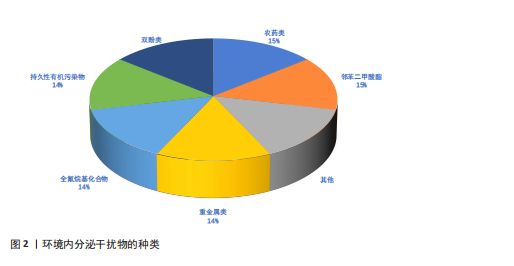
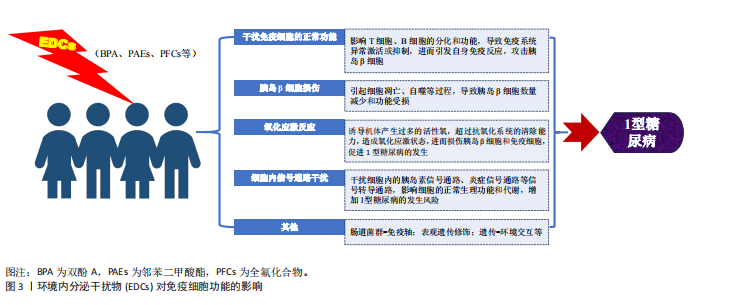
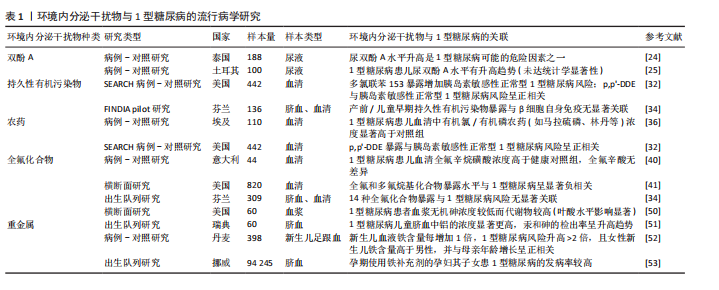
[1] HUANG S, LI F, QUAN C, et al. Intestinal flora: a potential pathogenesis mechanism and treatment strategy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes. 2024;16(1):2423024.
[2] IKEGAMI H, BABAYA N, NOSO S, et al. β-Cell failure in diabetes: Common susceptibility and mechanisms shared between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 2021;12(9):1526-1539.
[3] AHN C, JEUNG EB. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Disease Endpoints. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(6):5342.
[4] LIN S, LI J, YAN X, et al. Maternal pesticide exposure and risk of preterm birth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ Int. 2023;178:108043.
[5] CHEN Y, YANG J, YAO B, et al. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in the environment: Environmental sources, biological effects, remediation techniques, and perspective. Environ Pollut. 2022;310:119918.
[6] TUMU K, VORST K, CURTWILER G, et al. Endocrine modulating chemicals in food packaging: A review of phthalates and bisphenols. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023;22(2):1337-1359.
[7] MAHDAVIANPOUR M, CHAMKOURI N, CHAMKOURI H, et al. Determination of bisphenol a migration from food packaging by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. MethodsX. 2021;8:101415.
[8] PREDIERI B, IUGHEZZI L, BERNASCONI S, et al. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals’ Effects in Children: What We Know and What We Need to Learn? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11899.
[9] DUTTA S, RUDEN DM. Heavy Metals in Umbilical Cord Blood: Effects on Epigenetics and Child Development. Cells. 2024;13(21):1775.
[10] JAIN J, GUPTA N, MATHUR R, et al. A Study on Impact of BPA in the Adipose Tissue Dysfunction (Adiposopathy) in Asian Indian Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2020;35(4):451-457.
[11] ALY HM, IBRAHEEM RB, MAHMOUD RM, et al. The Relationship Between Polychlorinated and Polybrominated Biphenyls and Glycated Hemoglobin among Electronics Workers. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2024;28(2):143-147.
[12] NOWAK K, JABŁONSKA E, RATAJCZAK-WRONA W, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of synthetic endocrine disrupting chemicals on the development and functions of human immune cells. Environ Int. 2019;125:350-364.
[13] CASAS M, GASCON M. Prenatal Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Asthma and Allergic Diseases. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2020;30(4):215-228.
