中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5844-5858.doi: 10.12307/2026.193
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
转录因子EB介导自噬溶酶体通路改善阿尔茨海默病
胡亚琳,黄凤琴,杨伯银,罗兴梅
- 贵州医科大学附属医院,贵州省贵阳市 550004
-
收稿日期:2025-07-04接受日期:2025-08-25出版日期:2026-08-08发布日期:2025-12-27 -
通讯作者:罗兴梅,博士,主任医师,硕士生导师,贵州医科大学附属医院,贵州省贵阳市 550004 -
作者简介:胡亚琳,女,1999年生,贵州省毕节市人,汉族,硕士在读,主要从事认知功能障碍研究。 -
基金资助:贵州省科技计划项目(黔科合基础-ZK[2024]一般225),项目负责人:罗兴梅;国家自然科学基金培养项目(gyfynsfc[2023]-46),项目负责人:罗兴梅;贵州医科大学附属医院博士科研基金项目(gyfybsky-2023-28),项目负责人:罗兴梅
Transcription factor EB improves Alzheimer’s disease via the autophagy-lysosome pathway
Hu Yalin, Huang Fengqin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei
- Guizhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-07-04Accepted:2025-08-25Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-27 -
Contact:Luo Xingmei, PhD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Guizhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Hu Yalin, MS candidate, Guizhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. ZK[2024]General 225 (to LXM); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. gyfynsfc[2023]-46 (to LXM); Doctoral Research Fund Project of Guizhou Medical University Affiliated Hospital, No. gyfybsky-2023-28 (to LXM)
摘要:
文题释义:
哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1:是由哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白激酶核心亚基、雷帕霉素靶蛋白调节相关蛋白、哺乳动物致死SEC13蛋白8等组成的营养感应复合物,是转录因子EB的核心负调控因子,在阿尔茨海默病中呈现病理性过度激活。
神经纤维缠结:是阿尔茨海默病特征性病理结构,由过度磷酸化Tau蛋白丧失微管结合能力后通过β-折叠堆叠形成纤维并在神经元内聚集形成的双股螺旋纤维,其密度与认知衰退显著相关。激活转录因子EB可上调自噬受体p62,促进过度磷酸化Tau蛋白经自噬溶酶体降解,以达到神经保护作用。
背景:研究证实,转录因子EB及其依赖的自噬溶酶体通路在包括阿尔茨海默病在内的多种神经退行性疾病的发展中发挥作用。
目的:总结转录因子EB介导自噬溶酶体通路在阿尔茨海默病中的作用。
方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方、维普数据库中的相关文献,检索时限为各数据库建库至2025年1月,英文检索词为“Alzheimer Disease,AD,Transcription Factor EB,TFEB,Autophagy-lysosome Pathway,Autophagy,Lysosomes,Amyloid beta,Aβ,Tau,Tau protein”,中文检索词为“阿尔茨海默病,转录因子EB,自噬溶酶体,自噬,溶酶体,β-淀粉样蛋白,Tau”;同时手动补充检索相关综述的参考文献及灰色文献,最终纳入100篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:β-淀粉样蛋白沉积和Tau蛋白磷酸化是阿尔茨海默病的关键病理特征。自噬溶酶体通路异常会促进β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau等神经毒性蛋白聚集体的形成,引起以认知功能障碍和精神行为异常为主的阿尔茨海默病临床表现。转录因子EB是自噬溶酶体途径的主要调节因子,它调控着许多自噬相关基因的转录及溶酶体的生物发生。转录因子EB进入细胞核后通过上调自噬溶酶体通路相关基因表达清除β-淀粉样蛋白及Tau,显著减轻神经元毒性,因此,通过靶向转录因子EB影响自噬溶酶体生物活性,从而改善阿尔茨海默病病理及行为缺陷受到越来越多的关注,例如通过药物干预及非药物干预激活转录因子EB,减少β-淀粉样蛋白沉积及Tau蛋白磷酸化,改善阿尔茨海默病认知障碍。但转录因子EB持续激活有诱发溶酶体贮积症等风险,目前递送系统颅内靶向效率不足,未来需开发病理微环境响应型载体及联合疗法,以实现精准干预。
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-8396-9870 (胡亚琳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
胡亚琳, 黄凤琴, 杨伯银, 罗兴梅. 转录因子EB介导自噬溶酶体通路改善阿尔茨海默病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(22): 5844-5858.
Hu Yalin, Huang Fengqin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei. Transcription factor EB improves Alzheimer’s disease via the autophagy-lysosome pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5844-5858.
2.2 转录因子EB
2.2.1 转录因子EB结构特点与功能 亮氨酸拉链转录因子小眼畸形相关转录因子/转录因子E家族负责调控维持大脑功能的各种关键过程,包括自噬-溶酶体途径、脂质分解和线粒体稳态等。在哺乳动物中,小眼畸形相关转录因子/转录因子E家族成员包括转录因子EB、转录因子E3、转录因子EC和小眼畸形相关转录因子,其中转录因子EB被认为是自噬和溶酶体生物发生的主调控因子,它的核转位可以触发众多参与调控这一途径的基因转录[10]。转录因子EB主要包含4个结构域:即DNA结合碱性结构域、螺旋-环-螺旋结构域、亮氨酸拉链结构域、反式激活结构域,其中螺旋-环-螺旋构域和亮氨酸拉链结构域允许转录因子EB与其他含有相同结构域的蛋白质二聚化,从而激活结构域以实现上游调节[11]。转录因子EB游走在细胞核与溶酶体之间以调节细胞代谢,在营养充足时,磷酸化的转录因子EB被胞质伴侣14-3-3蛋白隔离,以非活性形式存在于细胞质中;而在营养缺乏、氧化应激或病原体入侵等刺激时,转录因子EB发生去磷酸化,以同源或异源二聚体转录因子EB的形式进入细胞核,并与启动子内的协调溶酶体表达和调节元件结合,发生液-液相分离,形成凝结物,中介复合物被招募到凝结物中,以诱导自噬和溶酶体相关基因的转录[12]。
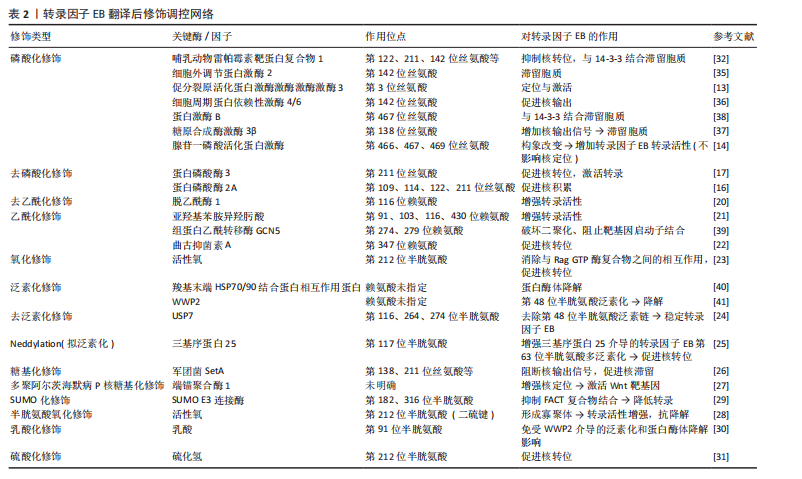
2.2.2 翻译后修饰对转录因子EB的调节 转录因子EB的调控机制目前并未完全明确,多项研究表明可能与转录因子EB发生翻译后修饰有关,如磷酸化、乙酰化、泛素化、糖基化、半胱氨酸氧化、活性氧氧化、小泛素相关修饰物(SUMO)化及乳酸化等[11]。
(1)激活型修饰转录因子EB的磷酸化修饰:决定转录因子EB核易位的主要应激反应中心是丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,有研究通过自噬调控模型发现,促分裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶激酶激酶3在哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1的上游可以通过直接物理作用介导转录因子EB的第3位丝氨酸位点磷酸化,从而实现转录因子EB与哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1-Rag GTP酶复合物-调节器复合物相互作用,对转录因子EB定位和激活起到作用[13]。部分激酶对于转录因子EB具有正向调控作用,比如,PAQUETTE等[14]发现腺苷一磷酸活化蛋白激酶可磷酸化转录因子EB 上第466/467/469位丝氨酸位点,通过构象改变使转录因子EB具有转录活性,同时不影响其核定位。PP2是一种调节蛋白代谢的蛋白磷酸酶,包括蛋白磷酸酶2A和蛋白磷酸酶3,它们利用催化亚基和调节亚基之间的组合、相互作用来实现底物特异性[15]。在近期研究中发现,亚砷酸钠可降低转录因子EB-第211位丝氨酸磷酸化导致其核积累,而蛋白磷酸酶2A磷酸酶的催化抑制或耗竭足以防止转录因子EB-第211位丝氨酸响应亚砷酸盐而去磷酸化,并且通过质谱分析发现蛋白磷酸酶2A使转录因子EB上第109/114/122/211位丝氨酸去磷酸化,确定了一种通过刺激蛋白磷酸酶2A而不抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白来促进转录因子EB激活的新机制[16]。除了蛋白磷酸酶2A以外,还有研究表明蛋白磷酸酶3在转录因子EB的调节过程中也起到了正向调节的作用,比如在经蛋白磷酸酶3抑制剂处理的运动神经元变性模型中,转录因子EB的第142 位点去磷酸化明显被抑制,转录因子EB核易位减少[17]。进一步研究还发现,蛋白磷酸酶3C还可通过Ca2+- SM阿尔茨海默病特异性E3泛素蛋白连接酶1-蛋白磷酸酶3通路或黏脂蛋白1-Ca2+-蛋
白磷酸酶3通路去磷酸化转录因子EB上第211位丝氨酸位点,以促进转录因子EB核输入[18-19]。
转录因子EB的乙酰化修饰:转录因子EB乙酰化是近年来被提出的一种新型翻译后修饰。最初,BAO等[20]发现脱乙酰酶1(组蛋白脱乙酰酶)通过与转录因子EB免疫复合物相互作用,去乙酰化转录因子EB第116位赖氨酸位点来增强其转录活性,从而增强溶酶体功能并促进β-淀粉样蛋白降解,显著减少淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1转基因小鼠脑内淀粉样蛋白斑块。但在随后的研究中发现,在被亚羟基苯胺异羟肟酸(组蛋白脱乙酰酶抑制剂)处理后的细胞中可以观察到增强的转录因子EB乙酰化,促进转录因子EB转录活性和溶酶体功能,这与脱乙酰酶1效应相悖,这可能源于亚羟基苯胺异羟肟酸诱导多位点联合乙酰化(如第91/103/116/430位赖氨酸)的协同效应,该功能超越了脱乙酰酶1对单一第116位赖氨酸位点的去乙酰化调控,并且脱乙酰酶1属于Ⅲ类组蛋白脱乙酰酶,不在其抑制范围内[21]。这些相互矛盾的研究都表明,在自噬溶酶体生物发生过程中,转录因子EB乙酰化是转录因子EB中一种新型且重要的翻译后修饰,不同的细胞内或环境线索可能会刺激不同的乙酰转移酶来控制转录因子EB活性,但没有进一步揭示转录因子EB的乙酰化/去乙酰化是依赖于还是独立于溶酶体生物发生过程中的转录因子EB磷酸化/去磷酸化。后续研究证据显示,经曲古抑菌素A处理后,哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1及糖原合成酶激酶-3β介导的转录因子EB磷酸化状态虽未改变,但仍可诱导转录因子EB的第347位赖氨酸位点乙酰化,促进其核转位并激活溶酶体生物发生[22],表明乙酰化是一种独立于去磷酸化的新型修饰机制,通过直接驱动转录因子EB核易位及下游功能发挥作用。
转录因子EB的氧化修饰:活性氧是细胞内产生的具有氧化活性的化学物质,关于活性氧调节转录因子EB活性的机制目前并不明确,可能与直接氧化和间接通路有关。WANG等[23]发现活性氧可直接氧化转录因子EB的第212位半胱氨酸残基(人类转录因子EB中唯一存在的半胱氨酸残基),进而消除转录因子EB与Rag GTP酶复合物之间的相互作用,促进转录因子EB进入细胞核参与相关自噬溶酶体通路基因转录。活性氧可以直接特异性激活溶酶体黏脂蛋白1通道,触发Ca2+释放,经蛋白磷酸酶3去磷酸化转录因子EB-第211位丝氨酸,增强转录因子EB转录活性[19]。
转录因子EB的泛素化修饰:由于核蛋白酶体的存在,像羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白这样的E3连接酶可同时定位于细胞质和细胞核,表明转录因子EB的降解可能不仅发生在细胞质中,也可能发生在细胞核内。最近研究发现,泛素特异性蛋白酶7对维持胞核和胞质区室中转录因子EB稳定性方面具有关键作用,它通过特异性去除转录因子EB赖氨酸残基(第116/264/274位赖氨酸)上的第48位赖氨酸连接的多聚泛素化信号保护转录因子EB免受蛋白酶体降解[24]。拟泛素化Neddylation是一种类似于泛素化的翻译后修饰,由E2酶泛素结合酶12介导神经前体细胞表达发育下调蛋白8转移至靶蛋白,如E3泛素连接酶三基序蛋白25的第117位赖氨酸位点。在最新的研究中发现,三基序蛋白25的拟泛素化修饰不仅减少了其RING结构域的空间位阻,增加它与转录因子EB的相互作用,促进转录因子EB上第63位赖氨酸-多泛素化,从而促进转录因子EB核转位和自噬相关基因的转录[25]。
