[1] 胡盛寿.《先天性心脏病外科治疗中国专家共识》述评[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2021,28(1):1-3.
[2] 宋晓琪,杜欣为,王顺民,等.基于回归分析和机器学习的先天性心脏病患儿术后住院死亡预测模型的建立—单中心12年大数据汇总分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2020,36(2):65-73.
[3] 葛同开,陈寄梅,庄建,等.改良Blalock-Taussig分流术治疗新生儿期紫绀型先天性心脏病的疗效分析[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2020,27(7):737-741.
[4] YUAN SM, SHINFELD A, RAANANI E. The Blalock-Taussig shunt. J Card Surg. 2009;24(2):101-108.
[5] BREDY C, MINISTERI M, KEMPNY A, et al. New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification in adults with congenital heart disease: relation to objective measures of exercise and outcome. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. 2018;4(1):51-58.
[6] 刘玉洁,徐卓明,朱丽敏,等.新生儿改良Blalock-Taussing分流术后疗效的影响因素[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2018,34(10):577-580.
[7] 严拓,刘雅文,吴灿,等.人工血管研究现状与应用优势[J].中国组织工程究,2018,22(30):4849-4854.
[8] 单亚平,张惠锋,叶明,等.生物修饰ePTFE促进内皮化的研究[J].中华小儿外科杂志,2018,39(3):219-224.
[9] POLLMANN AS, LEWIS DR, GUPTA RR. Structural integrity of intraocular lenses with eyelets in a model of transscleral fixation with the Gore-Tex suture. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2020;46(4):617-621.
[10] 何艳平,马德春,李磊,等.人工血管材料血液相容性及表面改性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(8):1272-1276.
[11] 杨柳,姜南,徐扬阳,等.膨体聚四氟乙烯与人脂肪干细胞的体外生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(12):1932-1937.
[12] HAGDORN QAJ, BERGER RMF. Setting the stage for increasing diversity in congenital cardiology: let’s celebrate the 75th anniversary of the Blalock-Thomas-Taussig shunt. Cardiol Young. 2020;30(3):446-447.
[13] DAVE HH. Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: simple but unpredictable. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;50(1):178-179.
[14] ZURAKOWSKI D, JONAS RA. The many factors leading to resurgence of the Blalock shunt for tetralogy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2): 396-399.
[15] 张本,龚德军,张锡武,等.磷酰胆碱表面改性增强聚四氟乙烯心脏瓣膜材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(34): 5509-5514.
[16] 陈宝林.王东安.用于心血管医疗装置的聚合物材料表面构建与生物相容性评价:聚合物生物材料表面的内皮细胞组织工程化改性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(30):4515-4523.
[17] MUMTAZ MA, ROSENTHAL G, QURESHI A, et al. Melbourne shunt promotes growth of diminutive central pulmonary arteries in patients with pulmonary atresia, ventricular septal defect, and systemic-to-pulmonary collateral arteries. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(6):2079-2084.
[18] LI D, WANG Y, LIN K, et al. Modified Blalock-Taussig Shunt: A Single-Center Experience and Follow-Up. Heart Surg Forum. 2020;23(1): E53-E57.
[19] CAO JY, PHAN K, AYER J, et al. Long term survival of hypoplastic left heart syndrome infants: Meta-analysis comparing outcomes from the modified Blalock-Taussig shunt and the right ventricle to pulmonary artery shunt. Int J Cardiol. 2018;254:107-116.
[20] 孙阳雪,闫军.改良Blalock-Taussig分流术分流管道选择策略研究进展[J].临床军医杂志,2020,48(4):472-474.
[21] 朱耀斌,张雅娉,李志强,等.先天性心脏病改良Blalock-Taussig管道闭塞的危险因素分析[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2020,34(2): 125-127.
[22] MOOFUVONG M, TANASANSUTTIPORN J, WASINWONG W, et al. Predictors of death after receiving a modified Blalock-Taussig shunt in cyanotic heart children: A competing risk analysis. PLoS One. 2021; 16(1):e245754.
[23] CHITTITHAVORN V, DUANGPAKDEE P, RERGKLIANG C, et al. Risk factors for in-hospital shunt thrombosis and mortality in patients weighing less than 3 kg with functionally univentricular heart undergoing a modified Blalock-Taussig shunt. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017;25(3): 407-413.
