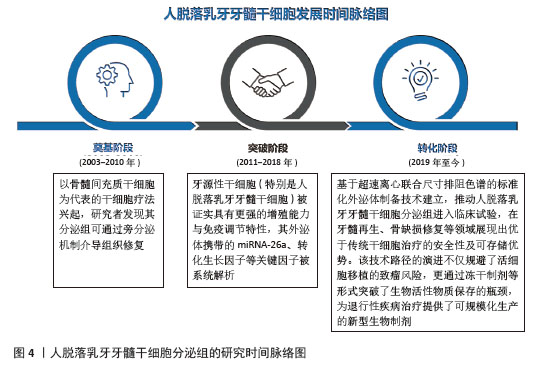
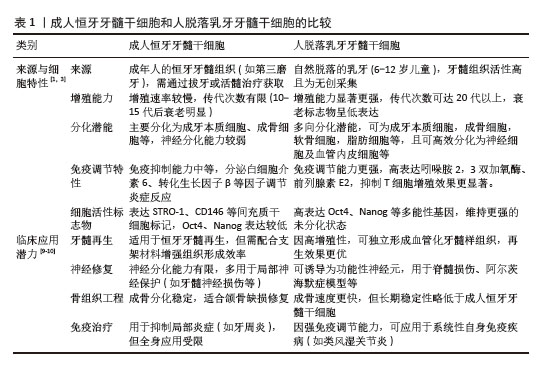
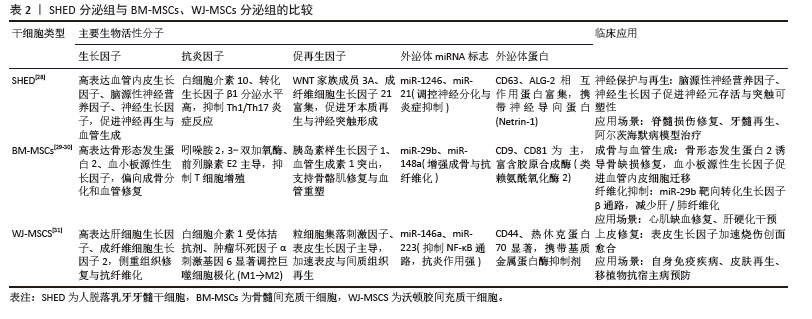
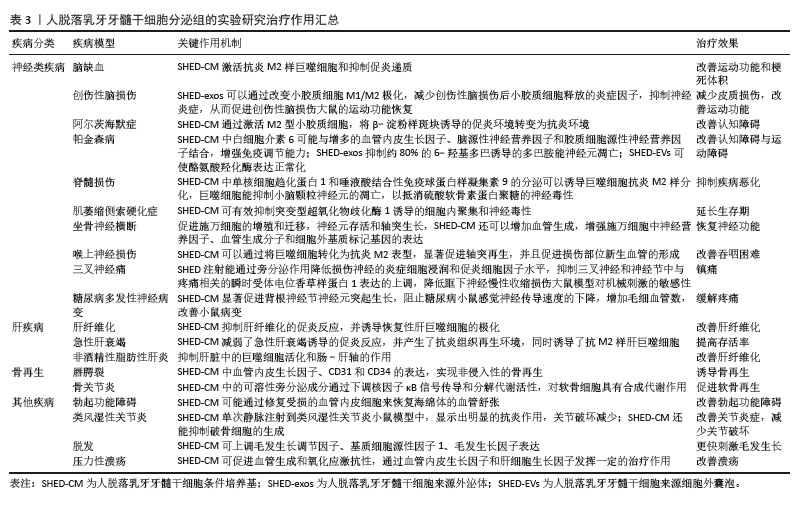
[1] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, CHAILAKHYAN RK, LATSINIK NV, et al. Stromal cells responsible for transferring the microenvironment of the hemopoietic tissues. Cloning in vitro and retransplantation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974;17(4):331-340.
[2] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[3] CHALISSERRY EP, NAM SY, PARK SH, et al. Therapeutic potential of dental stem cells. J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417702531.
[4] 万然,史旭,刘京松,等.间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):1088-1095.
[5] MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, ZHAO M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5807-5812.
[6] REN H, SANG Y, ZHANG F, et al. Comparative Analysis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord, Dental Pulp, and Menstrual Blood as Sources for Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3516574.
[7] BHANDI S, ALKAHTANI A, MASHYAKHY M, et al. Effect of Ascorbic Acid on Differentiation, Secretome and Stemness of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Tooth (SHEDs). J Pers Med. 2021;11(7):589.
[8] NAKAMURA S, YAMADA Y, KATAGIRI W, et al. Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J Endod. 2009;35(11):1536-1542.
[9] HUANG GT, SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, et al. The hidden treasure in apical papilla: the potential role in pulp/dentin regeneration and bioroot engineering. J Endod. 2008; 34(6):645-651.
[10] YAMAZA T, KENTARO A, CHEN C, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):5.
[11] GIORDANO G, LA MONACA G, ANNIBALI S, et al. Stem cells from oral niches: a review. Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2011;2(1-2):3-8.