转录因子EB的糖基化修饰:相关研究发现,嗜肺军团菌效应蛋白SetA利用其葡萄糖基转移酶活性来糖基化转录因子EB上多个丝氨酸/苏氨酸位点(如第138/195/196/203位丝氨酸和第201/208位苏氨酸),导致转录因子EB出现强烈核易位,以哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1非依赖方式引起转录因子EB的强烈核富集,该机制包括:SetA在转录因子EB的第211位丝氨酸位点附近的葡萄糖基化破坏转录因子EB与14-3-3蛋白之间的结合,解除胞质滞留,同时在第138位丝氨酸位点的葡萄糖基化还破坏了转录因子EB核输出的信号,增加核保留,这是嗜肺军团菌除哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1信号转导外的另一种通过激活自噬等代谢途径获取宿主营养物质的替代策略[26]。此外,在过表达端锚聚合酶1的HeLa细胞中, 端锚聚合酶1与转录因子EB相互作用并通过Wnt信号转导对其进行多聚阿尔茨海默病P核糖基化修饰,增加转录因子EB的核定位,特异性增强Wnt靶基因的表达,这可能与溶酶体基因调控机制不同[27]。
转录因子EB的半胱氨酸氧化修饰:哺乳动物的转录因子EB和TFE3具有单个半胱氨酸残基,该残基在应激下被修饰,允许形成分子间二硫键并产生转录活性增加的同源/异源寡聚体。在基础条件下,转录因子EB和TFE3主要以单体/二聚体形式存在,与14-3-3蛋白的结合抑制氧化修饰及寡聚化。在饥饿、营养剥夺等条件下,转录因子EB-第211位丝氨酸和TFE3-第321位丝氨酸去磷酸化并与14-3-3蛋白分离,暴露出单个半胱氨酸残基在活性氧介导下形成分子间二硫键,从而改变蛋白质的四级结构,驱动组装成高转录活性的同源/异源寡聚体,寡聚体在长时间的应激条件下进一步稳定,并显示出更高的抗灭活性[28]。值得注意的是,当第212位半胱氨酸突变时转录因子EB的第211位丝氨酸的磷酸化增加并与14-3-3的结合,但不会影响转录因子EB和Rag GTP酶复合物之间的相互作用或核易位能力[28]。此结果直接反驳既往“活性氧通过破坏Rag GTP酶复合物激活转录因子EB”的假说,这证实第211位丝氨酸磷酸化(失活)与第212位半胱氨酸氧化(活化)构成分子内拮抗开关。
转录因子EB的SUMO化修饰:SUMO化修饰是利用类似于泛素化的缀合系统,将小泛素样修饰物1(SUMO-1)共价连接至转录因子EB保守的KXE序列赖氨酸位点(第182/316位赖氨酸)。早期研究发现,上述位点突变为精氨酸后可在维持二聚化、DNA结合、稳定性及核定位不变的前提下显著增强转录因子EB转录活性,提示SUMO化修饰对于转录因子EB活性具有正向调控作用[29]。
转录因子EB的乳酸化修饰: 乳酸可以激活或抑制不同细胞的自噬。乳酸化(赖氨酸与乳酸的共价修饰)是最近发现的翻译后修饰。HUANG等[30]实验发现,乳酸将转录因子EB唯一的乳酸化位点第91赖氨酸突变为精氨酸或谷氨酰胺后,可保护转录因子EB免受E3泛素连接酶WWP2介导的泛素化和蛋白酶体降解的影响,导致溶酶体活性和自噬通量增加。
转录因子EB的硫酸化修饰:硫化氢主要由心血管组织中的胱硫醚γ裂解酶产生,是动脉粥样硬化中的保护性气体递质。CHEN等[31]在过表达或敲除胱硫醚γ裂解酶进行基因组修饰的人主动脉平滑肌细胞中发现,胱硫醚γ裂解酶-硫化氢可对转录因子EB的第212位半胱氨酸位点进行硫酸化修饰,以激活转录因子EB核易位核转录活性,调节自噬体形成、溶酶体生物发生和胆固醇代谢相关基因表达。
(2)抑制型修饰
转录因子EB的磷酸化修饰:哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1为调控转录因子EB磷酸化和核易位的关键激酶。在营养充足时,Rag GTP酶复合物活化后将哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1和转录因子EB招募至溶酶体表面,随后磷酸化转录因子EB上的第122/211/142位丝氨酸等位点,抑制转录因子EB活性并阻止核易位[32]。转录因子EB上第211位丝氨酸位点的磷酸化是与14-3-3蛋白结合位点的关键位点,目的是遮蔽核定位序列,导致转录因子EB失活并滞留胞质[33]。虽然有研究表明转录因子EB上第122位丝氨酸位点不涉及
14-3-3蛋白结合,但转录因子EB去磷酸化对于哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1抑制后转录因子EB核定位至关重要,这可能与调节蛋白相互作用或核转运有关,并且第122、211位丝氨酸位丝氨酸同步去磷酸化可实现转录因子EB最大的核富集[34]。在营养富足时,除了哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1,细胞外调节蛋白激酶2也可以磷酸化转录因子EB的第142位丝氨酸位点,导致其滞留胞质,这一点可在抑制细胞外调节蛋白激酶2后促进转录因子EB核易位得到证实[35]。同时也有实验表明,细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4/6通过磷酸化细胞核中转录因子EB上第142位丝氨酸位点促进其核输出;利用特异性抑制剂可抑制转录因子EB核输出,从而使HeLa细胞的溶酶体生物发生在细胞周期的S和G2/M期增加[36]。除此之外, 糖原合成酶激酶3β作为在进化上非常保守的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,有相关研究表明转录因子EB上第142位丝氨酸位点被细胞外调节蛋白激酶2和哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1磷酸化的同时,可引发糖原合成酶激酶3β磷酸化第138位丝氨酸位点,双重磷酸化增加了转录因子EB的核出口信号,导致转录因子EB被滞留胞质中,而葡萄糖限制可能通过哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白C2-蛋白激酶B通路抑制糖原合成酶激酶3β,促进转录因子EB核积累[37]。有趣的是,有研究使用体外蛋白激酶B测定发现,蛋白激酶B对转录因子EB上第467位丝氨酸位点磷酸化后可增强其与14-3-3蛋白的共定位和相互作用,促进转录因子EB细胞质保留[38],这与前述报道对转录因子EB 第467位丝氨酸位点的调控作用相互矛盾,可能与腺苷一磷酸活化蛋白激酶和蛋白激酶B在不同层次结构中磷酸化C端区域有关。由此可看出,大多数激酶对于转录因子EB磷酸化的调控多为抑制其活性,致使自噬和溶酶体相关基因转录减少。
转录因子EB的非磷酸化修饰:组蛋白乙酰转移酶 GCN5作为特异性乙酰转移酶,通过乙酰化转录因子EB的第274/ 279位赖氨酸位点破坏其二聚化以及与靶基因启动子结合的能力,以此减少自噬溶酶体的形成;同时在Tau神经退行性果蝇模型中,果蝇GCN5同源蛋白的缺失提高了Tau蛋白聚集体的清除率并改善了神经退行性表型,这表示靶向组蛋白乙酰转移酶 GCN5-转录因子EB通路或具治疗潜力[39]。羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白是一种伴侣依赖性E3泛素连接酶,在饥饿或哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白抑制时,羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白靶向磷酸化转录因子EB进行降解是增强转录因子EB活性的重要机制:一方面,羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白选择性识别并泛素化无活性的磷酸化转录因子EB,使其通过泛素-蛋白酶体途径降解;另一方面,去磷酸化的转录因子EB激活会包括转录因子EB本身在内的靶基因,这导致活性转录因子EB蛋白水平的整体提升(增加其细胞库),更多去磷酸化的转录因子EB转移到细胞核内发挥其转录活性,协同上调自噬及溶酶体相关基因表达。相反,在羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白缺失的细胞中,磷酸化的转录因子EB不能被泛素化标记和进行蛋白酶体有效降解,并且还会与去磷酸化的转录因子EB形成无活性的异二聚体,进一步降低了转录因子EB的活性[40]。最近的研究强调,曲古抑菌素A处理后在转录因子EB上第347位赖氨酸位点的乙酰化显著升高,而泛素化降低,有助于转录因子EB蛋白避免蛋白酶体介导的降解,这说明第347位赖氨酸位点是转录因子EB上的潜在泛素化位点[22]。除羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白外,还有研究在与转录因子EB共沉淀的蛋白中发现,截短型WWP2可显著降低细胞裂解物中的转录因子EB,而羧基末端HSP70/90结合蛋白相互作用蛋白过表达无此效应,结果表明WWP2是介导转录因子EB蛋白酶体降解的特异性E3泛素连接酶[30]。这些都进一步表明不同位点的泛素化可引起转录因子EB处于不同活性状态。FAcilitates Chromatin Transcription(FACT)复合物是一种由SSRP1-SUPT16H0异源二聚体组蛋白伴侣蛋白,介导核小体的拆分和组装,在相关研究发现该复合物可作为转录因子EB转录激活剂[41]。但进一步机制解析发现,在293T细胞模型中,利用质谱分析证实SUMO化修饰抑制了转录因子EB与FACT复合物的相互作用,在亚砷酸钠诱导的SUMO化修饰增强实验进一步验证该相互作用抑制效应,最终导致转录因子EB靶基因转录活性下降[42],这揭示了SUMO化修饰通过阻断FACT复合物招募而负调控转录的新机制,这可能与完整SUMO化修饰抑制活性,而去SUMO化修饰状态(点突变)则解除抑制有关。
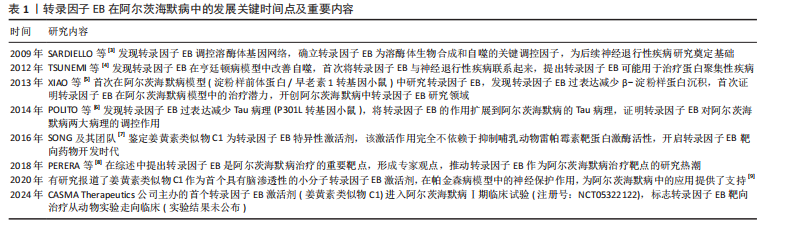
转录因子EB翻译后修饰调控网络,见表2。
2.3 转录因子EB介导自噬溶酶体途径参与的阿尔茨海默病发生机制
2.3.1 自噬溶酶体途径与阿尔茨海默病 自噬指通过溶酶体降解有缺陷的蛋白质或细胞器的过程,具有高度保守的途径和独特的机制。根据自噬物质传递到溶酶体的不同机制,可分为巨自噬、伴侣蛋白介导的自噬和微自噬3种类型。在病理生理学中,自噬通常是指巨自噬,主要被认为是一种促进机制,其作用可以表现为一把“双刃剑”,在生理条件下可循环细胞内容物以及去除聚集的蛋白质、受损的细胞器和入侵的病原体等,以维持正常的细胞功能和体内平衡[43]。然而在缺氧、营养物质耗尽、活性氧暴露、细胞器损伤或聚集蛋白过度积累等情况下,自噬功能出现紊乱,无论是上调还是下调,除了应对不同应激的重要清除途径或细胞存活途径外,已被认为与阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、肌萎缩性侧索硬化症等神经退行性疾病有关[44]。
阿尔茨海默病是痴呆症的主要形式,已经成为一项全球性的健康挑战,该病的病因错综复杂,确切的发病机
制并不完全明确,除了β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau起到关键作用之外,还发现其他一系列因素也参与阿尔茨海默病的形成,比如乙酰胆碱缺乏症、神经炎症、氧化应激、胰岛素抵抗、肠道微生物组异常、胆固醇稳态破坏、线粒体功能障碍和自噬异常等[45]。其中,自噬异常与阿尔茨海默病的发生和进展关系密切。淀粉样前体蛋白(β-淀粉样蛋白前体蛋白)是一种在神经元突触膜上强烈表达的Ⅰ型跨膜蛋白,它主要有2种代谢途径:一种是由α和γ-分泌酶介导的非淀粉样蛋白生成途径,产生无毒性的β-淀粉样蛋白(17-40)和 β-淀粉样蛋白(17-42);而由β-分泌酶1和γ-分泌酶介导的淀粉样蛋白生成途径主要产生β-淀粉样蛋白40和β-淀粉样蛋白42,其中β-淀粉样蛋白42因疏水性较强而容易聚集形成寡聚物或原纤维,最后形成阿尔茨海默病的主要组织学特征之一——老年斑[46]。相关体内和体外研究发现,自噬在远端轴突产生后会逆行移动到胞体参与溶酶体蛋白水解,而大量β-分泌酶1可被募集到自噬囊泡中并转运到体细胞中,从而增强了β-分泌酶1向溶酶体的转运以进行降解[47]。但阿尔茨海默病相关的自噬缺陷会导致逆行运输受损,导致β-分泌酶1的积累,从而增强β-分泌酶1在轴突中对淀粉样前体蛋白的加工,增加β-淀粉样蛋白的产生[48]。此外,在加入自噬抑制剂(3-甲基腺嘌呤)的SH-SY5Y细胞模型中发现,γ-分泌酶复合物的某些成分(如早老素 1、尼卡斯特林和早老素增强子2)表达上调,从而激活γ-分泌酶活性并促进β-淀粉样蛋白产生[48]。在5种阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中,研究发现疾病早期即出现溶酶体vATP酶(一种液泡型 H+-ATP 酶复合物)活性缺陷和脆弱神经元群的自噬功能障碍,导致淀粉样前体蛋白C端片段和β-淀粉样蛋白在低酸化自噬溶酶体中选择性地积累,并且在更受损但仍完整的神经元中大量β-淀粉样蛋白阳性自噬液泡堆积成大的膜泡,形成独特的花状核周莲座丛,称为 PANTHOS(毒花),值得注意的是PANTHOS也存在于阿尔茨海默病大脑中;后期通过定量分析证实,表现出PANTHOS的单个神经元是淀粉样蛋白前体蛋白阿尔茨海默病模型中老年斑的主要来源[49]。近年来相关研究发现,在阿尔茨海默病应激下星形胶质细胞特异性自噬功能失调时,微管相关蛋白1轻链3B和泛素结合蛋白p62的表达减少,显著增加淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠中β-淀粉样蛋白噬菌斑形成,同时神经元标志物和认知功能显著降低。相比之下,微管相关蛋白1轻链3B的星形胶质细胞特异性过表达可以减少淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠大脑中的β-淀粉样蛋白聚集体,而利用RFP-GFP-微管相关蛋白1轻链3B(一种用于监测自噬通量的报告基因)等各种分子工具进一步证实了星形胶质细胞通过微管相关蛋白1轻链3B和泛素结合蛋白p62依赖性自噬囊泡的起始和伸长来促进自噬通量响应β-淀粉样蛋白寡聚体,表明β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的星形胶质细胞自噬可塑性是调节阿尔茨海默病小鼠β-淀粉样蛋白清除和维持认知功能的重要细胞事件[50]。
