[1] GREGSON CL, ARMSTRONG DJ, BOWDEN J, et al. UK clinical guideline for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2022;17(1):58.
[2] 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查及“健康骨骼”专项行动结果发布[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2019,12(4):317-318.
[3] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2037.
[4] ONO T, HAYASHI M, SASAKI F, et al. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:2.
[5] NINKOV A, FRANK JR, MAGGIO LA. Bibliometrics: Methods for studying academic publishing. Perspect Med Educ. 2022;11(3):173-176.
[6] KOKOL P, BLAUN VH, ZAVRNIK J. Application of bibliometrics in medicine: a historical bibliometrics analysis. Health Info Libr J. 2021;38(2):125-138.
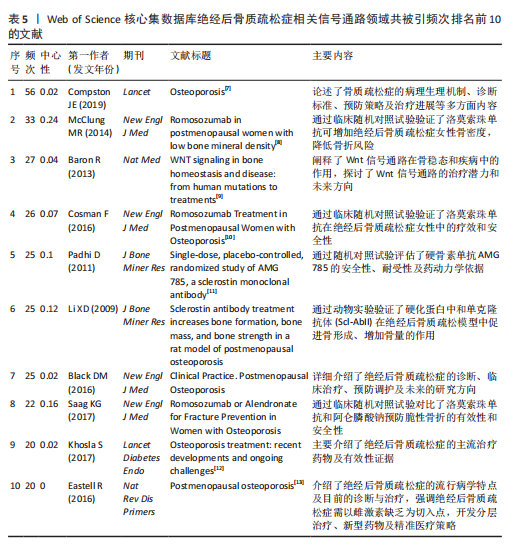
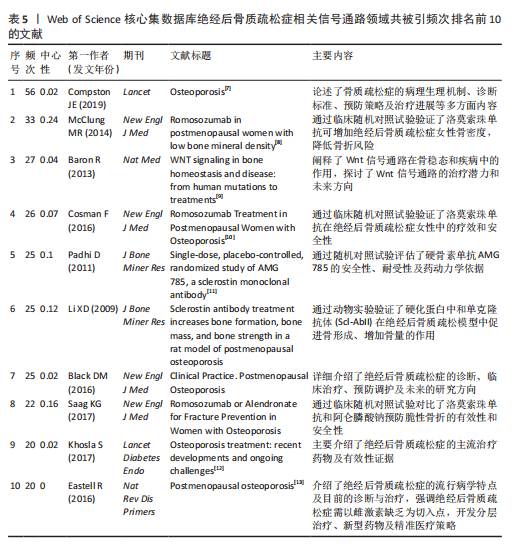
[7] COMPSTON JE, MCCLUNG MR, LESLIE WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169): 364-376.
[8] MCCLUNG MR, GRAUER A, BOONEN S, et al. Romosozumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(5):412-420.
[9] BARON R, KNEISSEL M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: from human mutations to treatments. Nat Med. 2013;19(2):179-192.
[10] COSMAN F, CRITTENDEN DB, ADACHI JD, et al. Romosozumab Treatment in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(16):1532-1543.
[11] PADHI D, JANG G, STOUCH B, et al. Single-dose, placebo-controlled, randomized study of AMG 785, a sclerostin monoclonal antibody. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(1):19-26.
[12] KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis treatment: recent developments and ongoing challenges. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(11):898-907.
[13] EASTELL R, O’NEILL TW, HOFBAUER LC, et al. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:6069.
[14] LU L, TIAN L. Postmenopausal osteoporosis coexisting with sarcopenia: the role and mechanisms of estrogen. J Endocrinol. 2023;259(1):e230116.
[15] WANG T, LIU Q, ZHOU L, et al. Andrographolide Inhibits Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss via the Suppression of RANKL Signaling Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):27470-27481.
[16] YANG X, LIANG J, WANG Z, et al. Sesamolin Protects Mice From Ovariectomized Bone Loss by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and RANKL-Mediated NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:664697.
[17] ZHANG L, SUN Y, XU W, et al. Baicalin inhibits Salmonella typhimurium-induced inflammation and mediates autophagy through TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;128(2):241-255.