[24] 姜正明,陈魁,胡彩娜.聚四氟乙烯人工血管对血小板聚集的影响及细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(47):7064-7069.
[25] MOUSAVI SR, MOATAMEDI MR, AKBARI-MM. Comparing frozen saphenous vein with Gore-tex in vascular access for chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial Int. 2011;15(4):559-562.
[26] 李建民.膨体聚四氟乙烯假体隆鼻整形的效果:随机对照临床试验方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):980-984.
[27] 侯亮,张扬,孙轶峰,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞复合两种填充材料体外生物相容性的比较[J].中国美容医学,2017,26(7):48-52.
[28] GEDICKE M, MORGAN G, PARRY A, et al. Risk factors for acute shunt blockage in children after modified Blalock-Taussig shunt operations. Heart Vessels. 2010;25(5):405-409.
[29] 李丹,王旭,李霞,等.先天性心脏病体-肺分流术后管道梗阻的早中期结果及危险因素分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2019, 35(3):145-149.
[30] AHMAD U, FATIMI SH, NAQVI I, et al. Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: immediate and short-term follow-up results in neonates. Heart Lung Circ. 2008;17(1):54-58.
[31] SAHOO M, SAHU M, KALE S, et al. Serous fluid leakage following modified Blalock-Taussig operation using PTFE grafts. Indian Heart J. 2001;53(3):328-331.
[32] ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Study on the correlation of modified Blalock Taussig duct occlusion and platelet parameters in congenital heart disease. Asian J Surg. 2019;42(5):599-603.
[33] WELLS WJ, YU RJ, BATRA AS, et al. Obstruction in modified Blalock shunts: a quantitative analysis with clinical correlation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(6):2072-2076.
[34] MOHAMMADI S, BENHAMEID O, CAMPBELL A, et al. Could we still improve early and interim outcome after prosthetic systemic-pulmonary shunt? A risk factors analysis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34(3):545-549.
[35] ZHOU T, WANG Y, LIU J, et al. Pulmonary artery growth after Modified Blalock-Taussig shunt: A single center experience. Asian J Surg. 2020; 43(2):428-437.
[36] ABDELMASSIH AF, MENSHAWEY R, MENSHAWEY E, et al. Blalock-Taussig Shunt versus Ductal Stent in the Palliation of Duct Dependent Pulmonary Circulation; A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2021;100885. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2021.100885.
[37] BOUMA BJ, MULDER BJ. Changing Landscape of Congenital Heart Disease. Circ Res. 2017;120(6):908-922.
[38] MOUSAVI SR, MOATAMEDI MR, AKBARI MM. Comparing frozen saphenous vein with Gore-tex in vascular access for chronic hemodialysis. Hemodial Int. 2011;15(4):559-562.
[39] WILLIAMS JA, BANSAL AK, KIM BJ, et al. Two thousand Blalock-Taussig shunts: a six-decade experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(6):2070-2075.
[40] LI JS, YOW E,BEREZNY KY, et al. Clinical outcomes of palliative surgery including a systemic-to-pulmonary artery shunt in infants with cyanotic congenital heart disease: does aspirin make a difference? Circulation. 2007;116(3):293-297.
[41] ALSAGHEIR A, KOZIARZ A, MAKHDOUM A, et al. Duct stenting versus modified alock-Taussig shunt in neonates and infants with duct-dependent pulmonary blood flow: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2021;161(2):379-390.
[42] GEDICKE M, MORGAN G, PARRY A, et al. Risk factors for acute shunt blockage in children after modified Blalock-Taussig shunt operations. Heart Vessels. 2010;25(5):405-409.
[43] SANTORO G, CAPOZZI G, CAIANIELLO G, et al. Pulmonary artery growth after palliation of congenital heart disease with duct-dependent pulmonary circulation: arterial duct stenting versus surgical shunt. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(23):2180-2186.
[44] ARNAZ A, PIŞKIN S, OĞUZ GN, et al.Effect of modified Blalock-Taussig shunt anastomosis angle and pulmonary artery diameter on pulmonary flow. Anatol J Cardiol. 2018;20(1):2-8.