除了参与β-淀粉样蛋白的产生和清除,自噬也参与调节Tau蛋白的聚集。Tau是一种微管相关蛋白,通过其微管结合区来稳定神经元微管,在病理条件下Tau将会从微管中分离并折叠成淀粉样蛋白原纤维。在阿尔茨海默病中,过度磷酸化会导致Tau蛋白失去与微管结合的能力,而畸形的、过度磷酸化的Tau蛋白最终形成一系列的不溶性纤维状聚集体,逐渐累积并形成阿尔茨海默病的另一个主要组织学特征——神经纤维缠结[51]。含缬氨酸的蛋白是自噬通路中的一个重要因子,通过调节自噬通量来影响Tau蛋白的清除,人类阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中含缬氨酸的蛋白表达严重下调,在Tau病小鼠模型中证实了含缬氨酸的蛋白过表达显著降低磷酸化和寡聚体/聚集体Tau的水平,并挽救了Tau诱导的认知行为表型,与含缬氨酸的蛋白在Tau蛋白清除中的作用一致[52]。此外有研究发现,杨梅素这种天然黄酮类化合物可以通过抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路,激活自噬相关蛋白5依赖的Tau自噬,促进过度磷酸化修饰Tau的清除,从而间接限制Tau聚集,达到几乎完全抑制神经细胞中的Tau蛋白毒性的作
用[53]。TAO等[54]研究发现阿尔茨海默病患者大脑中精脒合成酶蛋白水平表达明显上调,降低精脒合成酶的表达可以增强自噬来抑制Tau蛋白的病理磷酸化和错误折叠,减少Tau蛋白的积累,并在果蝇模型和人类细胞中改善神经退行性和细胞死亡。这些都表明自噬在阿尔茨海默病的发病机制中起重要作用,而自噬功能障碍会加剧淀粉样变性和Tau病理,并导致受损细胞器的积累,例如功能失调的线粒体[55]。
在阿尔茨海默病中,自噬溶酶体通路呈现未成熟自噬体累积、自噬体-溶酶体融合率下降、溶酶体酸化异常的三级功能障碍;其中溶酶体酸化障碍是核心放大器,一方面,β-淀粉样蛋白病理存在正反馈机制,即溶酶体酸化障碍激活β-分泌酶1,促进淀粉样前体蛋白切割生成β-淀粉样蛋白,同时β-淀粉样蛋白寡聚体抑制v-ATP酶功能,进一步恶化酸化,这一点在使用vATP酶激活剂可使5xF阿尔茨海默病小鼠斑块减少70%得以证实[56];另一方面,Tau呈现级联放大效应以及自噬流阻滞导致磷酸化Tau蛋白清除失败,其纤维破坏微管网络并劫持分子伴侣Hsc70阻断分子伴侣介导的自噬,随后也有研究表明过表达转录因子EB可使Tau转基因小鼠缠结减少50%[6]。自噬溶酶体通路功能障碍通过“溶酶体酸化障碍→β-淀粉样蛋白生成增加或/清除障碍→Tau聚集→微管破坏→自噬流阻滞加重”的闭环机制驱动阿尔茨海默病病理进程,靶向自噬溶酶体通路修复(如特异性转录因子EB激活等)可同步干预β-淀粉样蛋白/Tau病理,为阿尔茨海默病疾病修饰治疗提供新范式,但需突破颅内靶向递送与毒性控制等技术瓶颈。
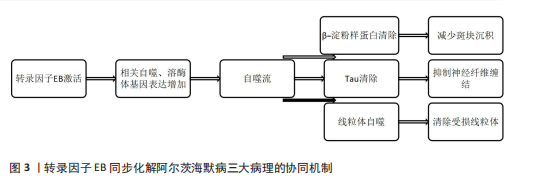
2.3.2 阿尔茨海默病中转录因子EB的信号转导 转录因子EB同步化解阿尔茨海默病三大病理的协同机制,见图3。
据报道,在稳定表达淀粉样前体蛋白695的N2a细胞中转染转录因子EB会刺激溶酶体生物发生,降低淀粉样前体蛋白和C末端片段的稳态水平,并通过增加内体溶酶体途径的通量来产生,表明神经元中转录因子EB的激活是减弱阿尔茨海默病中β-淀粉样蛋白生成和减轻淀粉样蛋白斑块沉积的有效策略[57]。越来越多研究发现,阿尔茨海默病动物大脑中小胶质细胞对于β-淀粉样蛋白斑块清除起着重要作用,而转录因子EB的激活可以通过提高小胶质细胞介导的β-淀粉样蛋白斑块清除,从而上调自噬来改善认知功能[58]。比如,小胶质细胞中转录因子EB在第116位赖氨酸位点被脱乙酰酶1脱乙酰可以通过刺激溶酶体生物发生加速细胞内可溶性β淀粉样蛋白降解,并显著减少淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1转基因小鼠脑切片中沉积的淀粉样蛋白斑块[20]。铜可能通过激活哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白促进转录因子EB磷酸化,从而破坏溶酶体生物发生和自噬通量,降低小胶质细胞的β-淀粉样蛋白清除。与此同时,更有临床研究发现,尿酸作为传统意义中被认为是一种应该积极控制的代谢废物,在阿尔茨海默病患者血清中尿酸水平较低或有降低的趋势,这支持尿酸对阿尔茨海默病具有潜在的神经保护作用[59]。研究发现,β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型血清尿酸水平均低于正常对照组,这与临床研究结果一致;进一步的实验发现,尿酸可以通过激活海马体小胶质细胞上调微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ型/Ⅰ比值、Beclin-1、L腺苷一磷酸1的表达来保护BV2细胞免受β-淀粉样蛋白毒性,这一点在转录因子EB的遗传抑制完全消除了这些保护作用上得以证实,说明尿酸可能作为一种新的转录因子EB激活剂,通过诱导小胶质细胞自噬促进β-淀粉样蛋白降解,从而改善阿尔茨海
默病模型小鼠的认知功能[60],表明维持适当范围的尿酸水平可能是一种安全、有效和可行的阿尔茨海默病治疗方法。
Tau蛋白被过度磷酸化并形成不溶性聚集体,从而失去稳定微管的能力,导致轴突运输障碍,最后导致神经元死亡,并伴有认知缺陷,故而人们认为Tau病理与阿尔茨海默病中认知功能受损密切相关[61]。转录因子EB作为自噬溶酶体途径的主要调节因子,它过表达后可增强自噬,从而促进Tau聚集体降解,改善阿尔茨海默病动物模型中的异常行为[6]。例如,三萜类化合物熊果酸通过以转录因子EB依赖性方式促进自噬后显著减少了Tau的积累,恢复了腹侧海马CA1微回路内的神经兴奋性以改善Tau受损的社交记忆[62]。转录因子EB上第211位和第142位丝氨酸位点的磷酸化/去磷酸化对于其活性的调控至关重要。近年来有研究发现,一种不依赖哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白和糖原合成酶激酶3β磷酸化转录因子EB的激酶,即RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1,是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,在人脑的神经元和神经胶质细胞中均有表达,特别在阿尔茨海默病个体大脑中显著升高。起初,HENDERSON等[63]发现RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1水平升高后增加了阿尔茨海默病小鼠大脑中β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau的水平,并在很大程度上损害溶酶体蛋白的水解,但具体机制并不明确。但他们在随后的实验中进一步验证了RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1是以前未知的转录因子EB上游激酶,是独立于哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白和糖原合成酶激酶3β的调控方式,它与转录因子EB直接结合并磷酸化第211位和第142丝氨酸位点,从而抑制转录因子EB核转移、减少溶酶体生物发生和干扰溶酶体介导的β-淀粉样蛋白清除,最终促进了淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠的病理特征和认知缺陷的发生[64]。除此之外,RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1升高导致β-淀粉样蛋白在细胞外大量沉积后,它与β-淀粉样蛋白受体结合并激活 RhoA/RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1,形成阿尔茨海默病发病机制的恶性循环[65]。
与此同时,转录因子EB基因敲除模型也进一步体现出转录因子EB在阿尔茨海默病病理中的重要作用。转录因子EB功能缺失导致溶酶体数量及活性明显减少,引起溶酶体功能障碍和自噬流破坏[35]。在阿尔茨海默病病理模型中,敲除转录因子EB可引起β-淀粉样蛋白沉积增加2.3倍,神经元丢失加剧,认知功能障碍提前出现[6],这些都反向验证了转录因子EB-自噬溶酶体轴与阿尔茨海默病病理的因果关联。
除了自噬溶酶体在阿尔茨海默病的发展过程中发挥重要作用,相关研究还发现线粒体自噬受损后导致功能失调的线粒体在神经元中积累,引起炎症并促进阿尔茨海默病中β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau的病理进展;而褪黑激素可以促进转录因子EB进入细胞核并改善了线粒体自噬,减轻线粒体损伤,拮抗β-淀粉样蛋白在阿尔茨海默病细胞中的细胞毒作用[66]。
2.4 转录因子EB在阿尔茨海默病治疗中的相关研究
2.4.1 转录因子EB治疗阿尔茨海默病的潜在药物疗法 自噬功能障碍被认为是阿尔茨海默病神经病理的早期事件,通过靶向转录因子EB影响自噬溶酶体生物活性,从而改善阿尔茨海默病病理及行为缺陷受到越来越多的关注。
哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白是转录因子EB磷酸化的主要调节激酶,目前发现有许多药物均通过介导哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白调控转录因子EB活性。紫杉醇是一种中药化合物,通过激活自噬来保护神经元免受侵袭。有研究表明,体外5xF阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型中,紫杉醇通过抑制蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号传导和刺激溶酶体钙释放(瞬时受体电位粘磷脂1)激活转录因子EB,增加神经元自噬和溶酶体的生物发生,降低了致病性淀粉样前体蛋白-羧基末端片段水平,并改善了小鼠学习记忆功能;随后在N2aSwed淀粉样前体蛋白细胞中进一步证明,转录因子EB敲除可以消除紫杉醇诱导的淀粉样前体蛋白-羧基末端片段降解,说明紫杉醇通过促进转录因子EB介导的自噬来减轻阿尔茨海默病模型中的β-淀粉样蛋白病理[67]。绿原酸是一种从水果和蔬菜中分离出来的酚酸。有研究表明,淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠在CA1海马中表现出认知功能障碍和神经元损伤,并伴有过度自噬和溶酶体功能受损,而绿原酸可以通过调节哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白/转录因子EB信号通路来抑制淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠的过度自噬,缓解CA1海马神经元细胞数量减少和神经元超微结构受损,改善认知功能[68]。Celastrol是一种瘦素增敏剂,最初是从雷公藤的根中分离出来的,通过抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1促进转录因子EB去磷酸化并激活自噬,促进β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau聚集体的降解,改善小鼠模型中与阿尔茨海默病相关的记忆缺陷[69]。异丁司特通过降低哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白的溶酶体定位来刺激溶酶体生物发生和自噬通量,并增强转录因子EB核易位,促进神经退行性疾病相关蛋白的TAR DNA结合蛋白43和超氧化物歧化酶1聚集体的清除,保护神经元细胞免受神经退行性疾病相关蛋白诱导的细胞毒性[70]。罗特勒素是一种从印度漆树中提取的植物化学物质,被发现可作为预防和治疗阿尔茨海默病的药物。因为罗特勒素不仅通过激活腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶后促进Raptor基因(该基因编码小鼠哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1的一个亚基)上第792 位丝氨酸位点磷酸化,从而抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1,使得转录因子EB活性增加,同时还增强核因子E2相关因子2活性,共同引起自噬作用增强及促进磷酸化Tau蛋白的降解[71],这一点在与其具有相同作用的非瑟酮(一种黄酮醇)上进一步得到证实[72]。
过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α是一种可以激活自噬的转录因子,并转录调节转录因子EB,是自噬溶酶体通路的关键调节因子。最初,青羊参被发现在治疗癫痫和肌肉损伤方面有着显著效果,但近年来发现它还具有神经保护活性。研究发现,口服青羊参提取物通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α-转录因子EB通路增强自噬溶酶体通路,减少脑内羧基末端片段、淀粉样前体蛋白、β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau聚集物,抑制脑内小胶质细胞增生和星形细胞增生,改善阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的学习和空间记
忆[73-74]。油酰乙醇酰胺是一种内源性脂质酰胺,已被证明可通过调节溶酶体到细胞核信号传导和细胞代谢来增加秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命。研究发现,油酰乙醇酰胺以过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α依赖性但哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1非依赖性方式促进转录因子EB溶酶体功能,导致小胶质细胞β淀粉样蛋白摄取和清除增强[75]。低剂量的阿司匹林通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α上调转录因子EB转录并增加脑细胞中的溶酶体生物发生,以过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α依赖性方式减少了5×F阿尔茨海默病小鼠的淀粉样斑块病理[76]。除此之外,乙酰水杨酸是一种有较高毒性和不良反应的药物,可以恢复部分异常表达的细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶 1/2/4,降低淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠神经元的凋亡,并且以过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α激活的转录因子EB依赖性方式产生微管相关蛋白1轻链3-Ⅱ型和溶酶体相关膜蛋白2蛋白,有助于减少β-淀粉样蛋白的产生和沉积[77]。吉非罗齐是过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α的激动剂,该药单独使用或与全反式维甲酸联合使用时可增强小鼠脑细胞中的转录因子EB表达并增加溶酶体生物发生[78]。进一步研究发现,在星形胶质细胞中,吉非罗齐-全反式维甲酸激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α后通过转录因子EB增强溶酶体生物发生以对β-淀粉样蛋白进行降解,减少斑块负荷并改善阿尔茨海默病小鼠模型的认知功能[79]。
