中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (27): 4369-4374.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0325
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
腰骶椎轴向螺钉的设计及生物力学测试
曾德辉1,王文军2,张 卫1,宋西正2,阳文任1,向 亮1,侯 威1
- 1南华大学附属南华医院骨科,湖南省衡阳市 421001;2南华大学附属第一医院脊柱外科,湖南省衡阳市 421001
Design of axial screw for lumbosacral vertebrae and the biomechanical analysis
Zeng De-hui1, Wang Wen-jun2, Zhang Wei1, Song Xi-zheng2, Yang Wen-ren1, Xiang Liang1, Hou Wei1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the Affiliated Nanhua Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
轴向内固定系统(AxiaLIF):是经骶骨前入路轴向行腰骶椎前柱融合的内固定系统,其手术入路经直肠后间隙,沿腰骶椎的中轴进行,其作为新型的微创手术系统最大限度地减少了手术对入路旁组织、椎旁组织及脊柱结构的损伤,降低脊柱融合病的发生率。
脊柱内固定器械的生物力学实验:主要基于器械在生理环境中的机械性能和内固定器械对脊柱的影响两个方面,前者主要研究器械在承受各种生理载荷时所表现出来的性能和器械的疲劳强度,为破坏性实验,后者则主要研究器械对脊柱稳定性的影响,为非破坏性实验,许多学者在此基础上不断完善和发展,形成了屈服强度实验、疲劳实验和稳定实验3个基本实验类型。
摘要
背景:经骶骨前入路的经皮腰骶椎前柱内固定系统即AxiaLIF先后在美国及欧洲应用于临床,取得较好的临床疗效,但是在应用过程中出现了如内固定下沉、内固定控制旋转能力较差等一系列问题。
目的:根据国人腰椎侧位片及CT横断面测量的解剖数据自行设计腰骶椎轴向螺钉,制成成品后在体外生物标本上进行三维运动实验和轴向抗压缩实验,对其固定节段的稳定性及轴向抗压刚度进行生物力学评价。
方法:选取新鲜成人脊柱标本(L3-S5节段)6具,按正常组、峡部裂组、普通轴向螺钉固定组、自行设计轴向螺钉固定组顺序依次进行生物力学测试,分别测试各实验组在屈伸、左侧屈、左旋转运动状态下L5/S1节段的运动范围及轴向抗压缩位移。
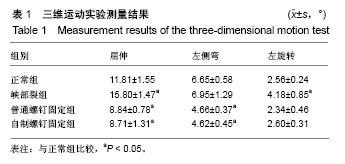
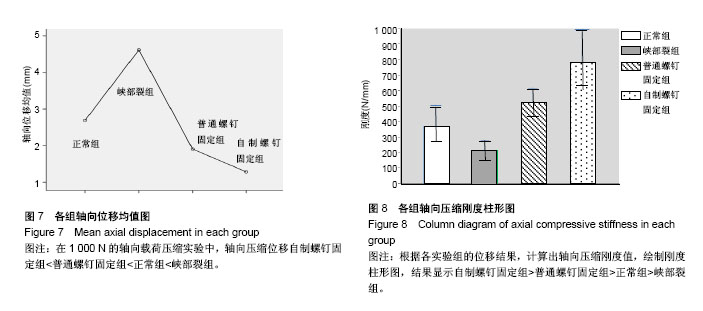
结果与结论:①在三维运动实验中,峡部裂组的ROM在屈伸及左旋转方向上均显著大于正常组(P < 0.05),在左侧弯方向上与正常组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②普通螺钉固定组与自制螺钉固定组的ROM在屈伸、左侧弯方向上均显著小于正常组(P < 0.05),在左旋转方向上与正常组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),普通螺钉固定组与自制螺钉固定组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③在1 000 N的轴向载荷压缩实验中,4组所产生的压缩位移差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),自制螺钉固定组<普通螺钉固定组<正常组<峡部裂组;④根据力学公式EF=P/vL,结合压缩位移结果,计算出轴向压缩刚度值,自制螺钉固定组>普通螺钉固定组>正常组>峡部裂组;⑤提示自行设计轴向螺钉可以显著提高腰骶椎在后柱失稳情况下各个运动方向的稳定性,与普通轴向螺钉相当,但在轴向抗压刚度方面明显强于普通轴向螺钉,为在防止轴向螺钉固定脊柱节段沉降和前凸损失方面提供了一种有效的解决思路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2653-7194(曾德辉)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)