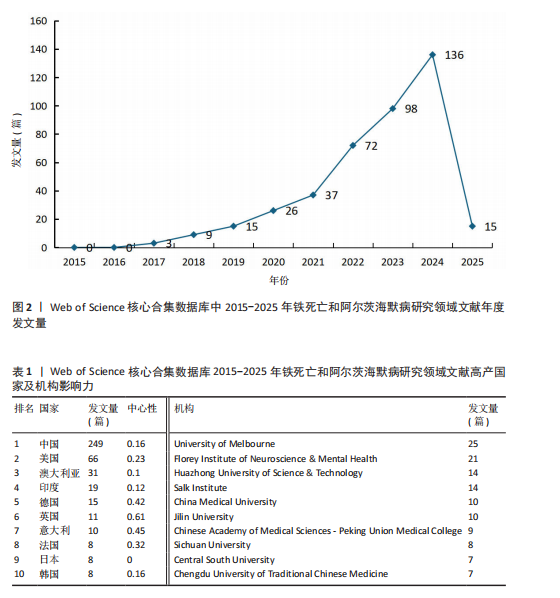
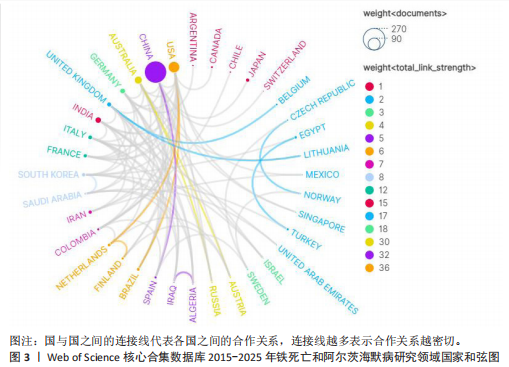
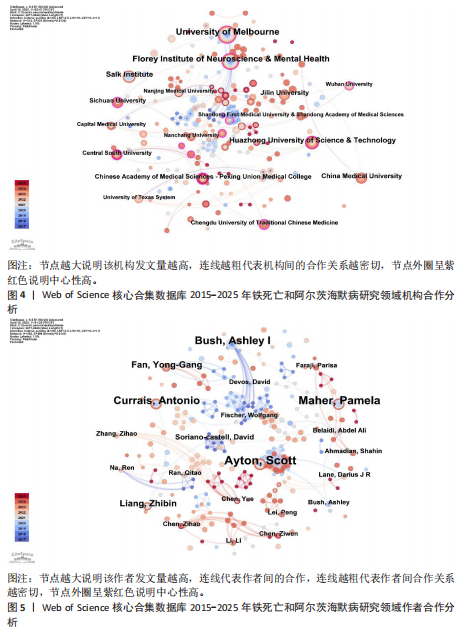
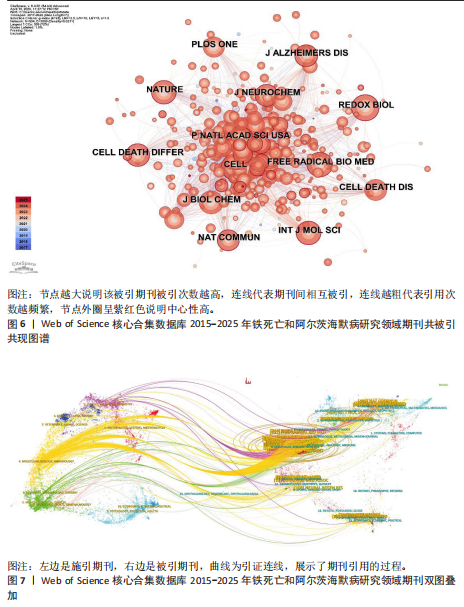
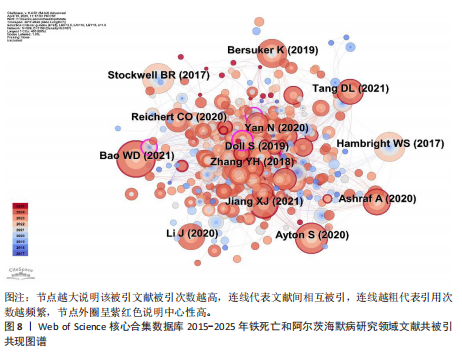
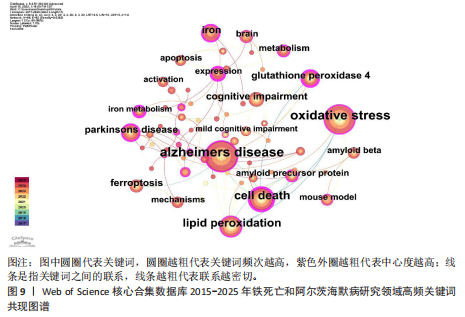
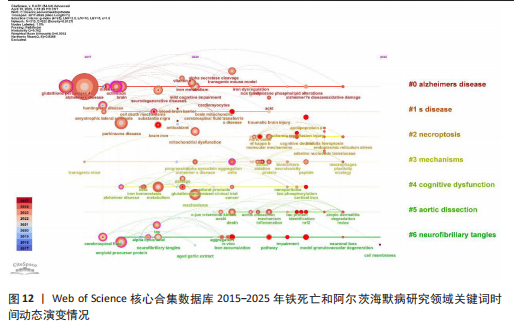
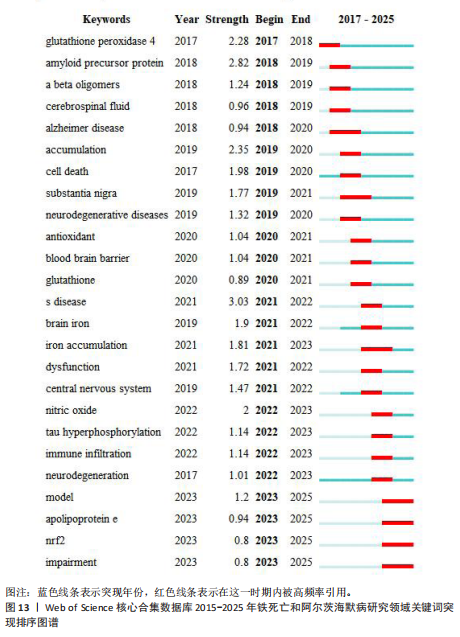
[1] SCHELTENS P, DE STROOPER B, KIVIPELTO M, et al. Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet. 2021; 397:1577-1590.
[2] GUSTAVSSON A, NORTON N, FAST T, et al. Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimers Demen. 2023;19(2):658-670.
[3] ZHANG XX, TIAN Y, WANG ZT, et al. The Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s Disease Modifiable Risk Factors and Prevention. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2021;8(3):313-321.
[4] GOETZL EJ. Current Developments in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am J Med. 2025; 138(1):15-20.
[5] THE LANCET N. Treatment for Alzheimer’s disease: time to get ready. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(6):455.
[6] LIU E, ZHANG Y, WANG JZ. Updates in Alzheimer’s disease: from basic research to diagnosis and therapies. Transl Neurodegener. 2024;13(1):45.
[7] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(4):266-282.
[8] FENG L, SUN J, XIA L, et al. Ferroptosis mechanism and Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2024;19(8):1741-1750.
[9] LEI P, AYTON S, BUSH AI. The essential elements of Alzheimer’s disease. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100105.
[10] BAO WD, PANG P, ZHOU XT, et al. Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(5):1548-1562.
