| [1] Sun G,Jin P,Li M,et al.Percutaneous cementoplasty for painful osteolytic humeral metastases: initial experience with an innovative technique.Skeletal Radiol. 2011;40(10): 1345-1348.[2] Ofluoglu O,Erol B,Ozgen Z,et al.Minimally invasive treatment of pathological fractures of the humeral shaft.Int Orthop. 2009; 33(3):707-712.[3] Liu XW,Jin P,Liu K,et al.Comparison of percutaneous long bone cementoplasty with or without embedding a cement-filled catheter for painful long bone metastases with impending fracture.Eur Radiol. 2017;27(1):120-127.[4] 杨毅,杨荣利,郭卫.59例肱骨转移癌手术治疗的回顾性分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2011,43(5):681-685.[5] Piccioli A,Maccauro G,Rossi B,et al.Surgical treatment of pathologic fractures of humerus.Injury. 2010;41(11): 1112-1116. [6] 严坤,锡林宝勒日.股骨近端溶骨性转移瘤三维有限元模型的力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(17):3101-3108.[7] Cotten A, Duquesnoy B.Percutaneous cementoplasty for malignant osteolysis of the acetabulum. Presse Med. 1995; 24(28):1308-1310.[8] 孙钢,金鹏,易玉海,等.经皮注射聚甲基异丁烯酸治疗溶骨性骨盆区与外周骨转移瘤[J].中华放射学杂志, 2005,39(8): 869-873.[9] Anselmetti GC,Manca A,Ortega C,et al. Treatment of extraspinal painful bone metastases with percutaneous cementoplasty: a prospective study of 50 patients.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008;31(6):1165-1173.[10] Cazzato RL,Buy X,Eker O,et al.Percutaneous long bone cementoplasty of the limbs: experience with fifty-one non-surgical patients. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(12):3059-3068.[11] Huskisson EC.Measurement of pain.Lancet. 1974;2(7889): 1127-1131.[12] de Kock I,Mirhosseini M,Lau FJ,et al.Conversion of Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG) to Palliative Performance Scale (PPS), and the interchangeability of PPS and KPS in prognostic tools.Palliat Care.2013;29(3):163-169.[13] Mirels H. Metastatic disease in long bones. A proposed scoring system for diagnosing impending pathologic fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1989;(249):256-264.[14] Edwards BJ,Sun M,West DP,et al.Incidence of Atypical Femur Fractures in Cancer Patients: The MD Anderson Cancer Center Experience.J Bone Miner Res.2016;31(8):1569-1576.[15] Baek SJ,Hur H,Min BS,et al.The Characteristics of Bone Metastasis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Long-Term Report from a Single Institution.World J Surg. 2016;40(4): 982-986.[16] Kim W,Han I,Jae HJ,et al.Preoperative embolization for bone metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. Orthopedics. 2015; 38(2):e99-e105.[17] 陈晓钟,张鸿未.骨转移瘤的临床研究进展[J].中国肿瘤, 2006, 15(3):183-186.[18] Conroy T,Malissard L,Dartois D,et al.Natural history and development of bone metastasis. Apropos of 429 cases.Bull Cancer.1988;75(9):845-857.[19] 李昂,谭震,傅传刚,等.结直肠癌根治术后5年内骨转移的危险因素分析[J].中华胃肠外科杂志,2017, 20(1):58-61.[20] Nozue M,Oshiro Y,Kurata M,et al.Treatment and prognosis in colorectal cancer patients with bone metastasis.Oncol Rep. 2002;9(1):109-112.[21] Baek SJ,Hur H,Min BS,et al.The Characteristics of Bone Metastasis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer: A Long-Term Report from a Single Institution.World J Surg. 2016;40(4): 982-986. [22] Park HS,Rha SY,Kim HS,et al.A prognostic model to predict clinical outcome in gastric cancer patients with bone metastasis. Oncology.2011;80(1-2):142-150. [23] Wedin R,Hansen BH,Laitinen M,et al.Complications and survival after surgical treatment of 214 metastatic lesions of the humerus.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2012;21(8):1049-1055.[24] Ruggieri P,Mavrogenis AF,Casadei R, et al. Protocol of surgical treatment of long bone pathological fractures. Injury. 2010;41(11):1161-1167.[25] Piccioli A,Maccauro G,Scaramuzzo L,et al.Surgical treatment of impending and pathological fractures of tibia.Injury. 2013; 44(8):1092-1096.[26] 廖前德,陈群,钟达,等.恶性骨肿瘤的保肢治疗[J].中南大学学报, 2006,31(5):723-727.[27] Matcuk GR Jr,Mahanty SR,Skalski MR,et al.Stress fractures: pathophysiology, clinical presentation, imaging features, and treatment options.Emerg Radiol.2016;23(4):365-375.[28] Uezono H,Tsujino K,Moriki K,et al.Pelvic insufficiency fracture after definitive radiotherapy for uterine cervical cancer: retrospective analysis of risk factors.J Radiat Res. 2013;54(6): 1102-1109.[29] Chow R,Hoskin P,Hollenberg D,et al.Efficacy of single fraction conventional radiation therapy for painful uncomplicated bone metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Palliat Med. 2017;6(2):125-142.[30] Hashmi A,Guckenberger M,Kersh R,et al.Re-irradiation stereotactic body radiotherapy for spinal metastases: a multi-institutional outcome analysis.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016; 25(5):646-653.[31] Ito T,Bilusic M,Chen D.Targeted radionuclides for prostate cancer bone metastases.Urol Oncol. 2015;33(1):2-6.[32] Hillegonds DJ,Franklin S,Shelton DK,et al.The management of painful bone metastases with an emphasis on radionuclide therapy.J Natl Med Assoc.2007;99(7):785-794.[33] Mirels H.Metastatic disease in long bones: A proposed scoring system for diagnosing impending pathologic fractures. 1989.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;415:S4-13. |
.jpg)
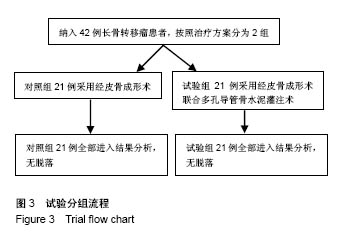
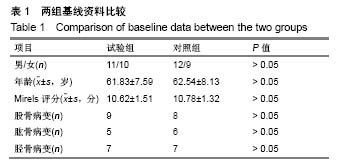
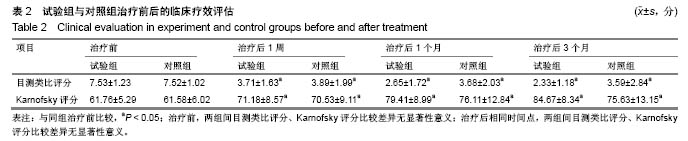
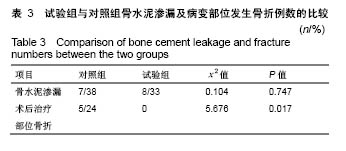
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)