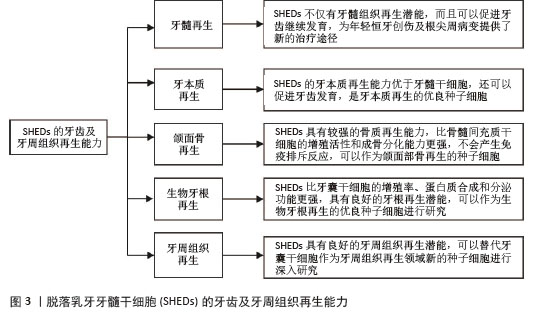
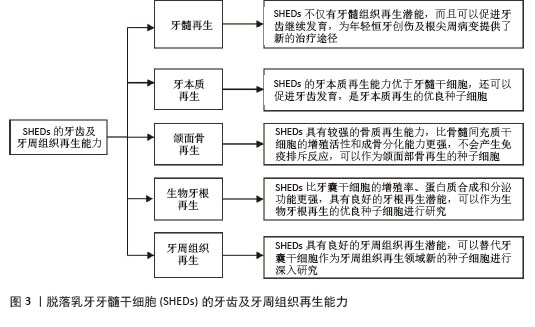
[1] GUO H, ZHAO W, LIU A, et al. SHED promote angiogenesis in stem cell-mediated dental pulp regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(4):1158-1164.
[2] HAN Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Guiding Lineage Specific Differentiation of SHED for Target Tissue/Organ Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(5):518-534.
[3] SABBAGH J, GHASSIBE-SABBAGH M, FAYYAD-KAZAN M, et al. Differences in osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation potential of DPSCs and SHED. J Dent. 2020;101:103413.
[4] ROSA V, ZHANG Z, GRANDE RH, et al. Dental pulp tissue engineering in full-length human root canals. J Dent Res. 2013;92(11):970-975.
[5] SUI B, CHEN C, KOU X, et al. Pulp Stem Cell-Mediated Functional Pulp Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2019;98(1):27-35.
[6] 李彩玉.FGF2对人乳牙牙髓干细胞成牙本质向分化能力影响的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2020.
[7] SUN X, MAO Y, LIU B, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Enhance 3D-Printed Scaffold Functions and Promote Alveolar Bone Defect Repair by Enhancing Angiogenesis. J Pers Med. 2023;13(2):180.
[8] ZHANG N, XU L, SONG H, et al. Tracking of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Labeled with Molday ION Rhodamine-B during Periodontal Bone Regeneration in Rats. Int J Stem Cells. 2023;16(1):93-107.
[9] WEI J, SONG Y, DU Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate adult bone loss in mice through promoting osteogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(4):455-466.
[10] MA S, JIANG Y, QIAN Y, et al. The Emerging Biological Functions of Exosomes from Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2023;25(2):53-64.
[11] WANG T, ZHOU Y, ZHANG W, et al. Exosomes and exosome composite scaffolds in periodontal tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;11:1287714.
[12] SUN Y, LIU J, XU Z, et al. Matrix stiffness regulates myocardial differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;13(2):2231-2250.
[13] SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One. 2006; 1(1):e79.
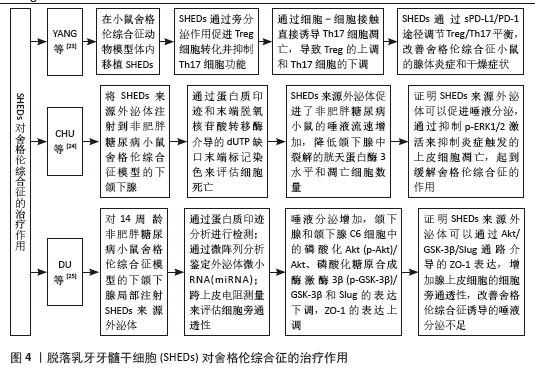
[14] YANG X, MA Y, GUO W, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an alternative cell source in bio-root regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(9):2694-2711.
[15] 张晓月,赵卿,王小聪,等.牙源性干细胞在生物牙根中的应用进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(8):502-504.
[16] GAO P, KAJIYA M, MOTOIKE S, et al. Application of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in periodontal regeneration: Opportunities and challenges. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2024;60:95-108.
[17] 陈宁馨,赖光云,汪俊.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞在口腔颌面部组织再生及免疫调节中应用的研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2021,14(2):220-224.
[18] RASHEED Z, AKHTAR N, HAQQI TM. Advanced glycation end products induce the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 by receptor for advanced glycation end product-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50(5):838-851.
[19] OGASAWARA N, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(6):831-841.
[20] 何睿.脱落人乳牙牙髓干细胞及其衍生物对大鼠颞下颌骨关节炎软骨退变转归的作用研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2022.
[21] LUO P, JIANG C, JI P, et al. Exosomes of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an anti-inflammatory agent in temporomandibular joint chondrocytes via miR-100-5p/mTOR. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):216.