[11] LI D, YU D, LI Y, et al. A bibliometric analysis of PROTAC from 2001 to 2021. Eur J Med Chem. 2022;244:114838.
[12] REDONDO M, LEON L, POVEDANO FJ, et al. A bibliometric study of the scientific publications on patient-reported outcomes in rheumatology. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2017;46(6):828-833.
[13] GLEASON A, BUSH AI. Iron and Ferroptosis as Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics. 2021;18(1):252-264.
[14] AYTON S, WANG Y, DIOUF I, et al. Brain iron is associated with accelerated cognitive decline in people with Alzheimer pathology. Mol Psychiatry. 2020;25(11):2932-2941.
[15] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell. 2017;171(2): 273-285.
[16] HAMBRIGHT WS, FONSECA RS, CHEN L, et al. Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 2017; 12:8-17.
[17] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019; 575(7784):688-692.
[18] DOLL S, FREITAS FP, SHAH R, et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature. 2019;575(7784):693-698.
[19] YAN N, ZHANG J. Iron Metabolism, Ferroptosis, and the Links With Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 2020;13:1443.
[20] ASHRAF A, JEANDRIENS J, PARKES HG, et al. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020;32:101494.
[21] LI J, CAO F, YIN HL, et al. Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2020; 11(2):88.
[22] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[23] INGOLD I, BERNDT C, SCHMITT S, et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell. 2018;172(3):409-422.e21.
[24] AYTON S, FAZLOLLAHI A, BOURGEAT P, et al. Cerebral quantitative susceptibility mapping predicts amyloid-β-related cognitive decline. Brain. 2017;140(8):2112-2119.
