中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (27): 4294-4299.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0342
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
桡骨远端骨折新型夹板的临床验证及改良设计
颜 威1,2,3,孔 博1,2,3,蒋 涛1,2,3,贾友冀1,奚小冰1,2,3
- 1上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,上海市 200025;2上海市中西医结合防治骨与关节病损重点实验室,上海市 200025;3上海市伤骨科研究所,上海市 200025
Clinical verification and improved design of the new traction splint for distal radius fractures
Yan Wei1, 2, 3, Kong Bo1, 2, 3, Jiang Tao1, 2, 3, Jia You-ji1, Xi Xiao-bing1, 2, 3
- 1Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China; 2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Diseases, Shanghai 200025, China; 3Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Shanghai 200025, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
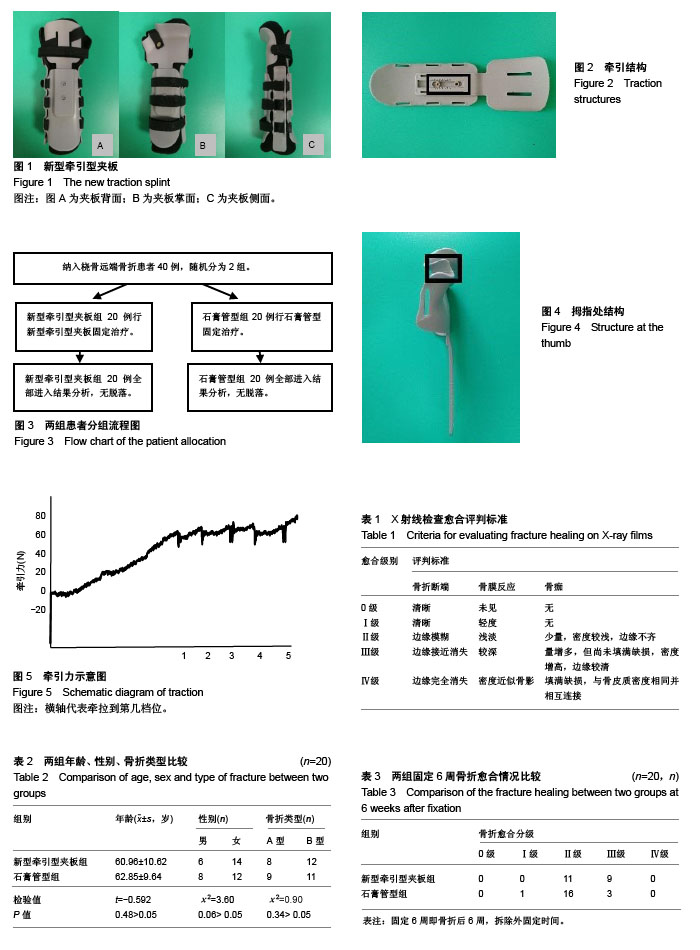
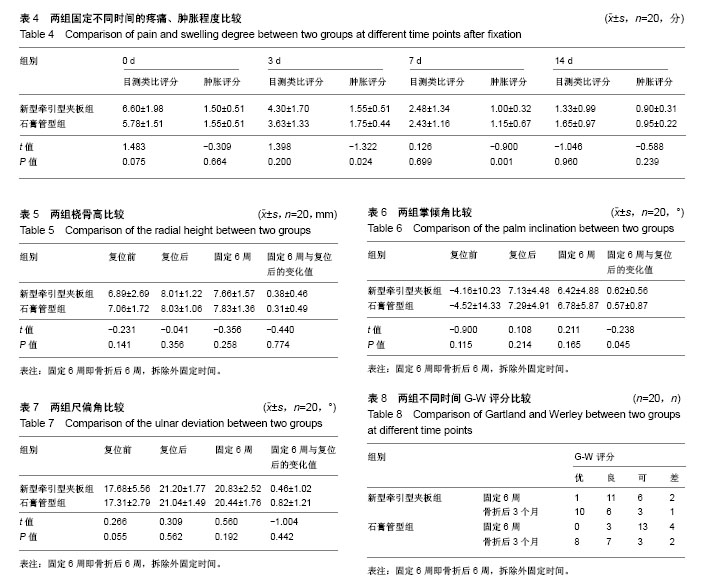
新型牵引型夹板:是依据传统小夹板的“弹性固定”理论以及促进骨折愈合的“微动”理论设计研发的一款新型夹板,在夹板的背侧板和掌侧板各加入齿轮状的牵引结构,通过不断牵拉夹板,起到对骨折断端拔伸牵引得作用,促进骨折的愈合。
新型牵引型夹板的优势:其中牵引功能模块的设计更是其亮点所在,通过不断地微牵引,既加快了骨折的愈合又减轻了局部的肿胀不适。此外它还具有以下特点:①可调性:可根据患肢的肿胀程度实时调节外固定带的松紧程度,避免了压疮以及骨筋膜室综合征的出现;②透光性:新型牵引型夹板具有良好的X射线透光性,与石膏相比可以清晰的观察骨折愈合的情况;③舒适性:新型牵引型夹板具有透气,柔软舒适的特点。
摘要
背景:新型牵引型夹板是依据传统小夹板的“弹性固定”理论以及促进骨折愈合的“微动”理论设计研发的一款新型夹板,治疗桡骨远端骨折具有广阔的应用价值与应用前景。
目的:通过对新型牵引型夹板进行临床验证来探讨其性能,并对其不足进行改良设计。
方法:将40例桡骨远端骨折患者按照就诊时间顺序随机分为新型牵引型夹板组和石膏管型组,每组20例。分别在复位固定后即刻、固定2周、固定6周摄腕关节正侧位X射线片,根据X射线片对2组固定6周的骨折愈合情况进行对比;运用PACS系统分析测量固定后即刻、固定6周的桡骨高、掌倾角以及尺偏角;同时比较2组固定0,3,7,14 d的疼痛、肿胀程度,并按照Gartland和Werley(G-W)腕关节评分系统对腕关节功能进行评价。
结果与结论:①新型牵引型夹板组在骨折愈合速度及减轻患肢的肿胀程度方面均显著优于石膏管型组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②在骨折固定6周,新型牵引型夹板组的临床疗效要优于石膏管型组(P < 0.05);骨折3个月后,2组临床疗效差异无显著性意义;③在复位后、固定6周桡骨高、掌倾角以及尺偏角方面新型牵引型夹板组与石膏管型组相比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),在复位后与固定6周掌倾角变化值方面,石膏管型组要稍优于新型牵引型夹板组;④此外新型牵引型夹板与石膏管型治疗都存在不同程度的并发症,但在较严重并发症方面新型牵引型夹板发生率要少于传统石膏管型固定治疗;⑤提示新型牵引型夹板治疗桡骨远端骨折具有明显的优势和确切疗效,但也存在许多不足,需要在轻量化、外形、牵引结构以及内衬等方面不断地进行改良设计。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4353-7970(颜威)
中图分类号:
.jpg)