曲美替尼对丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶/细胞外信号调节激酶信号转导的抑制作用抑制了转录因子EB在第142 位丝氨酸位点的磷酸化,并促进转录因子EB核转位,进而诱导自噬溶酶体相关基因表达,并通过阻止β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的神经毒性恢复5XF阿尔茨海默病小鼠受损的神经结构、认知功能和海马长期增强,从而达到神经元保护作用[80]。
SONG等[7]发现姜黄素类似物C1的N末端可与转录因子EB可发生特异性结合,在不抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/细胞外信号调节激酶2活性的情况下促进转录因子EB核转位,从而增强自噬和溶酶体生物发生,故确定姜黄素类似物C1为转录因子EB的哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白非依赖性激活剂。随后利用淀粉样前体蛋白病理学(5xF阿尔茨海默病小鼠)、Tau蛋白病(P301S小鼠)和淀粉样前体蛋白/Tau联合病理学(3xTg-阿尔茨海默病小鼠)的3种阿尔茨海默病动物模型,进一步确定了姜黄素类似物C1通过激活转录因子EB后促进自噬和溶酶体生物发生,降解淀粉样前体蛋白和Tau聚集体,降低β-淀粉样蛋白水平,逆转突触功能障碍并改善认知缺陷[9]。
芍药苷、阿魏酸和白术内酯Ⅲ具有抗炎和神经保护作用,研究揭示了三者对脂多糖诱导的BV2小胶质细胞神经炎症具有协同作用,它们的分子机制可能与腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶/UNC-51样自噬激活激酶1/转录因子EB 的激活有关[81]。
人参和三七中富含的皂苷绞股皂苷ⅩⅤⅡ能将磷酸化的转录因子EB从胞质伴侣14-3-3蛋白中释放,导致转录因子EB核易位,诱导自噬和溶酶体生物发生,促进淀粉样前体蛋白695swe细胞中基于自噬的β-淀粉样蛋白PP、β-淀粉样蛋白40和42的清除,并阻止淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠海马和大脑皮质中β-淀粉样蛋白斑块的形成,有利于淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠空间学习和记忆缺陷的恢复,而抑制转录因子EB则出现相反作用,这可能与磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物-蛋白激酶B-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号转导促进转录因子EB活化有关[82]。
克罗米芬柠檬酸盐作为组蛋白去乙酰化酶的潜在抑制剂,通过促进转录因子EB的乙酰化诱导的转录因子EB激活以促进其进行核转位,激活了神经元细胞中的自噬溶酶体途径;经克罗米芬柠檬酸盐治疗促进了7月龄和3月龄淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠β-淀粉样蛋白斑块的清除并改善认知功能[83]。
常春藤皂苷元是一种三萜化合物,在免疫调节、抗肿瘤、抗炎、保肝和抗菌活性等方面均有作用。近年来越来越多研究发现常春藤皂苷元还具有神经保护作用,比如常春藤皂苷元通过上调转录因子EB的mRNA和蛋白水平增加它在细胞核中的分布及其靶基因的表达,促进自噬和β-淀粉样蛋白降解,改善淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠的认知障碍和病理变化[84]。
除了上述以改善阿尔茨海默病为主的药物以外,有研究还发现一种可加速阿尔茨海默病发病机制风险的药物——咪达唑仑,咪达唑仑是一种常用于手术期间的镇静和平衡全身麻醉的静脉麻醉剂,实验发现30 μmol/L咪达唑仑可抑制HEK293-淀粉样前体蛋白中转录因子EB转入细胞核,导致细胞内β-淀粉样蛋白40和42的C末端前体片段水平均显著升高[85]。
2.4.2 针对转录因子EB的阿尔茨海默病非药物治疗 电针作为一种补充疗法在治疗人类疾病中已被广泛应用。现已有研究通过5xF阿尔茨海默病模型发现,三针电针不仅可以通过抑制蛋白激酶B/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1通路激活转录因子EB,还可激活小鼠海马体中的腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶,转录上调大脑中的自噬溶酶体途径,以降解淀粉样前体蛋白、C末端片段和β-淀粉样蛋白,抑制5xF阿尔茨海默病前额叶皮质和海马中的神经胶质细胞活化,从而抑制β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的神经炎症和认知障碍[86-87]。
斑块相关小胶质细胞中自噬受损会加速阿尔茨海默病发病机制中淀粉样蛋白斑块沉积和认知障碍,而间歇性缺氧疗法促进了转录因子EB在斑块相关小胶质细胞中的核定位,通过减轻具有β-淀粉样蛋白病理学的淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠神经元丢失和轴突损伤来改善认知功能,这可能与间歇性缺氧疗法抑制蛋白激酶B/丝裂原活化蛋白激酶/ 哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路从而激活转录因子EB有关[88]。同时有研究发现,间歇性缺氧疗法可以促进淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠小胶质细胞中转录因子EB与VPS35(是反转录酶复合物的核心亚基,通过将内吞的货物转移到质膜来调节内吞作用、自噬和溶酶体降解途径)的启动子区域结合来上调VPS35表达,从而改善阿尔茨海默病的病理[89]。
深部脑刺激是一种调节神经元活动以治疗神经和精神疾病的手术策略,对阿尔茨海默病患者产生了积极影响。近年来有研究发现,深部脑刺激的保护作用可能与突触活性诱导抑制哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1信号传导从而促进转录因子EB的核转位,增强病理性Tau的巨自噬/自噬通量和溶酶体降解有关,在阿尔茨海默病和额颞叶痴呆的小鼠模型中发挥保护作用[90]。
脂联素是一种由脂肪组织分泌的蛋白质激素,具有神经保护作用。脂联素受体1/2是脂联素的主要受体,广泛存在于大脑皮质、Meynert 基底核和海马体等各种脑区,其中脂联素受体1可以激活腺苷一磷酸/腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶通路。有研究显示,24周淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1双转基因阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的脑内脂联素受体1水平降低、自噬异常、β-淀粉样蛋白沉积增加、树突棘和认知功能降低,而12周的有氧运动通过激活阿尔茨海默病小鼠大脑中的脂联素受体1-腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶-转录因子EB 信号通路,增强溶酶体生物发生并减轻异常自噬,从而减轻β-淀粉样蛋白沉积及其相关的阿尔茨海默病样异常[91],表明运动可以显著改善阿尔茨海默病自噬异常。此外还有研究发现,长期运动显著增强了溶酶体功能和大脑中β-淀粉样蛋白的清除,减轻了阿尔茨海默病小鼠的认知功能障碍,可能是运动显著促进了转录因子EB的核易位并增加了细胞核内转录因子EB与腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶介导的乙酰辅酶A合成酶2之间的相互作用,从而增强了与溶酶体生物发生相关基因的转录[92]。
LI等[93]开发了一种多功能的治疗诊断剂水杨醛锌诊疗探针,它可以选择性地与β-淀粉样蛋白寡聚体结合,具有很强的荧光增强能力,也很容易穿过血脑屏障。相关研究发现,水杨醛锌诊疗探针对转录因子EB活性的调控并不抑制或不依赖于哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1及其下游靶标,而是剂量依赖性地将转录因子EB易位到细胞核中。具体而言,水杨醛锌诊疗探针除了抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/细胞外信号调节激酶2活性,以剂量和时间依赖性方式在转录因子EB的第142位丝氨酸位点触发转录因子EB去磷酸化以外,还可增强蛋白磷酸酶2A功能以使转录因子EB去磷酸化,导致转录因子EB发生核易位和核富集,不仅显著降低阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠大脑中自噬溶酶体降解途径的β-淀粉样蛋白寡聚体、Tau聚集体和斑块的水平,还可以显著降低淀粉样前体蛋白及其代谢物的水平[94]。此外,水杨醛锌诊疗探针可激活并促进小胶质细胞中转录因子EB核易位,减少星形胶质细胞活化和小胶质细胞增生,缓解神经炎症,恢复树突棘密度并增加了海马神经元之间突触可塑性的形成,从而挽救阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的学习和记忆障
碍[94]。
2.4.3 组织工程技术在转录因子EB通路调控中的应用 组织工程的核心在于利用生物材料支架、功能性细胞(或干细胞)以及调控因子(如生长因子、基因载体),在体外或体内构建具有特定结构与功能的组织。组织工程技术在转录因子EB 通路调控中的应用策略主要包括以下几个方面。
(1)基于转录因子EB的基因递送系统在阿尔茨海默病治疗中的潜力:传统小分子化合物(如雷帕霉素及其衍生物、海藻糖等)可以激活转录因子EB发挥一定效应,但通常存在特异性不足、脱靶效应、难以有效通过血脑屏障、难以持续激活、药物持续时间短暂需频繁给药以及潜在药物不良反应等问题。相比之下,通过基因递送系统将编码功能性转录因子EB或其激活形式的突变体的遗传物质递送至神经元、胶质细胞等特定靶细胞内以实现对转录因子EB表达水平及功能的精准、长效调控,这为阿尔茨海默病的治疗提供了一种新型的替代策略。
研究发现,用于靶向转录因子EB的中枢神经系统基因递送载体系统以病毒载体为主,而非病毒载体(如脂质纳米粒、聚合物纳米粒)直接递送转录因子EB的相关研究极少,主要用于递送转录因子EB激活剂(siRNA、小分子药物等)以间接增强溶酶体功能,病毒载体主要包括腺相关病毒及慢病毒。腺相关病毒已成为中枢神经系统靶向基因递送的首选病毒载体,拥有无致病性、低免疫原性、可控性基因组整合、基因表达长效稳定、高度灵活靶向性等优势,最重要的是能够通过衣壳工程化改造制定新型靶向载体,在目前已开发出多种腺相关病毒血清型(如AAV9、AAV-PHP.B、AAV-PHP.eB、AAVrh.10等)中,其中一些可有效穿越血脑屏障或特异性靶向神经元或星形胶质细胞,为腺相关病毒介导转录因子EB基因递送治疗阿尔茨海默病提供临床候选方案[95]。例如,POLITO等[6]利用腺相关病毒9血清型携带转录因子EB基因靶向注射至5xF阿尔茨海默病和rTg4510小鼠内嗅皮质/海马区,该治疗显著增强神经元中溶酶体生物合成基因(如CTSD、L腺苷一磷酸1)表达,促进自噬体-溶酶体融合,有效清除病理性Tau蛋白并挽救Tau介导的神经毒性,并显著改小鼠的运动和记忆缺陷,此方法克服了传统疗法的脱靶风险,提示着阿尔茨海默病治疗范式的转变。在随后的研究中,XIAO等[5]使用腺相关病毒载体(血清型未明确说明)向淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠的皮质和海马递送转录因子EB,显著增强了星形胶质细胞的溶酶体生物合成和功能,降低颅内的β-淀粉样蛋白斑块负荷,在行为学检测中显示识别记忆有改善趋势,证明通过基因手段(腺相关病毒)靶向星形胶质细胞转录因子EB活性,可以有效促进β-淀粉样蛋白清除,为阿尔茨海默病非神经元治疗策略提供新思路,但认知改善的完全验证需后续研究深化。SONG等[64]还发现腺相关病毒介导的海马RHO相关卷曲螺旋激酶1下调提高了转录因子EB核分布,促进了溶酶体功能和β-淀粉样蛋白降解,从而改善了淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1小鼠的认知缺陷。上述研究共同构成完整拼图,证明腺相关病毒-转录因子EB策略具有同时靶向阿尔茨海默病两大核心病理(β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau)的潜力,并且改善认知功能的结论也间接支持了腺相关病毒-转录因子EB在阿尔茨海默病综合模型中的认知获益预期。慢病毒属于反转录病毒,优势在于包装容量较大,可整合入宿主基因组以实现转基因稳定、长效甚至永久性表达,并能有效转导神经元。早期有研究将过表达转录因子EB的慢病毒直接注射到阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠(淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1)的海马体中,增强溶酶体清除能力以此减少β-淀粉样蛋白生成和淀粉样斑块病理[57]。但在临床应用中,基因组整合存在潜在插入突变风险,存在安全隐患,而非整合型慢病毒载体正在开发中,以降低风险为目的。
