| [1] 史洪飞.基于3种足弓参数的足弓与步幅特征的相关性研究[J].中国人民公安大学学报 (自然科学版),2017;23(4):10-17.[2] 左建刚,王海雄,桑志成.外翻足足弓的研究现状和进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015;23(15):1378-1382.[3] 夏迁洋.足弓与足跟痛关系的临床研究[J].中国医学工程,2014; 22(8):101-107.[4] 任结根.足弓不稳定性是引起腰椎间盘突出症的重要原因之一[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(30):123-129.[5] 赵敦旭,陈旧性跖跗关节脱位的足弓重建[J].中国修复重建外科杂志.2009,23(7):886-887.[6] 徐世明,孙大炜,黄东.Lisfranc损伤的诊断和治疗研究进展[J].山东医药 2018,58(7):111-114.[7] 宋谋珂,夏天,叶哲伟,等.跖跗关节复合体损伤的诊断与治疗方案的选择[J].中国骨与关节杂志.2013,2(7):382-385.[8] 俞平,邹国庆,单燕.跖跗关节隐匿性损伤三维CT的诊断价值[J].现代实用医学,2015,27(11):1514-1515.[9] 谢 伟,马俊芳,王文斌,等.应用数字化断层融合技术诊断足骨骨折的价值[J].放射性实践.2015,30(4):381-384.[10] 张军胜,邵旭辉,张华文.螺旋CT与DR平片在显示足部骨折细微结构的对比分析[J].陕西医学杂志,2017,46(8):1018-1019.[11] Herief TI, Mucci B, Greiss M. Lisfranc injury: how frequently does it get missed? And how can we improve? Injury. 2007; 38(7):856-860. [12] 温建民,孙卫东,成永忠,等.基于CT图像外翻足有限元模型的建立与临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012,20(11): 1026-1029.[13] 徐志庆,刘云鹏,华国军,等.前踝撞击征发生机制的生物力学有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(14):1303-1307.[14] Mc Cormaek AP, Niki H, Kiser P, et al. Two reconstructive techniques for flatfoot deformity comparing contact characteristics of the hindfoot joints. Foot Ankle Int. 1998;19: 452-461. [15] Wagner UA, Sangeorzan BJ, Harrington RM, et al. Contact characteristics of the subtalar joint: load distribution between the anterior and posterior facets. J Orthop Res. 1992;10: 535-543. [16] Pereira DS, Koval KJ, Resnick RB, et al. Tibiotalar contact area and Pressure distribution: the effect of mortise widening and syndesmosis fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 1996;17:269-274. [17] Cheung JT, Zhang M, Leung AK, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the foot during standing-a material sensitivity study. J Biomech. 2005;38:1045-1054. [18] Lakin RC, DeGnore LT, Pienkowski D. Contact mechanics of normal tarsometatarsal joints. J Bone joint surg Am. 2001;83: 520-528. [19] 郭国新,郭继涛,李伟,等.基于有限元模型的踝关节生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17):3056-3060.[20] 郭国新,赵长义,曹雷,等.踝关节内翻的有限元力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(24):4801-4806.[21] 周宇宁,张宏,陈相春,等.建立足部三维有限元数字模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):662-666.[22] Gaines RJ, Wright G, Stewart J. Injury to the tarsometatarsal joint complex during fixation of Lisfranc fracture dislocations: an anatomic study. J Trauma. 2009;66(4):1125-1128. [23] Myerson MS, Fisher RT, Burgess AR, et al. Fracture-dislocation of the tarsometatarsal joints and results correlated with pathology and treatment. Foot Ankle. 1986;6: 225-242. [24] Hardcastle PH, Reschauer R, Kutscha-Lissberg E, et al. Injuries to the tarsometatarsal joint. Incidence, classification and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982;64(3):349-356. [25] Buzzard BM, Briggs PJ. Surgical Management of. Acute Tarsometatarsal Fracture. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;353: 125-133. [26] 董骧,樊瑜波,张明.人体足部生物力学研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2002,19(1):148–153.[27] 袁刚,张木勋,王中琴,等.正常人足底压力分布及其影响因素分析[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2004,26(3):156-159.[28] Desmond EA, Chou LB. Current concepts review: Lisfranc injuries. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(8):653-660. [29] Raikin SM, Elias I, Dheer S, et al. Prediction of midfoot instability in the subtle Lisfranc injury. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging with intraoperative findings. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(4):892-899. |
.jpg)

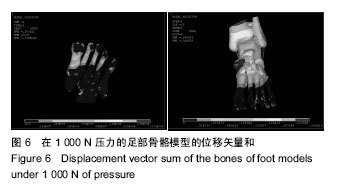
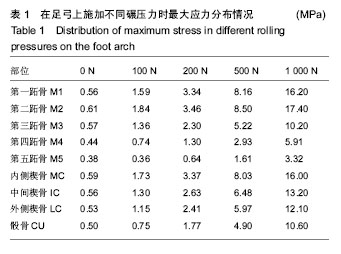
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)