trends Pharmacol Sci.2006;27: 525-530.[37] Paul S, Nairn AC, Wang P,et al. NMDA-mediated acti-vation of the tyrosine phosphatase STEP regulates the duration of ERK signaling. Nat Neurosci.2003;6:34-42. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。
文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。.jpg) 文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。
文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。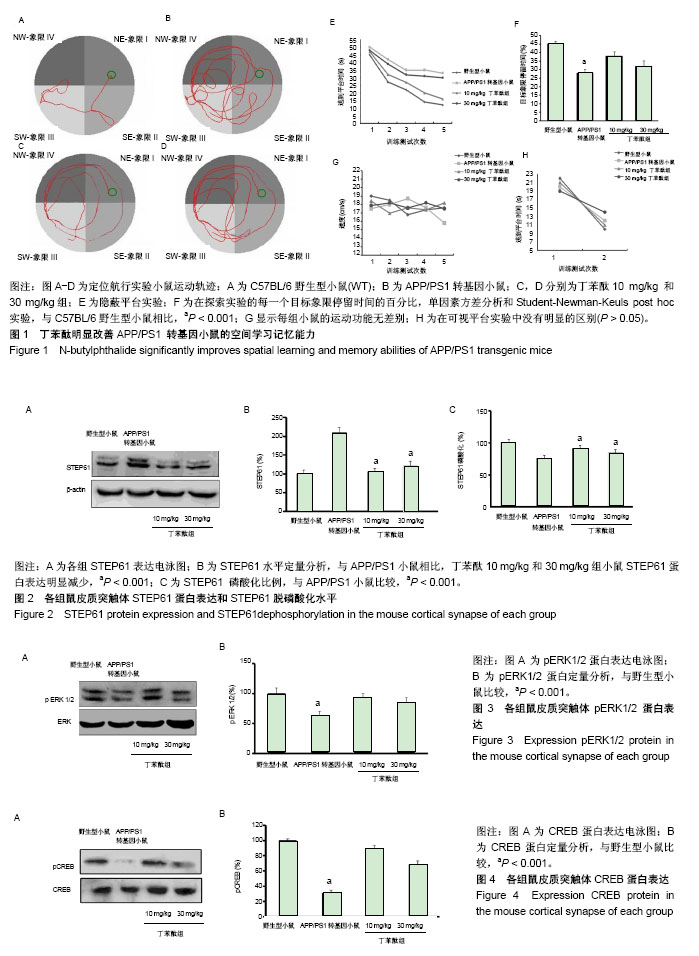
.jpg) 文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。
文题释义:
β-淀粉样蛋白(amyloid-β,Aβ):是由淀粉样前体蛋白( amyloid precursor protein,APP) 经β-和γ-分泌酶的蛋白水解作用而产生的含有39-43个氨基酸的多肽。它可由多种细胞产生,循环于血液、脑脊液和脑间质液中,大多与伴侣蛋白分子结合,少数以游离状态存在。人体内 Aβ最常见的亚型是Aβ1-40和Aβ1-42。在人脑脊液和血中,Aβ1-40分别比 Aβ1-42的含量水平高10倍和1.5倍,Aβ1-42具有更强的毒性,且更容易聚集,从而形成Aβ沉淀的核心,引发神经毒性作用 。
环磷酸腺苷反应单元结合蛋白(cAMP response element binding protein,CREB):是真核生物细胞核内一种重要的核蛋白,属于结构相关转录因子CREB家族成员之一,它的功能是调节基因转录,因此被称为调节转录的核因子。CREB在一些神经心理活动中如神经元的发育、再生、突触形成、学习记忆及细胞的修复等起着关键性的作用,是细胞内多种信号通路的一种关键成分。