[1] GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1789-1858.
[2] SHIMIZU Y, NTEGE EH, INOUE Y, et al. Optimizing mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles for chronic wound healing: Bioengineering, standardization, and safety. Regen Ther. 2024;26:260-274.
[3] YANAGIUCHI T, KATO T, HIRANO K, et al. Infrapopliteal 3-Vessel Occlusive Disease Is the Only Predictor of Wound Recurrence After Complete Wound Healing via Endovascular Therapy in Patients With Chronic Limb-threatening Ischemia. J J Endovasc Ther. 2025;32(4):999-1008.
[4] SUKMANA BI, MARGIANA R, ALMAJIDI YQ, et al. Supporting wound healing by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) therapy in combination with scaffold, hydrogel, and matrix; State of the art. Pathol Res Pract. 2023;248:154575.
[5] SERRA J, ALVES CPA, BRITO L, et al. Engineering of Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Encoding Minicircles for Angiogenic Ex Vivo Gene Therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2019;30(3):316-329.
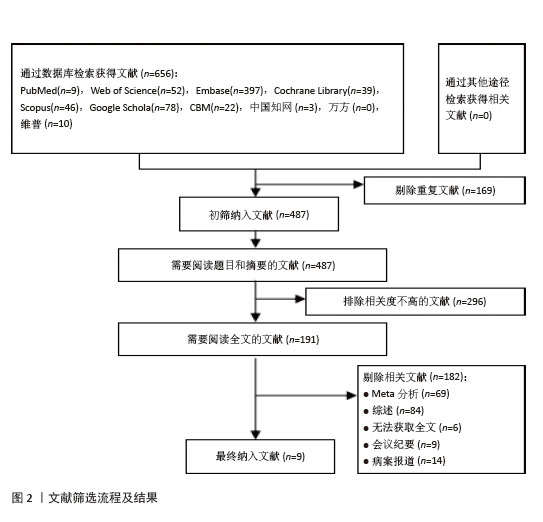
[6] PAGE MJ, MCKENZIE JE, BOSSUYT PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
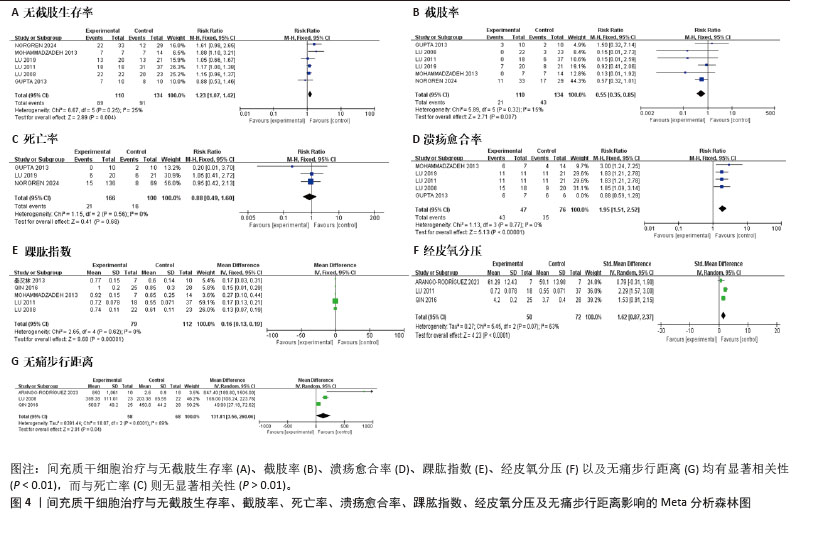
[7] 刘海宁,吴昊,姚灿,等.Meta分析中连续性数据的深度提取方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2017,17(1):117-121.