[18] CAPECE D, VERZELLA D, FLATI I, et al. NF-κB: blending metabolism, immunity, and inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2022; 43(9):757-775.
[19] WAJANT H, PFIZENMAIER K, SCHEURICH P. Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10(1):45-65.
[20] BAUD V, KARIN M. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8(1):33-40.
[21] HOESEL B, SCHMID JA. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:86.
[22] YAMASHITA T, YAO Z, LI F, et al. NF-kappaB p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL) and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(25): 18245-18253.
[23] ZHENG LW, WANG WC, MAO XZ, et al. TNF-α regulates the early development of avascular necrosis of the femoral head by mediating osteoblast autophagy and apoptosis via the p38 MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(9): 1881-1889.
[24] ZUO Q, LIU J, HUANG L, et al. AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene. 2018;37(24):3275-3289.
[25] WHANG YE, WU X, SUZUKI H, et al. Inactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN/MMAC1 in advanced human prostate cancer through loss of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(9):5246-5250.
[26] GAO X, QIN T, MAO J, et al. PTENP1/miR-20a/PTEN axis contributes to breast cancer progression by regulating PTEN via PI3K/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1): 256.
[27] LI X, MIAO C, WANG L, et al. Estrogen promotes Epithelial ovarian cancer cells proliferation via down-regulating expression and activating phosphorylation of PTEN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2023;743:109662.
[28] SUGATANI T, ALVAREZ U, HRUSKA KA. PTEN regulates RANKL- and osteopontin-stimulated signal transduction during osteoclast differentiation and cell motility. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(7):5001-5008.
[29] 叶恒,张卫华,韩俊,等.miR-26a-5p靶向PTEN基因影响成骨细胞分化及基质矿化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(8):1126-1130+1138.
[30] LORENZ J, RICHTER S, KIRSTEIN AS, et al. Pten knockout in mouse preosteoblasts leads to changes in bone turnover and strength. JBMR Plus. 2024;8(3):ziad16.
[31] SATO Y, HABARA M, HANAKI S, et al. Calcineurin/NFATc1 pathway represses cellular cytotoxicity by modulating histone H3 expression. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):14732.
[32] NEGISHI-KOGA T, TAKAYANAGI H. Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast differentiation. Immunol Rev. 2009;231(1):241-256.
[33] LEE JU, KIM LK, CHOI JM. Revisiting the Concept of Targeting NFAT to Control T Cell Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2747.
[34] OMATA Y, TACHIBANA H, AIZAKI Y, et al. Essentiality of Nfatc1 short isoform in osteoclast differentiation and its self-regulation. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18797.
[35] TAKAYANAGI H, KIM S, KOGA T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002;3(6):889-901.
[36] LI X, YANG L, GUO Z. miR-193-3p ameliorates bone resorption in ovariectomized mice by blocking NFATc1 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(11):4077-4086.
[37] LIU L, WU S, WEI L, et al. Romosozumab adverse event profile: a pharmacovigilance analysis based on the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 2019 to 2023. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2025;37(1):23.
[38] MILLER SA, ST OE, WHALEN KL. Romosozumab: A Novel Agent in the Treatment for Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. J Pharm Technol. 2021; 37(1):45-52.
[39] 彭越,岳梦圆,邹佳盈,等.传统中药与激素治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的有效性和安全性比较[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2023,25(1):46-55.
[40] CHEN Y, LI X, TANG X, et al. Combined Extracts of Herba Epimedii and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi Rebalance Bone Remodeling in Ovariectomized Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:1596951.
[41] LUO Y, XIA H, WANG J, et al. Jiawei Yanghe Decoction Regulates Bone-Lipid Balance through the BMP-SMAD Signaling Pathway to Promote Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:2885419.
[42] ZHANG R, ZHU X, BAI H, et al. Network Pharmacology Databases for Traditional Chinese Medicine: Review and Assessment. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:123.
[43] ZHOU Z, CHEN B, CHEN S, et al. Applications of Network Pharmacology in Traditional Chinese Medicine Research. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:1646905.
|