(2)干细胞定向分化中转录因子EB通路的组织工程化调控:干细胞定向分化技术是再生医学与组织工程的核心支柱,旨在将多能干细胞(胚胎干细胞、诱导多能干细胞)或成体干细胞精准、高效地诱导分化为具有特定功能的终末细胞(如神经元、胶质细胞等),可替代丢失神经元和修复受损神经网络。关于干细胞在阿尔茨海默病中的应用早已开始探索,例如,MURATORE等[96]使用来自淀粉样前体蛋白突变中携带显性、完全渗透性的家族性阿尔茨海默病突变患者的诱导多能干细胞建立了一个阿尔茨海默病模型,发现突变会影响淀粉样前体蛋白的β和γ-分泌酶切割,导致淀粉样前体蛋白和β-淀粉样蛋白水平升高,并改变了Tau 表达和磷酸化,同时证明了可以通过抗β-淀粉样蛋白抗体治疗来挽救Tau的增加,说明诱导多能干细胞衍生的神经元培养物可能是替代治疗策略在目标细胞类型中疗效的有用模型。随后有研究从1例82岁受散发性阿尔茨海默病影响的女性患者真皮成纤维细胞中提取并表征了诱导多能干细胞,成功检测到的特征基因表达模式生成了一个阿尔茨海默病相关的蛋白质关联网络,可为药物筛选和毒理学研究提供平台,为此类神经元疾病揭示新的治疗途径[97]。
近年来,CHOE等[98]通过构建阿尔茨海默病-人诱导多能干细胞来源的脑类器官发现,淀粉样前体蛋白和早老素1突变导致β-淀粉样蛋白积累、Tau蛋白病变和细胞凋亡增加,该模型有效概括了阿尔茨海默病病理学,可用于测试抗阿尔茨海默病药物的疗效。这些研究都进一步表明了干细胞定向分化技术在探索阿尔茨海默病发病机制中起到了重要作用。与此同时,越来越多研究聚焦于干细胞参与阿尔茨海默病疗法中,例如,静脉注射诱导神经干细胞来源的细胞外囊泡能有效减轻5XF阿尔茨海默病小鼠的阿尔茨海默病样症状,包括减少β-淀粉样蛋白沉积、改善认知功能,这与神经干细胞来源囊泡具有相同的治疗效果,展现了其在阿尔茨海默病治疗中的潜力[99]。
近年来,随着细胞自噬溶酶体通路的核心调控因子——转录因子EB在干细胞命运决定和分化成熟中的关键作用被不断揭示,将组织工程化策略应用于干细胞定向分化过程,特异性调控转录因子EB活性,有望生成更具抵抗力、功能更成熟且能有效应对阿尔茨海默病病理环境的“超级神经元”。虽然直接结合干细胞工程与转录因子EB调控在阿尔茨海默病中的研究仍处于早期探索阶段,但用于神经退行性变疾病的相关研究并不少,例如,MUBARIZ等[100]利用葡糖脑苷脂酶基因1突变(帕金森病最常见的遗传风险因素)患者的诱导多能干细胞分化为多巴胺神经元,在体外重现疾病表型,精准捕捉溶酶体-自噬轴缺陷并验证哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1-转录因子EB轴失调是α-突触核蛋白聚集的核心病理环节。而阿尔茨海默病中β-淀粉样蛋白和Tau积累均与溶酶体清除能力下降直接相关,转录因子EB同样作为调控溶酶体生物发生的关键因子可以借鉴该研究策略,利用阿尔茨海默病患者(如淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1突变)的诱导多能干细胞分化为神经元/小胶质细胞,探索过表达转录因子EB是否降低β-淀粉样蛋白/tau等沉积,同时利用阿尔茨海默病干细胞模型筛选转录因子EB 激活剂或哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合物1抑制剂库,加速阿尔茨海默病药物开发。

| [1] LLORET A, ESTEVE D, LLORET M, et al. When Does Alzheimer’s Disease Really Start? The Role of Biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5536. [2] SONG J, LIU J, JIANG Y, et al. Transcription factor EB: an emerging drug target for neurodegenerative disorders. Drug Discov Today. 2021;26(1):164-172. [3] SARDIELLO M, PALMIERI M, DI RONZA A, et al. A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science. 2009;325(5939):473-477. [4] TSUNEMI T, ASHE TD, MORRISON BE, et al. PGC-1α rescues Huntington’s disease proteotoxicity by preventing oxidative stress and promoting TFEB function. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4(142):142ra97. [5] XIAO Q, YAN P, MA X, et al. Enhancing astrocytic lysosome biogenesis facilitates Abeta clearance and attenuates amyloid plaque pathogenesis. J Neurosci. 2014; 34(29):9607-9620. [6] POLITO VA, LI H, MARTINI-STOICA H, et al. Selective clearance of aberrant tau proteins and rescue of neurotoxicity by transcription factor EB. EMBO Mol Med. 2014;6(9):1142-1160. [7] SONG J, SUN Y, PELUSO I, et al. A novel curcumin analog binds to and activates TFEB in vitro and in vivo independent of MTOR inhibition. Autophagy. 2016;12(8): 1372-1389. [8] PERERA RM, Di MALTA C, BALLABIO A. MiT/TFE Family of Transcription Factors, Lysosomes, and Cancer. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 2019;3:203-222. [9] SONG J, MALAMPATI S, ZENG Y, et al. A small molecule transcription factor EB activator ameliorates beta-amyloid precursor protein and Tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease models. Aging Cell. 2020;19(2):e13069. [10] AGOSTINI F, AGOSTINIS R, MEDINA DL, et al. The Regulation of MiTF/TFE Transcription Factors Across Model Organisms: from Brain Physiology to Implication for Neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2022; 59(8):5000-5023. [11] TAKLA M, KESHRI S, RUBINSZTEIN DC. The post-translational regulation of transcription factor EB (TFEB) in health and disease. EMBO Rep. 2023;24(11):e57574. [12] PUERTOLLANO R, FERGUSON SM, BRUGAROLAS J, et al. The complex relationship between TFEB transcription factor phosphorylation and subcellular localization. EMBO J. 2018;37(11):e98804. [13] HSU CL, LEE EX, GORDON KL, et al. MAP4K3 mediates amino acid-dependent regulation of autophagy via phosphorylation of TFEB. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):942. [14] PAQUETTE M, EL-HOUJEIRI L, C ZIRDEN L, et al. AMPK-dependent phosphorylation is required for transcriptional activation of TFEB and TFE3. Autophagy. 2021;17(12): 3957-3975. [15] CLARK AR, OHLMEYER M. Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in inflammation and neurodegeneration. Pharmacol Ther. 2019;201:181-201. [16] MARTINA JA, PUERTOLLANO R. Protein phosphatase 2A stimulates activation of TFEB and TFE3 transcription factors in response to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(32):12525-12534. [17] RUSMINI P, CORTESE K, CRIPPA V, et al. Trehalose induces autophagy via lysosomal-mediated TFEB activation in models of motoneuron degeneration. Autophagy. 2019;15(4):631-651. [18] XIA Q, ZHENG H, LI Y, et al. SMURF1 controls the PPP3/calcineurin complex and TFEB at a regulatory node for lysosomal biogenesis. Autophagy. 2024;20(4):735-751. [19] ZHANG X, CHENG X, YU L, et al. MCOLN1 is a ROS sensor in lysosomes that regulates autophagy. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12109. [20] BAO J, ZHENG L, ZHANG Q, et al. Deacetylation of TFEB promotes fibrillar Abeta degradation by upregulating lysosomal biogenesis in microglia. Protein Cell. 2016;7(6):417-433. [21] ZHANG J, WANG J, ZHOU Z, et al. Importance of TFEB acetylation in control of its transcriptional activity and lysosomal function in response to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Autophagy. 2018;14(6):1043-1059. [22] LI T, YIN L, KANG X, et al. TFEB acetylation promotes lysosome biogenesis and ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-relevant phenotypes in mice. J Biol Chem. 2022; 298(12):102649. [23] WANG H, WANG N, XU D, et al. Oxidation of multiple MiT/TFE transcription factors links oxidative stress to transcriptional control of autophagy and lysosome biogenesis. Autophagy. 2020;16(9):1683-1696. [24] KESHRI S, VICINANZA M, TAKLA M, et al. USP7 protects TFEB from proteasome-mediated degradation. Cell Rep. 2024; 43(11):114872. [25] ZHENG B, QIAN F, WANG X, et al. Neddylation activated TRIM25 desensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to paclitaxel via TFEB-mediated autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024;43(1):177. [26] BECK WHJ, KIM D, DAS J, et al. Glucosylation by the Legionella Effector SetA Promotes the Nuclear Localization of the Transcription Factor TFEB. iScience. 