中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5110-5116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0556
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症不同方案疗效差异:基于血清代谢组学的评价
陈丽虹1,岳容兆1,张永怡1,张 沁1,王燕君1,桂 前1,杨 敏1,徐桂华1,谢 彤2,彭琳秀2
- 南京中医药大学,1护理学院,2江苏省儿童呼吸疾病(中医药)重点实验室,江苏省南京市 210023
Differences in outcomes of different scraping therapy schemes for lumbar disc herniation based on metabonomics
Chen Li-hong1, Yue Rong-zhao1, Zhang Yong-yi1, Zhang Qin1, Wang Yan-jun1, Gui Qian1, Yang Min1, Xu Gui-hua1, Xie Tong2, Peng Lin-xiu2
- 1School of Nursing, 2Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Children Respiratory Diseases (Traditional Chinese Medicine), Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。摘要
背景:刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症在临床应用广泛,结合代谢组学等现代分析技术可多环节、多途径、多靶点对其机制效应进行研究。
目的:运用气相色谱-质谱联用技术,分析刮痧对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠血清代谢谱的影响及不同方案的疗效差异。探讨刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症的作用机制,为临床治疗提供新的思路和依据,推动刮痧疗法的规范化、标准化进程。
方法:48只雄性SD大鼠由浙江省实验动物中心提供,随机分为刮痧组(循经出痧组、循经不出痧组、穴位出痧组、穴位不出痧组)、模型组与空白组,每组8只。刮痧组和模型组制备自体髓核移植非压迫性腰椎间盘突出症模型。刮痧各组分别给予不同刮痧方案进行干预,隔日1次,3 d为一个疗程,共3个疗程。借助电子测痛仪,测定刮痧各组和模型组大鼠造模前后的机械阈值;使用气相色谱-质谱联用技术分析6组大鼠血清内源性差异代谢物。
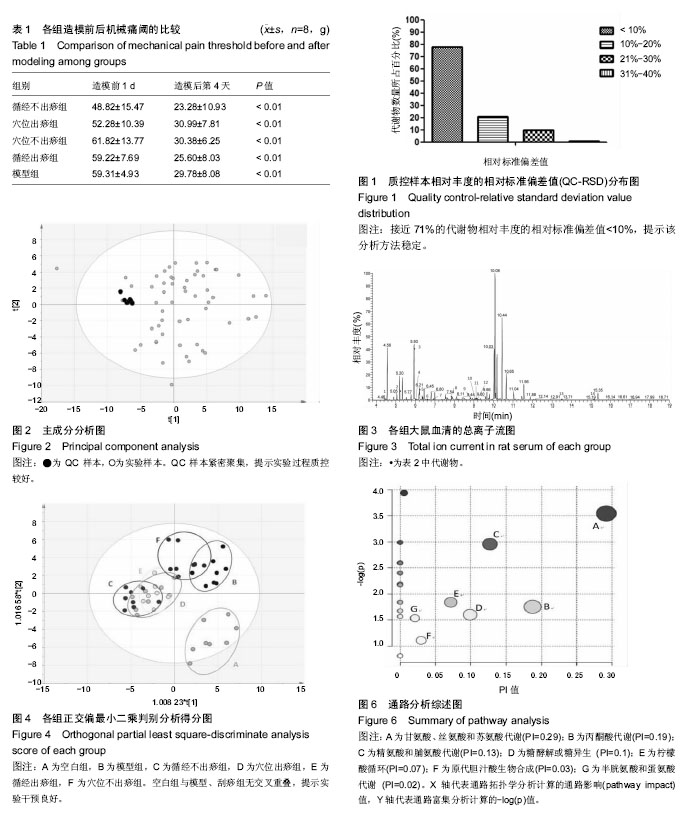
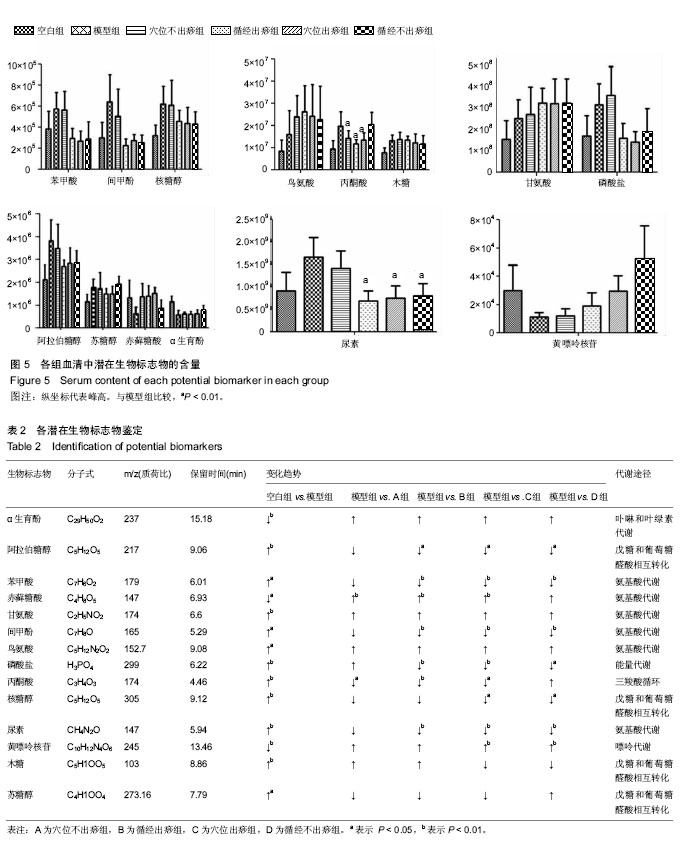
结果与结论:①刮痧各组和模型组造模后的机械痛阈值均较造模前显著降低(P < 0.01);②根据代谢组学分析,共筛选出甘氨酸、丙酮酸、鸟氨酸等14种潜在的生物标志物,涉及甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢,丙酮酸代谢和柠檬酸循环等7条代谢通路,其中刮痧通过调节尿素含量、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢、丙酮酸代谢通路对腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠起到抗炎作用,通过调节精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢通路达到镇痛效果;③分析刮痧4组甘氨酸、丙酮酸、鸟氨酸和尿素含量,发现循经出痧组的异常代谢物调节效果最好,由此推测其治疗效果也较其他3组更为显著;④今后还需大样本的临床试验进行更为深入的研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-9992-3061(陈丽虹)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。
文题释义:
代谢组学:是继基因组学和蛋白质组学之后新近发展起来的一门学科,是系统生物学的重要组成部分。其通过生物信息、模式识别分析等方法检测代谢产物,对代谢产物进行动态观察与全面的定性定量分析,阐明机体受外界刺激后代谢过程的动态反应规律。代谢组学的样品包括血清、尿液、血浆或唾液,以及细胞和组织的提取液等。
腰椎间盘突出症:为腰椎发生退行性变后,因外力作用诱发髓核或纤维环向外突出,刺激或压迫神经根引起的病变,是临床常见的脊柱疾病之一,主要症状为下肢放射性疼痛或伴腰痛。其疼痛发生机制主要包括机械压迫学说、炎症反应学说、自身免疫学说这3大类。