[12] ANOOP M, DATTA I. Stem Cells Derived from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth (SHED) in Neuronal Disorders: A Review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(5):535-550.
[13] NOURBAKHSH N, SOLEIMANI M, TAGHIPOUR Z, et al. Induced in vitro differentiation of neural-like cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth-derived stem cells. Int J Dev Biol. 2011;55(2):189-195.
[14] NUTI N, CORALLO C, CHAN BM, et al. Multipotent Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells: a Literature Review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2016;12(5):511-523.
[15] KERKIS I, AMBROSIO CE, KERKIS A, et al. Early transplantation of human immature dental pulp stem cells from baby teeth to golden retriever muscular dystrophy (GRMD) dogs: Local or systemic? J Transl Med. 2008;6:35.
[16] GLASSBERG MK, MINKIEWICZ J, TOONKEL RL, et al. Allogeneic Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Intravenous Delivery (AETHER): A Phase I Safety Clinical Trial. Chest. 2017;151(5):971-981.
[17] LI JK, YANG C, SU Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Acute Kidney Injury. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 684496.
[18] BERMUDEZ MA, SENDON-LAGO J, EIRO N, et al. Corneal epithelial wound healing and bactericidal effect of conditioned medium from human uterine cervical stem cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(2): 983-992.
[19] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852.
[20] 李佳林,张耀东,娄艳茹,等.间充质干细胞分泌组发挥作用的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(7):1512-1522.
[21] KATAGIRI W, OSUGI M, KAWAI T, et al. Novel cell-free regeneration of bone using stem cell-derived growth factors. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(4):1009-1016.
[22] LEE Y, EL ANDALOUSSI S, WOOD MJ. Exosomes and microvesicles: extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy. Hum Mol Genet. 2012; 21(R1):R125-134.
[23] RAPOSO G, STOORVOGEL W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.
[24] KIM KO, CHOI SM, KIM HS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretome and microvesicles as a cell-free therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;10:93-101.
[25] SHIN S, LEE J, KWON Y, et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretome from Adipose, Bone Marrow, Placenta and Wharton’s Jelly. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(2):845.
[26] KONALA VBR, BHONDE R, PAL R. Secretome studies of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) isolated from three tissue sources reveal subtle differences in potency. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020;56(9):689-700.
[27] INOUE T, SUGIYAMA M, HATTORI H, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous tooth-derived conditioned medium enhance recovery of focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(1-2):24-29.
[28] NICOLA F, MARQUES MR, ODORCYK F, et al. Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Modulate Early Astrocyte Response after Spinal Cord Contusion. Mol Neurobiol. 2019; 56(1):748-760.
[29] MARTINO MM, TORTELLI F, MOCHIZUKI M, et al. Engineering the growth factor microenvironment with fibronectin domains to promote wound and bone tissue healing. Sci Transl Med. 2011; 3(100):100ra89.
[30] NENG W, SHUANG-YING L, JUN X, et al. A ‘jump-to-coalescence’ mechanism during nanoparticle growth revealed by in situ aberration-corrected transmission electron microscopy observations. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(20):205605.
[31] WANG J, ZHANG XR, HE WF, et al. Research advances on the mechanism of dendritic epidermal T lymphocytes in wound healing. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021;37(3): 296-300.
[32] GUO H, LI B, WU M, et al. Odontogenesis-related developmental microenvironment facilitates deciduous dental pulp stem cell aggregates to revitalize an avulsed tooth. Biomaterials. 2021;279:121223.
[33] WU M, LIU X, LI Z, et al. SHED aggregate exosomes shuttled miR-26a promote angiogenesis in pulp regeneration via TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signalling. Cell Prolif. 2021; 54(7):e13074.
[34] XUAN K, LI B, GUO H, et al. Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(455): eaaf3227.
[35] LAN BY, LIN X, CHEN WJ, et al. Effect of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated exosomes from human dental pulp stem cells combined with stromal cell-derived factor-1 on dental pulp regeneration. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022; 57(1):60-67.
[36] GAO Y, YUAN Z, YUAN X, et al. Bioinspired porous microspheres for sustained hypoxic exosomes release and vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;14: 377-388.
[37] YUAN X, YUAN Z, WANG Y, et al. Vascularized pulp regeneration via injecting simvastatin functionalized GelMA cryogel microspheres loaded with stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Mater Today Bio. 2022;13:100209.
[38] KATAN M, LUFT A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin Neurol. 2018;38(2):208-211.
[39] MASEL BE, DEWITT DS. Traumatic brain injury: a disease process, not an event. J Neurotrauma. 2010;27(8):1529-1540.
[40] KUMAR A, LOANE DJ. Neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury: opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Brain Behav Immun. 2012;26(8):1191-1201.
[41] LI Y, YANG YY, REN JL, et al. Exosomes secreted by stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth contribute to functional recovery after traumatic brain injury by shifting microglia M1/M2 polarization in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):198.
[42] 杨泽若,张燚,胡柳,等.亚洲人阿尔兹海默症miRNA-mRNA网络的生物信息学分析[J].生物信息学,2022,20(1):46-55.