2020;23(7):101300. [27] KIM S, SONG G, LEE T, et al. PARsylated transcription factor EB (TFEB) regulates the expression of a subset of Wnt target genes by forming a complex with beta-catenin-TCF/LEF1. Cell Death Differ. 2021; 28(9):2555-2570. [28] MARTINA JA, GUERRERO-GOMEZ D, GOMEZ-ORTE E, et al. A consved cysteine-based redox mechanism sustains TFEB/HLH-30 activity under persistent stress. EMBO J. 2021;40(3):e105793. [29] MILLER AJ, LEVY C, DAVIS IJ, et al. Sumoylation of MITF and its related family members TFE3 and TFEB. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(1):146-155. [30] HUANG Y, LUO G, PENG K, et al. Lactylation stabilizes TFEB to elevate autophagy and lysosomal activity. J Cell Biol. 2024; 223(11):e202308099. [31] CHEN Z, OUYANG C, ZHANG H, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell-derived hydrogen sulfide promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability via TFEB (transcription factor EB)-mediated autophagy. Autophagy. 2022;18(10):2270-2287. [32] CUI Z, NAPOLITANO G, De ARAUJO MEG, et al. Structure of the lysosomal mTORC1-TFEB-Rag-Ragulator megacomplex. Nature. 2023;614(7948):572-579. [33] XU Y, REN J, HE X, et al. YWHA/14-3-3 proteins recognize phosphorylated TFEB by a noncanonical mode for controlling TFEB cytoplasmic localization. Autophagy. 2019;15(6):1017-1030. [34] VEGA-RUBIN-DE-CELIS S, PENA-LLOPIS S, KONDA M, et al. Multistep regulation of TFEB by MTORC1. Autophagy. 2017; 13(3):464-472. [35] SETTEMBRE C, Di MALTA C, POLITO VA, et al. TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science. 2011;332(6036):1429-1433. [36] YIN Q, JIAN Y, XU M, et al. CDK4/6 regulate lysosome biogenesis through TFEB/TFE3. J Cell Biol. 2020;219(8):e201911036. [37] LI L, FRIEDRICHSEN HJ, ANDREWS S, et al. A TFEB nuclear export signal integrates amino acid supply and glucose availability. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2685. [38] PALMIERI M, PAL R, NELVAGAL HR, et al. mTORC1-independent TFEB activation via Akt inhibition promotes cellular clearance in neurodegenerative storage diseases. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14338. [39] WANG Y, HUANG Y, LIU J, et al. Acetyltransferase GCN5 regulates autophagy and lysosome biogenesis by targeting TFEB. EMBO Rep. 2020;21(1): e48335. [40] RAO L, SHA Y, EISSA NT. The E3 ubiquitin ligase STUB1 regulates autophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis by modulating TFEB activity. Mol Cell Oncol. 2017;4(6): e1372867. [41] JEONG E, MARTINA JA, CONTRERAS PS, et al. The FACT complex facilitates expression of lysosomal and antioxidant genes through binding to TFEB and TFE3. Autophagy. 2022;18(10):2333-2349. [42] WANG K, ZHOU W, HU G, et al. TFEB SUMOylation in macrophages accelerates atherosclerosis by promoting the formation of foam cells through inhibiting lysosomal activity. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80(12):358. [43] ZHAO YG, CODOGNO P, ZHANG H. Machinery, regulation and pathophysiological implications of autophagosome maturation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(11):733-750. [44] RANA T, BEHL T, SEHGAL A, et al. Exploring the Role of Autophagy Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(10):4886-4905. [45] ZHANG J, ZHANG Y, WANG J, et al. Recent AD vances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):211. [46] DUNYS J, VALVERDE A, CHECLER F. Are N- and C-terminally truncated Abeta species key pathological triggers in Alzheimer’s disease? J Biol Chem. 2018;293(40):15419-15428. [47] FENG T, TAMMINENI P, AGRAWAL C, et al. Autophagy-mediated Regulation of BACE1 Protein Trafficking and Degradation. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(5):1679-1690. [48] CACACE R, SLEEGERS K, VAN BROECKHOVEN C. Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12(6):733-748. [49] LEE J, YANG D, GOULBOURNE CN, et al. Faulty autolysosome acidification in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models induces autophagic build-up of Abeta in neurons, yielding senile plaques. Nat Neurosci. 2022;25(6):688-701. [50] KIM S, CHUN H, KIM Y, et al. Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Abeta clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2024;19(1):55. [51] SOEDA Y, YOSHIMURA H, BANNAI H, et al. Intracellular tau fragment dropletsserve as seeds for tau fibrils. Structure. 2024; 32(10):1793-1807. [52] GIONG H, HYEON SJ, LEE J, et al. Tau accumulation is cleared by the induced expression of VCP via autophagy. Acta Neuropathol. 2024;148(1):46. [53] DAI B, ZHONG T, CHEN Z, et al. Myricetin slows liquid-liquid phase separation of Tau and activates ATG5-dependent autophagy to suppress Tau toxicity. J Biol Chem. 2021; 297(4):101222. [54] TAO X, LIU J, DIAZ-PEREZ Z, et al. Reduction of spermine synthase enhances autophagy to suppress Tau accumulation. Cell Death Dis. 2024;15(5):333. [55] KERR JS, ADRIAANSE BA, GREIG NH, et al. Mitophagy and Alzheimer’s Disease: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Trends Neurosci. 2017;40(3):151-166. [56] JIANG Y, SATO Y, IM E, et al. Lysosomal Dysfunction in Down Syndrome Is APP-Dependent and Mediated by APP-βCTF (C99). J Neurosci. 2019;39(27):5255-5268. [57] XIAO Q, YAN P, MA X, et al. Neuronal-Targeted TFEB Accelerates Lysosomal Degradation of APP, Reducing Abeta Generation and Amyloid Plaque Pathogenesis. J Neurosci. 2015;35(35): 12137-12151. [58] YAMAMOTO F, TANIGUCHI K, MAMADA N, et al. TFEB-mediated Enhancement of the Autophagy-lysosomal Pathway Dually Modulates the Process of Amyloid beta-Protein Generation in Neurons. Neuroscience. 2019;402:11-22. [59] BOCCARDI V, CARINO S, MARINELLI E, et al. Uric acid and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: results from the ReGAl 2.0 project. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(2):361-366. [60] XIAO Q, WANG J, TIAN Q, et al. Uric Acid Mitigates Cognitive Deficits via TFEB-Mediated Microglial Autophagy in Mice Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(6):3678-3696. [61] TAN X, GUAN H, YANG Y, et al. Cu(II) disrupts autophagy-mediated lysosomal degradation of oligomeric Aβ in microglia via mTOR-TFEB pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020;401:115090. [62] LEI H, PI G, HE T, et al. Targeting vulnerable microcircuits in the ventral hippocampus of male transgenic mice to rescue Alzheimer-like social memory loss. Mil Med Res. 2024; 11(1):16. [63] HENDERSON BW, GENTRY EG, RUSH T, et al. Rho-associated protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) is increased in Alzheimer’s disease and ROCK1 depletion reduces amyloid-β levels in brain [J]. J Neurochem. 