[45] AZBOY D, TEMIZTÜRK Z. Clinical Outcomes after Biologic Graft Use for the Creation of Blalock-Taussig Shunt in Critically Ill Patients with Thrombophilia. Heart Surgery Forum. 2020;23(6):E718-E724.
[46] PEA-TRUJILLO V, GALLO-BERNAL S, MELO JFF. Cardiology in the Young Mediastinal mass after a Blalock-Taussig shunt: utility of CT angiography. Cardiology in the Young. 2020;30(5):722-723.
[47] 张程,王鹏程,吴柯叶,等.新型国产生物源性胶原涂层涤纶血管抗血浆渗出及抗出血性能研究初探[J].中国体外循环杂志,2021, 19(4):235-238.
|
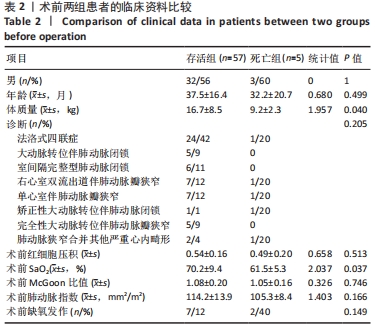
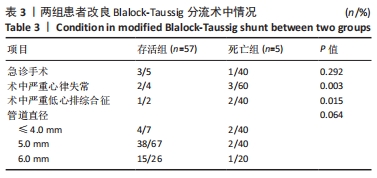

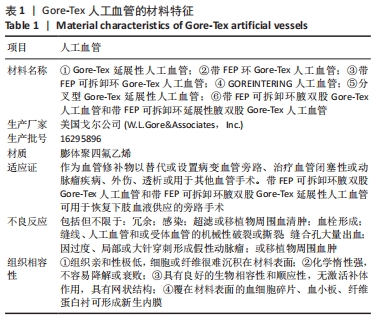
 电镜扫描表面结构显示,膨体聚四氟乙烯人工血管由很多无数细通孔的微细纤维经结点连接成网状结构构成(微孔直径约30 µm)[9]。膨体聚四氟乙烯医用制品柔软富有弹性、强度高、易缝合,裁剪时无毛边和散开现象。国内外研究报道,众多因素影响体-肺动脉分流术后早期分流管道的栓塞或扭曲[28-29]。AHMAD等[30]报道,影响术后早期分流管道栓塞的危险因素是低龄、低体质量和肺动脉细小。人体组织细胞及血管可长入膨体聚四氟乙烯,并在管壁形成内膜,最终紧密地与周围组织结合。人工血管管壁渗液常发生于改良Blalock-Taussig分流术后[31],术中应避免直接钳夹人工血管壁,否则易使管道内表面受损,致疏水性改变,从而造成渗液。可通过工艺条件将膨体聚四氟乙烯纤维网孔大小控制在合理范围内。因此与传统硅橡胶相比,膨体聚四氟乙烯不易漏血,无需进行预凝血处理,组织愈合方式更加优越。
电镜扫描表面结构显示,膨体聚四氟乙烯人工血管由很多无数细通孔的微细纤维经结点连接成网状结构构成(微孔直径约30 µm)[9]。膨体聚四氟乙烯医用制品柔软富有弹性、强度高、易缝合,裁剪时无毛边和散开现象。国内外研究报道,众多因素影响体-肺动脉分流术后早期分流管道的栓塞或扭曲[28-29]。AHMAD等[30]报道,影响术后早期分流管道栓塞的危险因素是低龄、低体质量和肺动脉细小。人体组织细胞及血管可长入膨体聚四氟乙烯,并在管壁形成内膜,最终紧密地与周围组织结合。人工血管管壁渗液常发生于改良Blalock-Taussig分流术后[31],术中应避免直接钳夹人工血管壁,否则易使管道内表面受损,致疏水性改变,从而造成渗液。可通过工艺条件将膨体聚四氟乙烯纤维网孔大小控制在合理范围内。因此与传统硅橡胶相比,膨体聚四氟乙烯不易漏血,无需进行预凝血处理,组织愈合方式更加优越。