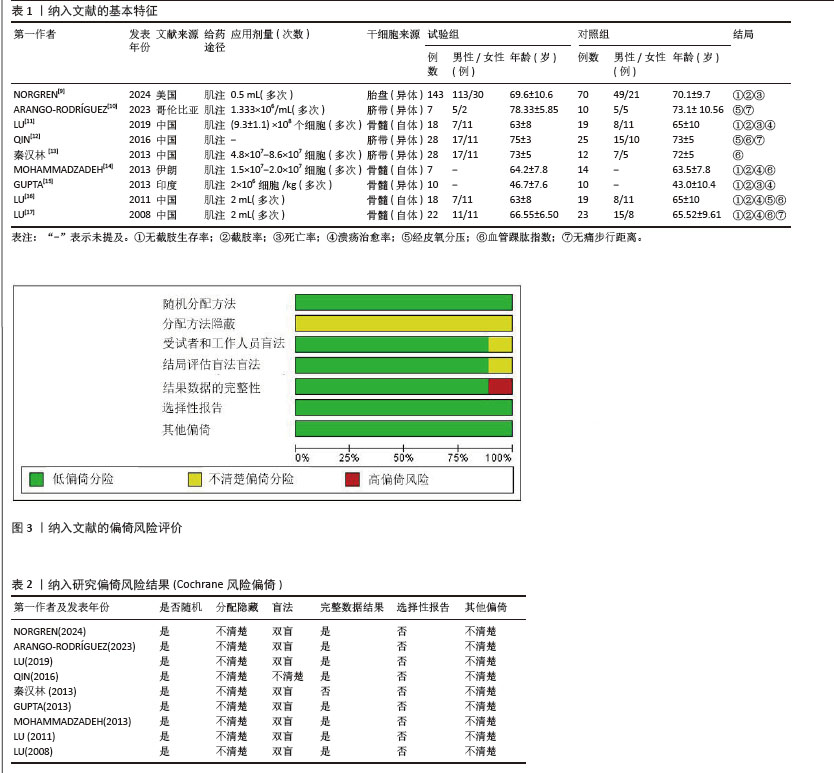
[8] STERNE JAC, SAVOVIĆ J, PAGE MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366:l4898.
[9] NORGREN L, WEISS N, NIKOL S, et al. PACE: randomized, controlled, multicentre, multinational, phase III study of PLX-PAD for critical limb ischaemia in patients unsuitable for revascularization: randomized clinical trial. Br J Surg. 2024;111(2):znad437.
[10] ARANGO-RODRÍGUEZ ML, MATEUS LC, SOSSA CL, et al. A novel therapeutic management for diabetes patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia: comparison of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells versus allogenic Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):221.
[11] LU D, JIANG Y, DENG W, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of BMMSC Compared with BMMNC for Treatment of Critical Limb Ischemia and Foot Ulcer in Patients with Diabetes. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(5):645-652.
[12] QIN HL, ZHU XH, ZHANG B, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation After Angioplasty for Diabetic Foot. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2016;124(8):497-503.
[13] 秦汉林,贺克武,高斌,等.血管成形与脐带干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足:3个月血管造影评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(14):2544-2551.
[14] MOHAMMADZADEH L, SAMEDANIFARD SH, KESHAVARZI A, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of transplanting autologous granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilised peripheral mononuclear cells in diabetic patients with critical limb ischaemia. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013;121(1): 48-53.
[15] GUPTA PK, CHULLIKANA A, PARAKH R, et al. A double blind randomized placebo controlled phase I/II study assessing the safety and efficacy of allogeneic bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell in critical limb ischemia. J Transl Med. 2013; 11:143.
[16] LU D, CHEN B, LIANG Z, et al. Comparison of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells for treatment of diabetic critical limb ischemia and foot ulcer: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;92(1):26-36.
[17] LU D, JIANG Y, LIANG Z, et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic patients with lower limb ischemia. Journal of Medical Colleges of PLA. 2008;23(2):106-115.
[18] LIU Y, WANG M, YU Y, et al. Advances in the study of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells and cardiac cells for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):202.
[19] JALUVKA F, IHNAT P, MADARIC J, et al. Current Status of Cell-Based Therapy in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):8999.
[20] RIGATO M, MONAMI M, FADINI GP. Autologous Cell Therapy for Peripheral Arterial Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Nonrandomized, and Noncontrolled Studies. Circ Res. 2017;120(8):1326-1340.
[21] 王承恩,杨敏,佟小强,等.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗下肢缺血性疾病疗效的Meta分析[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2019, 16(1):21-26.