2016;138(4):525-531. [64] SONG C, HUANG W, ZHANG P, et al. Critical role of ROCK1 in AD pathogenesis via controlling lysosomal biogenesis and acidification. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1):54. [65] HU Y, REN R, ZHANG Y, et al. Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase 1 activation mediates amyloid precursor protein site-specific Ser655 phosphorylation and triggers amyloid pathology. Aging Cell. 2019;18(5):e13001. [66] LI Y, ZHANG J, WAN J, et al. Melatonin regulates Abeta production/clearance balance and Abeta neurotoxicity: A potential therapeutic molecule for Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;132:110887. [67] GUAN X, DENG Z, LIU J, et al. Corynoxine promotes TFEB/TFE3-mediated autophagy and alleviates Abeta pathology in Alzheimer’s disease models. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024;45(5):900-913. [68] GAO L, LI X, MENG S, et al. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates Abeta(25-35)-Induced Autophagy and Cognitive Impairment via the mTOR/ TFEB Signaling Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:1705-1716. [69] YANG C, SU C, IYASWAMY A, et al. Celastrol enhances transcription factor EB (TFEB)-mediated autophagy and mitigates Tau pathology: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022; 12(4):1707-1722. [70] CHEN Y, WANG H, YING Z, et al. Ibudilast enhances the clearance of SOD1 and TDP-43 aggregates through TFEB-mediated autophagy and lysosomal biogenesis: The new molecular mechanism of ibudilast and its implication for neuroprotective therapy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;526(1):231-238. [71] KAM MK, PARK J, YUN GH, et al. Rottlerin Enhances the Autophagic Degradation of Phosphorylated Tau in Neuronal Cells. Mol Neurobiol. 2024;61(11):9633-9645. [72] KIM S, CHOI KJ, CHO S, et al. Fisetin stimulates autophagic degradation of phosphorylated tau via the activation of TFEB and Nrf2 transcription factors. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24933. [73] IYASWAMY A, KRISHNAMOORTHI SK, ZHANG H, et al. Qingyangshen mitigates amyloid-beta and Tau aggregate defects involving PPARα-TFEB activation in transgenic mice of Alzheimer’s disease. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153648. [74] KRISHNAMOORTHI S, IYASWAMY A, SREENIVASMURTHY SG, et al. PPARa Ligand Caudatin Improves Cognitive Functions and Mitigates Alzheimer’s Disease Defects By Inducing Autophagy in Mice Models. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2023;18(3): 509-528. [75] COMEROTA MM, GEDAM M, XIONG W, et al. Oleoylethanolamide facilitates PPARα-TFEB signaling and attenuates Abeta pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2023;18(1):56. [76] CHANDRA S, JANA M, PAHAN K. Aspirin Induces Lysosomal Biogenesis and Attenuates Amyloid Plaque Pathology in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease via PPARα. J Neurosci. 2018;38(30): 6682-6699. [77] GUAN P, DING W, WANG P. Molecular mechanism of acetylsalicylic acid in improving learning and memory impairment in APP/PS1 transgenic mice by inhibiting the abnormal cell cycle re-entry of neurons. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:1006216. [78] GHOSH A, JANA M, MODI K, et al. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α induces lysosomal biogenesis in brain cells: implications for lysosomal storage disorders. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(16):10309-10324. [79] RAHA S, GHOSH A, DUTTA D, et al. Activation of PPARα enhances astroglial uptake and degradation of beta-amyloid. Sci Signal. 2021;14(706):eabg4747. [80] CHUN YS, KIM M, LEE S, et al. MEK1/2 inhibition rescues neurodegeneration by TFEB-mediated activation of autophagic lysosomal function in a model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(11):4770-4780. [81] ZHOU X, CHEN X, CHENG X, et al. Paeoniflorin, ferulic acid, and atractylenolide III improved LPS-induced neuroinflammation of BV2 microglia cells by enhancing autophagy. J Pharmacol Sci. 2023;152(2):151-161. [82] MENG X, LUO Y, LIANG T, et al. Gypenoside XVII Enhances Lysosome Biogenesis and Autophagy Flux and Accelerates Autophagic Clearance of Amyloid-beta through TFEB Activation. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;52(3):1135-1150. [83] LIN J, YUAN Y, HUANG C, et al. TFEB agonist clomiphene citrate activates the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease symptoms in mice. J Biol Chem. 2024;300(12):107929. [84] XIE Z, ZHAO J, WU L, et al. Hederagenin improves Alzheimer’s disease through PPARα/TFEB-mediated autophagy[J]. Phytomedicine. 2023;112:154711. [85] CHENG D, TAN Q, ZHU Q, et al. TFEB Probably Involved in Midazolam-Disturbed Lysosomal Homeostasis and Its Induced beta-Amyloid Accumulation. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019;13:108. [86] ZHENG X, LIN W, JIANG Y, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates beta-amyloid pathology and cognitive impairment in Alzheimer disease via a novel mechanism involving activation of TFEB (transcription factor EB). Autophagy. 2021;17(11): 3833-3847. [87] LIN W, LI Z, LIANG G, et al. TNEA therapy promotes the autophagic degradation of NLRP3 inflammasome in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via TFEB/TFE3 activation. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):21. [88] WANG X, XIE Y, CHEN G, et al. Intermittent hypoxia therapy ameliorates beta-amyloid pathology via TFEB-mediated autophagy in murine Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2023;20(1):240. [89] WANG X, XIE Y, FAN X, et al. Intermittent hypoxia training enhances Abeta endocytosis by plaque associated microglia via VPS35-dependent TREM2 recycling in murine Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024;16(1):121. [90] AKWA Y, Di MALTA C, ZALLO F, et al. Stimulation of synaptic activity promotes TFEB-mediated clearance of pathological MAPT/Tau in cellular and mouse models of tauopathies. Autophagy. 