[14] SCHJENKEN JE, GREEN ES, OVERDUIN TS, et al. Endocrine Disruptor Compounds-A Cause of Impaired Immune Tolerance Driving Inflammatory Disorders of Pregnancy? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:607539.
[15] HOWARD SG. Developmental Exposure to Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:513.
[16] ALJADEFF G, LONGHI E, SHOENFELD Y. Bisphenol A: A notorious player in the mosaic of autoimmunity. Autoimmunity. 2018;51(8):370-377.
[17] VIDAL OS, DEEPIKA D, SCHUHMACHER M, et al. EDC-induced mechanisms of immunotoxicity: a systematic review. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2021;51(7):634-652.
[18] ZHANG Q, LI M, WANG P, et al. Integrated analysis reveals the immunotoxicity mechanism of BPs on human lymphocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 2024;423:107872.
[19] GAO L, LUO D, WU D, et al. Effects of mammalian target of rapamycin and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediating autophagy signaling on the balance of Th17/Treg cells during perinatal bisphenol A exposure in female offspring mice. Environ Toxicol. 2022;37(7):1781-1789.
[20] WANG S, DONG Y, ZHAI L, et al. Decreased Treg cells induced by bisphenol A is associated with up-regulation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and Foxp3 DNA methylation in spleen of adolescent mice. Chemosphere. 2024;357:141957.
[21] HUANG RG, Li XB, WANG YY, et al. Endocrine-disrupting chemicals and autoimmune diseases. Environ Res. 2023; 231(Pt 2):116222.
[22] WANG Y, WU H, LI K, et al. Environmental triggers of autoimmunity: The association between bisphenol analogues and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;278:116452.
[23] FISCHER F, ERMER MR, HOWANSKi J, et al. Single and mixture effects of bisphenol A and benzophenone-3 on in vitro T helper cell differentiation. Chem Biol Interact. 2024;395:111011.
[24] TOSIRISUK N, SAKORN N, JANTARAT C, et al. Increased bisphenol A levels in Thai children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr Int. 2022;64(1):e14944.
[25] INCE T, BALCI A, YALÇIN S, et al. Urinary bisphenol-A levels in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018;31(8):829-836.
[26] XU J, HUANG G, NAGY T, et al. Sex-dependent effects of bisphenol A on type 1 diabetes development in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(4):997-1008.
[27] XU J, HUANG G, NAGY T, et al. Bisphenol A alteration of type 1 diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) female mice is dependent on window of exposure. Arch Toxicol. 2019; 93(4):1083-1093.
[28] HONG Y, WANG D, LIN Y, et al. Environmental triggers and future risk of developing autoimmune diseases: Molecular mechanism and network toxicology analysis of bisphenol A. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;288:117352.
[29] BODIN J, KOCBACH BÖLLING A, WENDT A, et al. Exposure to bisphenol A, but not phthalates, increases spontaneous diabetes type 1 development in NOD mice. Toxicol Rep. 2015;2:99-110.
[30] CETKOVIC-CVRLJE M, THINAMANY S, BRUNER KA. Bisphenol A (BPA) aggravates multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes in C57BL/6 mice. J Immunotoxicol. 2017;14:160-168.
[31] AHN C, KANG HS, LEE JH, et al. Bisphenol A and octylphenol exacerbate type 1 diabetes mellitus by disrupting calcium homeostasis in mouse pancreas. Toxicol Lett. 2018;295:162-172.
[32] BRESSON SE, ISOM S, JENSEN ET, et al. Associations between persistent organic pollutants and type 1 diabetes in youth. Environ Int. 2022;163:107175.
[33] DUFOUR P, PIRARD C, LEBRETHON MC, et al. Associations between endocrine disruptor contamination and thyroid hormone homeostasis in Belgian type 1 diabetic children. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2023;96(6):869-881.
[34] SALO HM, KOPONEN J, KIVIRANTA H, et al. No evidence of the role of early chemical exposure in the development of -cell autoimmunity. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019;26:1370-1378.
[35] SINIOJA T, BODIN J, DUBERG D, et al. Exposure to persistent organic pollutants alters the serum metabolome in non-obese diabetic mice. Metabolomics. 2022; 18(11):87.