[25] ATES G, GOLDBERG J, CURRAIS A, et al. CMS121, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, protects against excess lipid peroxidation and inflammation and alleviates cognitive loss in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2020;36: 101648.
[26] BELAIDI AA, BUSH AI. Iron neurochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: targets for therapeutics. J Neurochem. 2016;139 Suppl 1:179-197.
[27] RU Q, LI Y, CHEN L, et al. Iron homeostasis and ferroptosis in human diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):271.
[28] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13(1):91-98.
[29] GALLUZZI L, VITALE I, AARONSON SA, et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(3):486-541.
[30] AI Y, XING Y, YAN L, et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Depression: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2001 to 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:775329.
[31] ZHOU X, KANG C, HU Y, et al. Study on insulin resistance and ischemic cerebrovascular disease: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace. Front Public Health. 2023;11:1021378.
[32] LIU S, SUN YP, GAO XL, et al. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in Alzheimer’s disease: a scientometric review based on CiteSpace analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9):1643-1650.
[33] 《中国应对阿尔茨海默病战略行动计划》建议书[J].科技导报,2021,39(20):149.
[34] BERNDT C, ALBORZINIA H, AMEN VS, et al. Ferroptosis in health and disease. Redox Biol. 2024;75:103211.
[35] NIKSERESHT S, BUSH AI, AYTON S. Treating Alzheimer’s disease by targeting iron. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(18):3622-3635.
[36] AYTON S, BARTON D, BREW B, et al. Deferiprone in Alzheimer Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2025;82(1):11-18.
[37] SCHUBERT D, CURRAIS A, GOLDBERG J, et al. Geroneuroprotectors: Effective Geroprotectors for the Brain. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(12):1004-1007.
[38] MAHER P, CURRAIS A, SCHUBERT D. Using the Oxytosis/Ferroptosis Pathway to Understand and Treat Age-Associated Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(12):1456-1471.
[39] KEPCHIA D, CURRAIS A, DARGUSCH R, et al.Geroprotective effects of Alzheimer’s disease drug candidates. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(3):3269-3289.
[40] XU D, WANG YL, WANG KT, et al. A Scientometrics Analysis and Visualization of Depressive Disorder. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(6):766-786.
[41] HIRSCHHORN T, STOCKWELL BR. The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;133:130-143.
[42] STOCKWELL BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 2022;185(14):2401-2421.
[43] CHEN Z, TAO S, LI X, et al. Anagliptin protects neuronal cells against endogenous amyloid β (Aβ)-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):2213-2220.
[44] MOU Y, WANG J, WU J, et al. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12(1):34.
[45] LIU JL, FAN YG, YANG ZS, et al. Iron and Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Implications. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:632.
[46] BENSENY-CASES N, KLEMENTIEVA O, COTTE M, et al. Microspectroscopy (μFTIR) reveals co-localization of lipid oxidation and amyloid plaques in human Alzheimer disease brains. Anal Chem. 2014;86(24):12047-12054.
[47] PEÑA-BAUTISTA C, BAQUERO M, VENTO M, et al. Free radicals in Alzheimer’s disease: Lipid peroxidation biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;491:85-90.
[48] LLORET A, ESTEVE D, MONLLOR P, et al. The Effectiveness of Vitamin E Treatment in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(4):879.
[49] JIMÉNEZ-JIMÉNEZ FJ, ALONSO-NAVARRO H, GARCÍA-MARTÍN E, et al. Coenzyme Q10 and Dementia: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(2):533.
[50] WANG F, WANG J, SHEN Y, et al. Iron Dyshomeostasis and Ferroptosis: A New Alzheimer’s Disease Hypothesis? Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:830569.
[51] JIANG S, LIU Y, ZHENG H, et al. Evolutionary patterns and research frontiers in neoadjuvant immunotherapy: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Surg. 2023;109(9):2774-2783.
[52] SELKOE DJ, HARDY J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med. 2016;8(6):595-608.
[53] OROBETS KS, KARAMYSHEV AL. Amyloid Precursor Protein and Alzheimer’s Disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2011;34:185-204.
[54] CHO Y, BAE HG, OKUN E, et al. Physiology and pharmacology of amyloid precursor protein. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;235:108122.
[55] ZHENG J, CONRAD M. The Metabolic Underpinnings of Ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020;32(6):920-937.
[56] PENG Y, CHANG X, LANG M. Iron Homeostasis Disorder and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12442.
[57] WU L, XIAN X, TAN Z, et al. The Role of Iron Metabolism, Lipid Metabolism, and Redox Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease: from the Perspective of Ferroptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(5):2832-2850.
|