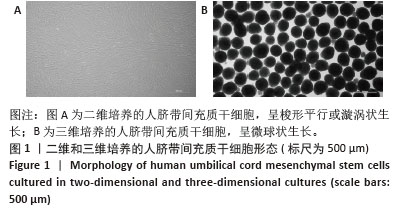
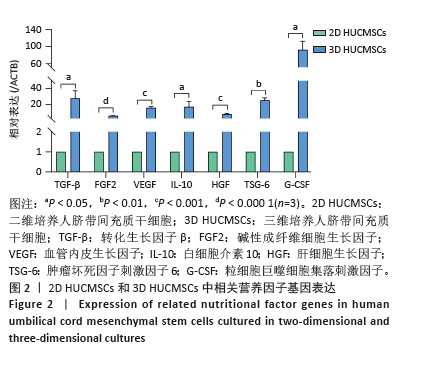
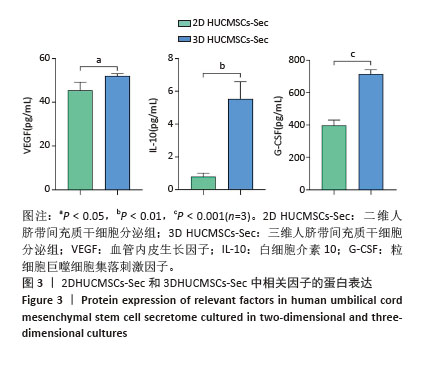
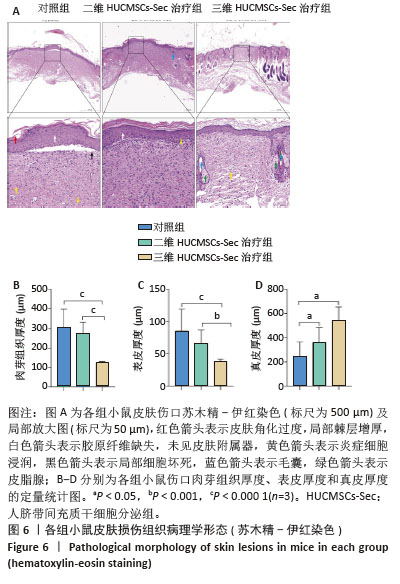
[1] HSU YC, FUCHS E. Building and Maintaining the Skin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022;14(7):a040840.
[2] QI L, ZHANG C, WANG B, et al. Progress in Hydrogels for Skin Wound Repair. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(7):e2100475.
[3] DING JY, CHEN MJ, WU LF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in skin wound healing: roles, opportunities and challenges. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):36.
[4] VAZQUEZ-ZAPIEN GJ, MARTINEZ-CUAZITL A, GRANADOS-JIMENEZ A, et al. Skin wound healing improvement in diabetic mice through FTIR microspectroscopy after implanting pluripotent stem cells. APL Bioeng. 2023;7(1):016109.
[5] LUO R, DAI J, ZHANG J, et al. Accelerated Skin Wound Healing by Electrical Stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(16):e2100557.
[6] SADEGHI-AGHBASH M, RAHIMNEJAD M, ADELI H, et al. Wound Healing: An Overview of Wound Dressings on Health Care. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(9):1079-1093.
[7] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223.
[8] JU C, LIU D. Exosomal microRNAs from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Therapeutic Effect in Wound Healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(5):647-660.
[9] ZHOU C, ZHANG B, YANG Y, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):107.
[10] TERATANI T, KASAHARA N, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretions Enhanced ATP Generation on Isolated Islets during Transplantation. Islets. 2022;14(1):69-81.
[11] LI JY, REN KK, ZHANG WJ, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells and their paracrine factors promote wound healing by inhibiting heat stress-induced skin cell apoptosis and enhancing their proliferation through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):247.
[12] FANG Z, CHEN P, TANG S, et al. Will mesenchymal stem cells be future directions for treating radiation-induced skin injury? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):179.
[13] KOLIMI P, NARALA S, NYAVANANDI D, et al. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells. 2022;11(15):2439.
[14] PITTENGER MF, DISCHER DE, PÉAULT BM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:22.
[15] FUGGLE NR, COOPER C, OREFFO ROC, et al. Alternative and complementary therapies in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(4): 547-560.
[16] YAO H, YUAN X, WU Z, et al. Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of Gelatin/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel-Based Macrophage and MSC Cell-Encapsulated Paracrine System with Potential Application in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1240.
[17] L PK, KANDOI S, MISRA R, et al. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:1-9.
[18] ZHANG C, XIAO J, FA L, et al. Advances in the applications of mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium in ocular diseases. Exp Eye Res. 2023;233:109560.
[19] CHEN W, SUN Y, GU X, et al. Conditioned medium of human bone marrow-derived stem cells promotes tendon-bone healing of the rotator cuff in a rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120714.