2023;19(2): 660-677. [91] JIAN Y, YUAN S, YANG J, et al. Aerobic Exercise Alleviates Abnormal Autophagy in Brain Cells of APP/PS1 Mice by Upregulating AdipoR1 Levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9921. [92] WANG X, ZHU Y, ZHU Y, et al. Long-term running exercise alleviates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PSEN1 transgenic mice via enhancing brain lysosomal function. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(4):850-861. [93] LI Y, XU D, HO S, et al. A theranostic agent for in vivo near-infrared imaging of beta-amyloid species and inhibition of beta-amyloid aggregation. Biomaterials. 2016;94:84-92. [94] IYASWAMY A, WANG X, KRISHNAMOORTHI S, et al. Theranostic F-SLOH mitigates Alzheimer’s disease pathology involving TFEB and ameliorates cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease models. Redox Biol. 2022;51:102280. [95] ITTNER LM, KLUGMANN M, KE YD. Adeno-associated virus-based Alzheimer’s disease mouse models and potential new therapeutic avenues. Br J Pharmacol. 2019; 176(18):3649-3665. [96] MURATORE CR, RICE HC, SRIKANTH P, et al. The familial Alzheimer’s disease APPV717I mutation alters APP processing and Tau expression in iPSC-derived neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(13):3523-3536. [97] HOSSINI AM, MEGGES M, PRIGIONE A, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuronal cells from a sporadic Alzheimer’s disease donor as a model for investigating AD-associated gene regulatory networks. BMC Genomics. 2015;16(1):84. [98] CHOE MS, YEO HC, KIM JS, et al. Simple modeling of familial Alzheimer’s disease using human pluripotent stem cell-derived cerebral organoid technology. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):118. [99] GAO G, LI C, MA Y, et al. Neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):228. [100] MUBARIZ F, SAADIN A, LINGENFELTER N, et al. Deregulation of mTORC1-TFEB axis in human iPSC model of GBA1-associated Parkinson’s disease. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1152503. |
| [1] | 刘安南, 李建辉, 高 伟, 李 雪, 宋 婧, 邢丽萍, 李虹霖. 铁死亡与阿尔茨海默病的文献计量学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4278-4288. |
| [2] | 苏 琴, 贾思玮, 郭敏芳, 孟 涛, 李雁冰, 穆秉桃, 宋丽娟, 马存根, 尉杰忠. 枸杞多糖干预β-淀粉样蛋白1-42诱导SH-SY5Y细胞损伤:线粒体自噬的保护作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(31): 6688-6696. |
| [3] | 郭敏芳, 张慧宇, 章培军, 苏 琴, 贾思玮, 尉杰忠. 法舒地尔缓解β-淀粉样蛋白1-42诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(23): 4939-4946. |
| [4] | 张松江, 李龙洋, 周春光. α7烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体与阿尔茨海默病的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(18): 3915-3924. |
| [5] | 江 强, 于 洁, 耿子翔, 王 宁, 郭 嘉, 杨光月, 王培歌, 赵咏芳. 两种肌少症小鼠模型的功能表型、肌肉质量及力量特点比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(14): 2922-2929. |
| [6] | 温华能, 林 润, 王逸潇, 王冰水, 刘 璐, 刘传耀, 蔡灿鑫, 崔韶阳, 许明珠. 电针“智三针”对5xFAD小鼠Notch信号通路及突触可塑性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(32): 5148-5153. |
| [7] | 温小雨, 孙玉浩, 夏 猛. 五脏温阳化瘀汤含药血清干预阿尔茨海默症细胞模型磷酸化tau蛋白的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1068-1073. |
| [8] | 周世成, 韩宏光, 季 芳, 徐莉莹, 张晓慧, 孙 畅. 改良Blalock-Taussig分流术中应用膨体聚四氟乙烯人工血管的效果与组织相容性分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(21): 3394-3400. |
| [9] | 王金春, 刘慧影, 曹云鹏. tau蛋白与阿尔茨海默病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(17): 2775-2781. |
| [10] | 王 薇,张海廷,王淑辉,张拥波. 阿尔茨海默病与Wnt信号通路及神经干细胞的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(19): 3566-3572. |
| [11] | 马惠萍,吕心瑞,史鸿云,石镇霞,李新春,李 峥. 神经生长因子预处理阿尔茨海默病大鼠海马神经原磷酸化Tau蛋白的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(46): 8641-8646. |
| [12] | 赵庆霞,李冰华,韩雪飞,许 燕,吴国华. 人参皂苷Rb1对β-淀粉样蛋白25-35诱导神经干细胞分化过程中Tau蛋白过度磷酸化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(41): 7713-7716. |
| [13] | 李 俊,赵天春,段 萍,韩雪飞,梁 晨,邢 莹. β-淀粉样蛋白诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化过程中Tau蛋白的过度磷酸化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011, 15(40): 7425-7428. |
| [14] | 王海红,董为人,张 琳,晏 芳,刘忠英,李 妍. 真核表达质粒pcDNA3.1-tau的构建及在HEK293细胞中的稳定表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011, 15(28): 5295-5298. |
| [15] | 赵庆霞,刘小转,李 博,鄢文海,韩雪飞,邢 莹. β-淀粉样蛋白25~35和人参皂苷Rb1对神经干细胞分化过程中tau蛋白磷酸化水平的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2011, 15(27): 5076-5079. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2025年1月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2025年1月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方、维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Alzheimer Disease,AD,Transcription Factor EB,TFEB,Autophagy-lysosome Pathway,Autophagy,Lysosomes,Amyloid beta,Aβ,Tau,Tau protein”,中文检索词为“阿尔茨海默病,转录因子EB,自噬溶酶体,自噬、溶酶体,β-淀粉样蛋白,Tau”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 检索文献类型主要是研究原著。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 手工补充检索与该文主题相关的参考文献。
1.1.7 检索策略 以中国知网与PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索得到文献4 307篇,包括英文文献3 477篇、中文文献830篇,其中PubMed数据库1 287篇,Web of Science数据库2 178篇,和Cochrane Library数据库12篇,中国知网327篇、万方数据库235篇、维普数据库268篇。手动补充与该文主题相关的英文文献5篇。
1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:①研究内容与阿尔茨海默病相关,必须涉及以下至少一个关键词:转录因子EB、自噬-溶酶体通路、自噬、溶酶体、β-淀粉样蛋白、Tau;②研究类型选择原创性研究(如基础研究、临床研究),即研究原著
(article);③优先选择最近15内发表的文献;④主要收录中英文文献。
排除标准:①非研究原著,如综述、评论、病例报告、会议摘要、社论、信件等;②没有涉及上述关键词的研究;③重复发表文献,同一研究在不同期刊发表,则只保留最先发表或主要版本;④无法获取全文或数据不全的文献以及观点陈旧或存在争议的文献。1.3 文献质量评价和筛选 共检索到4 307篇文献,初筛剔除重复文献2 013篇后,通过泛读对剩余文献的标题、摘要进行筛选,选取与该文主题更为相符的文献,最终纳入符合要求的文献100篇。文献筛选流程详见图2。
阿尔茨海默病是一种极其复杂的疾病,发病机制并不完全明确,但目前许多现有研究已强调自噬溶酶体途径损伤导致β-淀粉样蛋白及Tau等毒性蛋白聚集清除受阻,在阿尔茨海默病发病机制中发挥着重要作用。而转录因子EB是自噬溶酶体途径的主要调节因子,它的活性调控着许多自噬相关基因的转录及溶酶体的生物发生。随着对转录因子EB在阿尔茨海默病病理的深入研究,人们也发现了一些转录因子EB激动剂及非药物手段在阿尔茨海默病动物模型中的神经保护作用,故而体现出转录因子EB介导的自噬溶酶体在阿尔茨海默病的治疗中的巨大潜力。然而,转录因子EB的功能研究和临床转化面临显著技术瓶颈,主要体现在修饰检测技术的滞后导致调控工具设计缺乏分子基础,而递送技术的局限又阻碍了修饰机制的体内验证,同时转录因子EB与其他通路交互网络解析困难。在修饰检测方面,转录因子EB的生理病理功能受多重翻译后修饰动态调控,但现有技术在临床转化后难以量化调控转录因子EB的激酶网络在体内活性状态,翻译后修饰功能关联机制研究受阻,构建模拟特定修饰状态的转基因动物模型成本高昂且难以复现复杂修饰网络;在调控工具方面,递送系统中载体血脑屏障穿透性差且存在脱靶风险,小分子激活剂因脱靶效应和缺乏修饰特异性(如无法选择性调节泛素化或磷酸化),无法实现病变神经元的精准靶向;在交互网络方面,转录因子EB与线粒体自噬、免疫信号、炎症因子等通路存在复杂串扰,但缺乏多通路同步分析工具,存在过度激活后可能诱发溶酶体贮积症或肿瘤等风险。在后续研究中可通过腺相关病毒衣壳定向进化构建携带转录因子EB的神经元载体、类器官模型筛选和设计变构调控剂等方法,逐步破解技术层面障碍,方能释放转录因子EB作为阿尔茨海默病治疗靶点的转化潜力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
转录因子EB调控自噬溶酶体通路代表阿尔茨海默症治疗的范式转变:从单一靶点转向“清除-保护-调节”三位一体策略。其独特价值在于同步化解β淀粉样蛋白/Tau毒性、重建神经元代谢稳态,且新兴递送技术已初步攻克脑靶向难题。未来需聚焦病理阶段适应性给药及转录因子EB联合免疫调节的精准方案,推动临床转化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||