[36] EL-MORSI DA, RAHMAN RH, ABO-ARAB AA. Pesticides residues in Egyptian diabetic children: A preliminary study. J Clin Toxicol. 2012;2:138-142.
[37] GUPTA HP, JHA RR, AHMAD H, et al. Xenobiotic mediated diabetogenesis: Developmental exposure to dichlorvos or atrazine leads to type 1 or type 2 diabetes in Drosophila. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019; 141:461-474.
[38] CETKOVI-CYRLJE M, OLSON M, SCHINDLER B, et al. Exposure to DDT metabolite p,p’-DDE increases autoimmune type 1 diabetes incidence in NOD mouse model. J Immunotoxicol 2016;13:1-11.
[39] MCGLINCHFY A, SINIOJA T, LAMICHHANE S, et al. Prenatal exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances modulates neonatal serum phospholipids, increasing risk of type 1 diabetes. Environ Int. 2020;143:105935.
[40] PREDIERI B, IUGHEZZI L, GUERRANTI C, et al. High levels of perfluorooctane sulfonate in children at the onset of diabetes. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:234358.
[41] CONWAY B, INNES KE, LONG D. Perfluoroalkyl substances and beta cell deficient diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2016;30(6):993-998.
[42] KERKVLIET NI, STEPPAN LB, VORACHEK W, et al. Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor by TCDD prevents diabetes in NOD mice and increases Foxp3+ T cells in pancreatic lymph nodes. Immunotherapy. 2009;1(4):539-547.
[43] PRASAD SINGH N, NAGARKATTI M, NAGARKATTI P, et al. From Suppressor T cells to Regulatory T cells: How the Journey That Began with the Discovery of the Toxic Effects of TCDD Led to Better Understanding of the Role of AhR in Immunoregulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(21):7849.
[44] MUSTAFA A, HOLLADAY SD, WITONSKY S, et al. A single mid-gestation exposure to TCDD yields a postnatal autoimmune signature, differing by sex, in early geriatric C57BL/6 mice. Toxicology. 2011;290(2-3):156-168.
[45] CASTRO-CORREIA C, CORREIA-SÁ L, NORBERTO S, et al. Phthalates and type 1 diabetes: is there any link? Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018;25(18):17915-17919.
[46] LIN Y, WEI J, Li Y, et al. Developmental exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate impairs endocrine pancreas and leads to long-term adverse effects on glucose homeostasis in the rat. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301:E527-E538.
[47] SUN Y, LIN Q, HUANG Q, et al. Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced apoptosis in rat INS-1 cells is dependent on activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppression of antioxidant protection. J Cell Mol Med. 2015;19(3):581-594.
[48] LOURENÇO AC, GALBIATI V, CORTI D, et al. The plasticizer dibutyl phthalate (DBP) potentiates chemical allergen-induced THP-1 activation. Toxicol in Vitro. 2015;29(8):2001-2008.
[49] WU Y, LI J, YAN B, et al. Oral exposure to dibutyl phthalate exacerbates chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis through oxidative stress in female Wistar rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7: 15469.
[50] LUDVIGSSON J, ANDERSSON-WHITE P, GUERRERO-BOSAGNA C, et al. Toxic metals in cord blood and later development of Type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Dimens. 2019;4(2): 10.15761/PD.1000186.
[51] KYVSGAARD JN, OVERGAARD AJ, THORSEN SU, et al. High Neonatal Blood Iron Content Is Associated with the Risk of Childhood Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2017; 9(11):1221.
[52] GRAU-PÉREZ M, KUO CC, SPRATLEN M, et al. The Association of Arsenic Exposure and Metabolism With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Youth: The SEARCH Case-Control Study. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):46-53.
[53] STØRDAL K, MCARDLE HJ, HAYES H, et al. Prenatal iron exposure and childhood type 1 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9067.
[54] CHEN YW, HUANG CF, YANG CY, et al. Inorganic mercury causes pancreatic beta-cell death via the oxidative stress-induced apoptotic and necrotic pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;243(3): 323-331.
[55] RAMDAS M, SHARMA S, KAUL D, et al. Possible role of miR-2909 RNomics in arsenic mediated pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018; 50:263-267.
|