[43] LIU PP, XIE Y, MENG XY, et al. History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2019;4:29.
[44] MITA T, FURUKAWA-HIBI Y, TAKEUCHI H, et al. Conditioned medium from the stem cells of human dental pulp improves cognitive function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2015;293:189-197.
[45] MHYRE TR, BOYD JT, HAMILL RW, et al. Parkinson’s disease. Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:389-455.
[46] ZHANG N, LU X, WU S, et al. Intrastriatal transplantation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth reduces motor defects in Parkinsonian rats. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(5):670-686.
[47] CHEN YR, LAI PL, CHIEN Y, et al. Improvement of Impaired Motor Functions by Human Dental Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Stem Cell-Derived Factors in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3807.
[48] ZIMMER MB, NANTWI K, GOSHGARIAN HG. Effect of spinal cord injury on the respiratory system: basic research and current clinical treatment options. J Spinal Cord Med. 2007; 30(4):319-330.
[49] YIU G, HE Z. Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(8): 617-627.
[50] SAKAI K, YAMAMOTO A, MATSUBARA K, et al. Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(1):80-90.
[51] MATSUBARA K, MATSUSHITA Y, SAKAI K, et al. Secreted ectodomain of sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin-9 and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 promote recovery after rat spinal cord injury by altering macrophage polarity. J Neurosci. 2015;35(6):2452-2464.
[52] ALJABRI A, HALAWANI A, BIN LAJDAM G, et al. The Safety and Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy as an Emerging Therapy for ALS: A Systematic Review of Controlled Clinical Trials. Front Neurol. 2021;12:783122.
[53] UEDA T, ITO T, INDEN M, et al. Stem Cells From Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth-Conditioned Medium (SHED-CM) is a Promising Treatment for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:805379.
[54] WANG J, ZUZZIO K, WALKER CL. Systemic Dental Pulp Stem Cell Secretome Therapy in a Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Brain Sci. 2019;9(7):165.
[55] SUGIMURA-WAKAYAMA Y, KATAGIRI W, OSUGI M, et al. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration by Secretomes of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(22):2687-2699.
[56] TSURUTA T, SAKAI K, WATANABE J, et al. Dental pulp-derived stem cell conditioned medium to regenerate peripheral nerves in a novel animal model of dysphagia. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0208938.
[57] 冯保会,李世亭.原发性三叉神经痛治疗研究进展[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2009,8(3):280-282.
[58] BAI X, ZHANG X, WANG C, et al. Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Attenuate Trigeminal Neuralgia in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2021; 2021:8819884.
[59] ZENKER J, ZIEGLER D, CHRAST R. Novel pathogenic pathways in diabetic neuropathy. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36(8):439-449.
[60] 董荣芳,张铭,郑丹枫,等.糖尿病周围神经病的病理学研究[J].诊断病理学杂志,2015,22(3):133-138.
[61] MIURA-YURA E, TSUNEKAWA S, NARUSE K, et al. Secreted factors from cultured dental pulp stem cells promoted neurite outgrowth of dorsal root ganglion neurons and ameliorated neural functions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Diabetes Investig. 2020;11(1):28-38.
[62] ROEHLEN N, CROUCHET E, BAUMERT TF. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells. 2020;9(4):875.
[63] HIRATA M, ISHIGAMI M, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. Multifaceted Therapeutic Benefits of Factors Derived From Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Mouse Liver Fibrosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10):1416-1424.
[64] ITO T, ISHIGAMI M, MATSUSHITA Y, et al. Secreted Ectodomain of SIGLEC-9 and MCP-1 Synergistically Improve Acute Liver Failure in Rats by Altering Macrophage Polarity. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44043.
[65] MUTO H, ITO T, TANAKA T, et al. Conditioned medium from stem cells derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates NASH via the Gut-Liver axis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):18778.
[66] OMORI M, TSUCHIYA S, HARA K, et al. A new application of cell-free bone regeneration: immobilizing stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth-conditioned medium onto titanium implants using atmospheric pressure plasma treatment. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):124.
[67] HIRAKI T, KUNIMATSU R, NAKAJIMA K, et al. Stem cell-derived conditioned media from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote bone regeneration. Oral Dis. 2020; 26(2):381-390.
[68] MUHAMMAD SA, NORDIN N, HUSSIN P, et al. Protective effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth derived conditioned medium on osteoarthritic chondrocytes. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0238449.
[69] OGASAWARA N, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(6):831-841.
[70] KOGA S, HORIGUCHI Y. Efficacy of a cultured conditioned medium of exfoliated deciduous dental pulp stem cells in erectile dysfunction patients. J Cell Mol Med. 2022; 26(1):195-201.
[71] ISHIKAWA J, TAKAHASHI N, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2016;83:210-219.
[72] GUNAWARDENA TNA, MASOUDIAN Z, RAHMAN MT, et al. Dental derived stem cell conditioned media for hair growth stimulation. PLoS One. 2019;14(5): e0216003.
[73] KATAHIRA Y, MURAKAMI F, INOUE S, et al. Protective effects of conditioned media of immortalized stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth on pressure ulcer formation. Front Immunol. 2023;13:1010700. |