中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (15): 2373-2377.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0249
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
构建新鲜颈椎标本椎动脉流量测定模型:观察体位改变对椎动脉流量的影响
冯敏山1,2,尹逊路1,朱立国1,2,张法尧1,3,刘广伟2,展嘉文1,银 河1,高春雨1,李 健4
- 1中国中医科学院望京医院,北京市 100102;2中医正骨技术北京市重点实验室,北京市 100102;3齐齐哈尔市中医医院,黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市 161005;4北京理工大学自动化研究所,北京市 100102
Construction of fresh cervical vertebral artery determination model: influence of variant positions on vertebral artery flow
Feng Min-shan1, 2, Yin Xun-lu1, Zhu Li-guo1, 2, Zhang Fa-yao1, 3, Liu Guang-wei2, Zhan Jia-wen1, Yin He1, Gao Chun-yu1, Li Jian4
- 1Wangjing Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China; 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Palasy Technology, Beijing 100102, China; 3Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Qiqihaer, Qiqihaer 161005, Heilongjiang Province, China; 4School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100102, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
椎动脉流量:是反映椎-基底动脉供血的一个关键指标,其流量减小是导致椎动脉型颈椎病患者发生眩晕症的重要因素。目前临床常采用经颅多普勒超声检查测定椎动脉流量,但该项检查需要患者卧位,而颈椎体位及位置的变化对椎动脉流速会产生一定的影响;同时患者自身神经调节也会影响该指标的测定。因此,如何准确、高效的测定椎动脉流量成为当前急需解决的问题。
人体颈椎新鲜离体标本:作为可靠的生物力学研究模型,为从椎动脉流量角度研究颈性眩晕发病机制提供了基础。目前国内外尚无既能模拟颈椎生理状态、实现复杂体位,又能进行椎动脉流量测量的离体颈椎模型报道。
摘要
背景:人体颈椎新鲜离体标本作为可靠的生物力学研究模型,为从椎动脉流量角度研究颈性眩晕发病机制提供了基础。目前国内外尚无既能模拟颈椎生理状态、实现复杂体位,又能进行椎动脉流量测量的离体颈椎模型报道。
目的:通过构建新鲜颈椎标本椎动脉测定模型,观察体外环境下新鲜人尸颈椎体位改变对椎动脉流量的影响。
方法:取6具新鲜人尸颈椎标本构建椎动脉流量测定模型,通过调节压力泵模拟人体椎动脉压力;采用数字动作捕捉系统动态测量容量瓶内生理盐水液面高度的变化,实现在旋转相关体位下椎动脉流量测定。
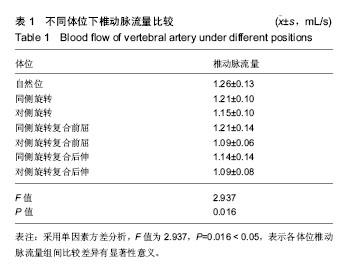
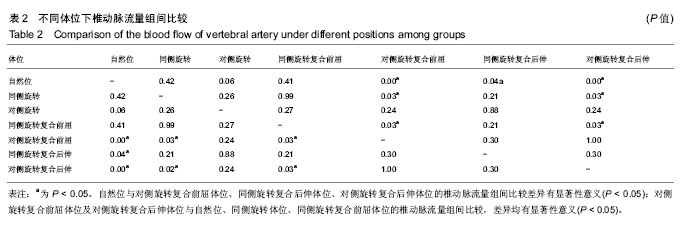
结果与结论:①6个模型中8条椎动脉通畅性完好;②自然位椎动脉流量明显大于对侧旋转复合前屈体位、同侧旋转复合后伸体位、对侧旋转复合后伸体位的椎动脉流量(P < 0.05);③对侧旋转复合前屈体位及对侧旋转复合后伸体位的椎动脉流量明显小于自然位、同侧旋转体位及同侧旋转复合前屈体位的椎动脉流量 (P < 0.05);④结果表明,成功构建了生理载荷下新鲜颈椎标本椎动脉循环模型,并实现了旋转相关体位下椎动脉流量的测量;不同的旋转体位对椎动脉流速有不同的影响。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-7640-7494(张法尧)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)