中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (23): 3670-3674.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0322
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
腰椎黄韧带肥厚与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡相关性的影像学评价
彭嘉杰1,钟的桂1,王 竣1,赖俊辉1,黄永铨2,苏海涛2
- 1广州中医药大学第二临床医学院,广东省广州市 510405;2广东省中医院骨科,广东省广州市 510006
Correlations between hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum and sagittal spinopelvic balance evaluated by radiography
Peng Jia-jie1, Zhong De-gui1, Wang Jun1, Lai Jun-hui1, Huang Yong-quan2, Su Hai-tao2
- 1the Second Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
腰椎黄韧带肥厚:黄韧带是连接上下相邻2个椎板的黄色弹性韧带,起到维持脊柱固有稳定性、控制椎间运动、保持硬膜后囊表面光滑的作用。黄韧带肥厚被认为是腰椎管狭窄发展中的重要致病因素之一,肥厚的黄韧带压迫硬膜囊和根,进而出现腰痛和坐骨神经痛。黄韧带肥厚的原因是多方面的,包括年龄、脊柱机械应力和生长因子等。
脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡:是对脊柱曲度形态、骨盆角度位置的描述,包括胸椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角、骶骨倾斜角、骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角和矢状面平衡。这对患者脊柱疾病的发生、发展及预后起到一定的预测和评估作用。
摘要
背景:腰椎黄韧带肥厚存在多种发病机制,但是否与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡存在相关性,目前尚不清楚。
目的:分析腰椎黄韧带肥厚与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡参数间的关系。
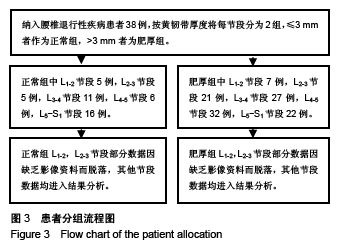
方法:回顾性分析2015年1月至2017年12月收入院治疗腰椎退行性疾病38例患者的临床资料,在患者站立位脊柱全长正侧位X射线片上进行脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数的测量,包括胸椎后凸角、腰椎前凸角、骶骨倾斜角、骨盆入射角、骨盆倾斜角和矢状面平衡。在患者腰椎MRI轴位关节突层面T2WI图像上对L1-2,L2-3,L3-4,L4-5,L5-S1节段黄韧带厚度进行测量;将黄韧带≤3 mm者作为正常组,>3 mm者为肥厚组,分析腰椎黄韧带肥厚与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡参数间的关系。
结果与结论:①各节段性别、体质量指数黄韧带正常组与肥厚组间差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),而年龄组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②L1-2节段胸椎后凸角组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),L2-3节段胸椎后凸角、骨盆倾斜角组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),L3-4节段胸椎后凸角组间比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.054),L4-5节段腰椎前凸角组间比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),L5-S1节段各参数间比较差异均无显著性意义;③L5-S1节段黄韧带厚度与矢状面平衡存在负相关关系(r=-0.33,P < 0.05);④提示黄韧带肥厚与脊柱-骨盆矢状面参数存在密切联系。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3670-1410(彭嘉杰)
中图分类号:

.jpg)