[22] MUHAMMAD SA, NORDIN N, HUSSIN P, et al. Protective effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth derived conditioned medium on osteoarthritic chondrocytes. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0238449.
[23] YANG N, LIU X, CHEN X, et al. Stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth transplantation ameliorates Sjögren’s syndrome by secreting soluble PD-L1. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(5): 1043-1055.
[24] CHU WX, DING C, DU ZH, et al. SHED-exos promote saliva secretion by suppressing p-ERK1/2-mediated apoptosis in glandular cells. Oral Dis. 2024;30(5):3066-3080.
[25] DU Z, WEI P, JIANG N, et al. SHED-derived exosomes ameliorate hyposalivation caused by Sjögren’s syndrome via Akt/GSK-3β/Slug-mediated ZO-1 expression. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023;136(21):2596-2608.
[26] 周绍兰,梁燕,袁媛园.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞在神经系统疾病的应用及研究进展[J].疑难病杂志,2023,22(3):324-327.
[27] 张军伟,郝晓宁,杨晓慧,等.磁共振 SWI 技术在急性脊髓损伤中 的应用及对神经功能的评价[J].疑难病杂志,2022,21( 5): 492- 496.
[28] ALIDOUST L, AKHOONDIAN M, ATEFI AH, et al. Stem cell-conditioned medium is a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114543.
[29] CHEN YR, LAI PL, CHIEN Y, et al. Improvement of Impaired Motor Functions by Human Dental Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Stem Cell-Derived Factors in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3807.
[30] GUGLIANDOLO A, MAZZON E. Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: An Intriguing Approach for Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 23(1):456.
[31] ASADI-GOLSHAN R, RAZBAN V, MIRZAEI E, et al. Efficacy of dental pulp-derived stem cells conditioned medium loaded in collagen hydrogel in spinal cord injury in rats: Stereological evidence. J Chem Neuroanat. 2021;116:101978.
[32] LIU Y, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Conditioned Medium From the Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain in a Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation Model. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:745020.
[33] LUO L, HE Y, JIN L, et al. Application of bioactive hydrogels combined with dental pulp stem cells for the repair of large gap peripheral nerve injuries. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):638-654.
[34] YUNIARTHA R, YAMAZA T, SONODA S, et al. Cholangiogenic potential of human deciduous pulp stem cell-converted hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):57.
[35] DAL NE, AFAGH A, KANIT N, et al. TGF-β1 promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing REELIN expression. Gene. 2020;724:143923.
[36] XIONG X, GAO C, MENG X, et al. Research progress in stem cell therapy for Wilson disease. Regen Ther. 2024;27:73-82.
[37] ZHOU YK, ZHU LS, HUANG HM, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by protecting hepatocytes from apoptosis. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(12):1623-1639.
[38] MUTO H, ITO T, TANAKA T, et al. Conditioned medium from stem cells derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates NASH via the Gut-Liver axis. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):18778.
[39] WU M, LIU X, LI Z, et al. SHED aggregate exosomes shuttled miR-26a promote angiogenesis in pulp regeneration via TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signalling. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7): e13074.
[40] LIU P, ZHANG Q, MI J, et al. Exosomes derived from stem cells of human deciduous exfoliated teeth inhibit angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro via the transfer of miR-100-5p and miR-1246. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):89.
[41] QIU X, LIU J, ZHENG C, et al. Exosomes released from educated mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing via promoting angiogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(8):e12830.
[42] HATTORI Y, KIM H, TSUBOI N, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth in Models of Acute Kidney Injury. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140121.
[43] RAO N, WANG X, XIE J, et al. Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorate Diabetic Nephropathy In Vivo and In Vitro by Inhibiting Advanced Glycation End Product-Activated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2751475.
[44] 蒋志寒,徐凌.人脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗非口腔疾病的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(24):3067-3073.
[45] ISHIKAWA J, TAKAHASHI N, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2016;83:210-219.
[46] TYAGI A, SHETTY J, SHETTY S, et al. Antibacterial and Immunomodulatory Properties of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth: An In Vitro Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023; 16(Suppl 3):240-246.
[47] 朱凌肃.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗小鼠自身免疫性肝炎的研究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2019.
[48] LI W, JIAO X, SONG J, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth infusion into patients with type 2 diabetes depends on basal lipid levels and islet function. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(7):956-967.
[49] KANAFI MM, BHONDE RR. Diverse Approaches toward Application of Dental Pulp Stem Cells from Human Permanent and Deciduous Teeth in the Treatment of Diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(1):e210323214822.
[50] LIANG TY, LU LH, TANG SY, et al. Current status and prospects of basic research and clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome. World J Stem Cells. 2023;15(4):150-164.
[51] HERRMAN H, PATEL V, KIELING C, et al. Time for united action on depression: a Lancet-World Psychiatric Association Commission. Lancet. 2022;399(10328):957-1022.
[52] 沈钊舟.人脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗重度抑郁症的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2022. |