Distal radius fracture is a common consequence of fall and sports injuries, which has a high incidence in children (aged 6-10 years) and old women (60-69 years) especially in older women
[21]. Due to older women with osteoporosis, once fall, comminuted intra-articular fractures usually occur. Moreover, fractures are extremely unstable and serious destruction of the surface of wrist joint. Conservative treatment due to lack of effective supporting tends to fracture shorten and results in displacement. Loss of the ulnar and palmar tilt angles of distal radius leads to rough articular surface, and then results in malunion and obvious joint deformity, further causes joint dysfunction and traumatic arthritis
[21]. Although surgical treatment for the anatomical structure and function recovery of injured limb fractures has a good effect, the trauma of surgery itself and second trauma of removal of the internal fixators and high medical costs have increased the pain of patients and the family burden to large extent
[22]. The arrival of Chinese aging society, a high incidence of falls-induced distal radius fractures not only leads to discomfort activity of daily life and physical pain, but also brings about economic burden because of family nursing time and expense. Therefore, preventing distal radius fractures is of great significance.
To effectively prevent the senile distal radius fracture due to fall, we should protect the elderly from falling, such as strengthening the training on the balance function, strengthening the nursing of daily life and advocating the prevention and education of anti-fall[23]. Additionally, understanding the biomechanical mechanism of fall-induced wrist injury aims to developing an effective and safe protector of wrist joint, thus reducing the damage of falling to the wrist joint, and decreasing the incidence of distal radius fracture in older adults[24].
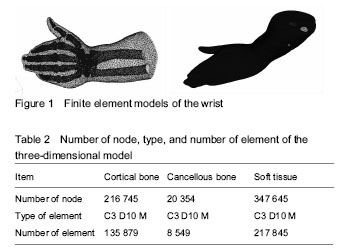
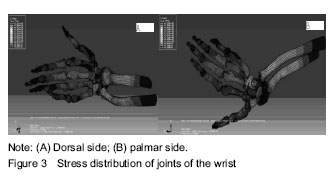
There are many biomechanical research methods, and finite element analysis has been extensively applied in the diagnosis and treatment of medical diseases, especially traumatic orthopedics, because of its advantages, such as good repeatability, the analysis results reflected in many forms, and high controllability. At the same time, there are a lot of scholars at home and abroad have performed finite element analysis on the biomechanical mechanism of distal radius fracture. They have study the fracture stress, fracture mechanics, transfer, the evaluation about microstructure and the biomechanics of internal fixation and external fixation of fractures[25-29]. But, biomechanical analysis of the entire wrist joint has not been reported from the viewpoint of fall. In this study, we analyzed the stress distribution of the whole wrist joint including soft tissues and bones during the falling by palm supporting. The wrist was placed in a fully extended state to simulate the dorsal position of the human hand and the original data were obtained, when the load was applied, the palm of the hand was constrained to simulate the stress point of the palm, and a 2 m/s load was applied instead of a single stress load. The constraints and the loading conditions are more in line with the injury mechanism of the human hand in the condition of fall, and the results of the analysis are more realistic to reflect the mechanical basis of the distal radius fracture caused by fall. From the results of finite element analysis, the skeletal stress mainly concentrated on the dorsal ulnar and distal radius, and the maximum compressive stress is in the dorsal distal radius. These results may explain the mechanism of Colles distal radius fractures when falls.
Through the finite element simulation analysis, we found that the dorsal stress mainly concentrated on the hypothenar, dorsal wrist and the dorsal of distal radius when the body falls and is supported by palm. The stress is gradually decreased from the back of the wrist to the elbow. Therefore, to prevent fall-induced injury, we should focus on the protection of the hypothenar, wrist, and distal radius. In sports injuries, professional athletes are often wearing a protective device[29]. However, for the common people, especially old adults who are prone to fall, there is lack corresponding protective equipment. To reduce the distal radius fractures caused by falls, it is necessary to start from the results of biomechanical analysis, and to design a convenient and economical wrist protection device. Domestic scholars have conducted some researches on the wrist falling protection device, but the research and design of the device is not easy to be accepted by the elder, so the actual liability of the protection still needs further investigation[30]. It is believed that with the biomechanical analysis results of the human body falling to the wrist, it is necessary to make an effective wrist protective device.
In this study, we analyzed the biomechanical mechanism of distal radius fractures by the finite element method when the body falls supported by palm. Our results can provide biomechanical basis for prevention of wrist injury due to fallings. However, due to the influence of the research conditions and the complexity of finite element modeling, this study still has the following problems: 1) The simulation of soft tissue modeling is not fine enough, and it has not been able to distinguish tendon from ligament; 2) The effect of muscle contraction on the stress values of soft tissue and bones was not considered when the human body fall; 3) There was no difference in the bone mineral density, and there was no comparative study on the normal bone and osteoporosis. All of these need to be solved in the future research, so as to provide a more effective basis for the development of the human hand protection device.
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)