[20] ALIDOUST L, AKHOONDIAN M, ATEFI AH, et al. Stem cell-conditioned medium is a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114543.
[21] LI X, ZHANG D, YU Y, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell secretome promotes skin regeneration and rejuvenation: From mechanism to therapeutics. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(4):e13586.
[22] WANG X, WANG Q, YIN P, et al. Secretome of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell maintains skin homeostasis by regulating multiple skin physiological function. Cell Tissue Res. 2023;391(1): 111-125.
[23] SON YH, YANG DH, URICOLI B, et al. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture System for Tendon Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023; 20(4):553-562.
[24] BIAŁKOWSKA K, KOMOROWSKI P, BRYSZEWSKA M, et al. Spheroids as a Type of Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures-Examples of Methods of Preparation and the Most Important Application. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(17):6225.
[25] MAEDA Y, MITSUHARA T, TAKEDA M, et al. Repeated human cranial bone-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improved electrophysiological recovery in a spinal cord injury rat model. Neurosci Lett. 2025;844:138031.
[26] CHENG Y, SONG G. Mesenchymal stem cells and skin injury repair. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021;38(2):387-392.
[27] 程延思危,宋关斌.间充质干细胞与皮肤的损伤修复[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2021,38(2):387-392.
[28] KIM JH, GREEN DS, JU YM, et al. Identification and characterization of stem cell secretome-based recombinant proteins for wound healing applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:954682.
[29] LASOCKA I, JASTRZĘBSKA E, SZULC-DĄBROWSKA L, et al. The effects of graphene and mesenchymal stem cells in cutaneous wound healing and their putative action mechanism. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14: 2281-2299.
[30] LI Z, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Self-Assembled DNA Composite-Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Improved Skin-Wound Repair. Small. 2024;20(31):e2310241.
[31] DAMAYANTI RH, RUSDIANA T, WATHONI N. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for Dermatology Application: A Review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1401-1412.
[32] RAJESH A, JU EDE, OXFORD KA, et al. The mesenchymal stromal cell secretome promotes tissue regeneration and increases macrophage infiltration in acute and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected skin wounds in vivo. Cytotherapy. 2024;26(11):1400-1410.
[33] SUN J, ZHANG Y, SONG X, et al. The Healing Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Radiation-Induced Skin Wounds in Rats. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(1):105-115.
[34] LIN H, CHEN H, ZHAO X, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium-mediated periodontal tissue regeneration. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):456.
[35] LIU G, DAVID BT, TRAWCZYNSKI M, et al. Advances in Pluripotent Stem Cells: History, Mechanisms, Technologies, and Applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(1):3-32.
[36] KIM MH, WU WH, CHOI JH, et al. Galectin-1 from conditioned medium of three-dimensional culture of adipose-derived stem cells accelerates migration and proliferation of human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 2018;26 Suppl 1:S9-S18.
[37] RAJA IS, JANG HJ, KANG MS, et al. Role of Graphene Family Nanomaterials in Skin Wound Healing and Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1351:89-105.
[38] BRUNCHUKOV V, ASTRELINA T, USUPZHANOVA D, et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cells of the Placenta and Their Conditioned Medium in Local Radiation Injuries. Cells. 2020;9(12):2558.
[39] ZHANG G, LI J, WANG D, et al. The mechanisms related to fibroblasts in burn surface. Skin Res Technol. 2023;29(8):e13431.
[40] AKITA S, AKINO K, IMAIZUMI T, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor accelerates and improves second-degree burn wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(5):635-641.
[41] MANDLA S, DAVENPORT HUYER L, RADISIC M. Review: Multimodal bioactive material approaches for wound healing. APL Bioeng. 2018; 2(2):021503.
[42] MŰZES G, SIPOS F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome: A Potential Therapeutic Option for Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(15):2300.
[43] JO H, BRITO S, KWAK BM, et al. Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2410.
[44] KWON JW, SAVITRI C, AN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretomes-enriched alginate/ extracellular matrix hydrogel patch accelerates skin wound healing. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):107.
[45] WERNER S, GROSE R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003;83(3):835-870.
[46] WU S, SUN S, FU W, et al. The Role and Prospects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Repair and Regeneration. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):743.
[47] WANG Y, CAO Z, WEI Q, et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022;147:342-355.
[48] HEYDARI MB, GHANBARI-MOVAHED Z, HEYDARI M, et al. In vitro study of the mesenchymal stem cells-conditional media role in skin wound healing process: A systematic review. Int Wound J. 2022;19(8): 2210-2223.
[49] NIE S, REN C, LIANG X, et al. Supramolecular Hydrogel-Wrapped Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cutaneous Radiation Injury. Cells. 2022;11(19):3089.
|