[22] MCKINNIREY F, HERBERT B, VESEY G, et al. Immune modulation via adipose derived Mesenchymal Stem cells is driven by donor sex in vitro. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12454.
[23] WEI S, WANG W, LI L, et al. Recombinant human epidermal growth factor combined with vacuum sealing drainage for wound healing in Bama pigs. Mil Med Res. 2021; 8(1):18.
[24] SIRPILLA O, SAKEMURA RL, HEFAZI M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells with chimaeric antigen receptors for enhanced immunosuppression. Nat Biomed Eng. 2024;8(4):443-460.
[25] BACAKOVA L, ZARUBOVA J, TRAVNICKOVA M, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(4):1111-1126.
[26] ASSIS-RIBAS T, FORNI MF, WINNISCHOFER SMB, et al. Extracellular matrix dynamics during mesenchymal stem cells differentiation. Dev Biol. 2018;437(2):63-74.
[27] THEODORIDIS K, AGGELIDOU E, VAVILIS T, et al. Hyaline cartilage next generation implants from adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Comparative study on 3D-printed polycaprolactone scaffold patterns. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(2):342-355.
[28] SHI J, ZHAO YC, NIU ZF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles in the treatment of human diseases: Progress and prospect. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(1):49-63.
[29] MAACHA S, SIDAHMED H, JACOB S, et al. Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:4356359.
[30] OSUGI M, KATAGIRI W, YOSHIMI R, et al. Conditioned media from mesenchymal stem cells enhanced bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(13-14):1479-1489.
[31] LALU MM, MCINTYRE L, PUGLIESE C, et al. Safety of cell therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (SafeCell): a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47559.
[32] MOLL G, DRZENIEK N, KAMHIEH-MILZ J, et al. MSC Therapies for COVID-19: Importance of Patient Coagulopathy, Thromboprophylaxis, Cell Product Quality and Mode of Delivery for Treatment Safety and Efficacy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1091.
[33] BARANOVSKII DS, KLABUKOV ID, ARGUCHINSKAYA NV, et al. Adverse events, side effects and complications in mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Stem Cell Investig. 2022;9:7.
[34] CAPLAN H, OLSON SD, KUMAR A, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapeutic Delivery: Translational Challenges to Clinical Application. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1645.
[35] JIANG W, XU J. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(1):e12712.
[36] NAMMIAN P, ASADI-YOUSEFABAD SL, DANESHI S, et al. Comparative analysis of mouse bone marrow and adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells for critical limb ischemia cell therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):58.
[37] WIJNAND JGJ, TERAA M, GREMMELS H, et al. Rationale and design of the SAIL trial for intramuscular injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells in no-option critical limb ischemia. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67(2):656-661.
[38] ZHU Z, ZHANG Q, LIU L, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells’ Cultivation and Treatment of Liver Diseases. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;18(3): 286-298.
[39] EL-NASEERY NI, ELEWA YHA, EL-BEHERY EI, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells restored hematopoiesis by improving radiation induced bone marrow niche remodeling in rats. Ann Anat. 2023;250:152131.
[40] LIU L, YU Y, HOU Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation promotes cutaneous wound healing of severe burned rats. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88348.
[41] LI L, LI J, GUAN H, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in diabetes mellitus and its complications: applications and research advances. Int J Med Sci. 2023; 20(11):1492-1507.
[42] HEO JS, KIM S, YANG CE, et al. Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Key Player in Wound Healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(4):537-548.
[43] ZHANG L, OUYANG P, HE G, et al. Exosomes from microRNA-126 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis by targeting the PIK3R2-mediated PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):2148-2162.
[44] LIU W, YU M, XIE D, et al. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):259.
[45] JIAO YR, CHEN KX, TANG X, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in diabetes and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(4):271.
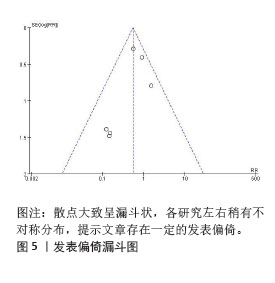
[46] STERNE JA, SUTTON AJ, IOANNIDIS JP, et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d4002. |