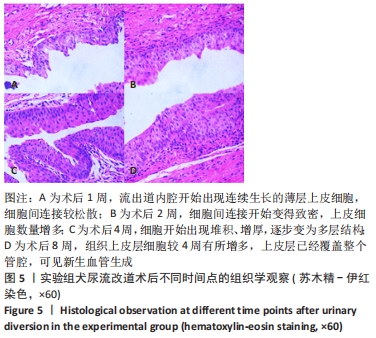
[1] CHUA ME, FARHAT WA, MING JM, et al. Review of clinical experience on biomaterials and tissue engineering of urinary bladder. World J Urol. 2020;38(9): 2081-2093.
[2] ATALA A, DANILEVSKIY M, LYUNDUP A, et al. The potential role of tissue-engineered urethral substitution: clinical and preclinical studies. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(1):3-19.
[3] MACRI A. Modified double-barrelled wet colostomy after total pelvic exenteration. Updates Surg. 2017;69(4):545-548.
[4] ZHOU Z, YAN H, LIU Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem-cell-implanted poly(-caprolactone)/chitosan scaffold improves bladder regeneration in a rat model. Regen Med. 2018;13(3):331-342.
[5] SHIN JH, RYU CM, YU HY, et al. Current and Future Directions of Stem Cell Therapy for Bladder Dysfunction. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(1):82-93.
[6] ADAMOWICZ J, POKRYWCZYNSKA M, VAN BREDA SV, et al. Concise Review: Tissue Engineering of Urinary Bladder; We Still Have a Long Way to Go? Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(11):2033-2043.
[7] ABBAS TO, ALI TA, UDDIN S. Urine as a Main Effector in Urological Tissue Engineering-A Double-Edged Sword. Cells. 2020;9(3):538.
[8] WANG Q, XIAO DD, YAN H, et al. The morphological regeneration and functional restoration of bladder defects by a novel scaffold and adipose-derived stem cells in a rat augmentation model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):149.
[9] SMOLAR J, HORST M, SULSER T, et al. Bladder regeneration through stem cell therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018;18(5):525-544.
[10] MENG L, LIAO W, YANG S, et al. Tissue-engineered tubular substitutions for urinary diversion in a rabbit model. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(2):147-156.
[11] SI Z, WANG X, SUN C, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: Sources, potency, and implications for regenerative therapies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;114:108765.
[12] CHEN Y, TILLMAN B, GO C, et al. A novel customizable stent graft that contains a stretchable ePTFE with a laser-welded nitinol stent. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(4):911-923.
[13] ZHUO Z, DAN H, GENSONG L, et al. Design of a Mechatronics Model of Urinary Bladder and Realization and Evaluation of Its Prototype. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2019;2019:9431781.
[14] HORST M, EBERLI D, GOBET R, et al. Tissue Engineering in Pediatric Bladder Reconstruction-The Road to Success. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:91.
[15] 熊云鹤,杨嗣星,孟令超,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞向尿路上皮分化后构建膀胱组织工程化移植物[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(32):5097-5102.
[16] 李欣慧,廖文彪,李永伟,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与膀胱脱细胞基质的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(51):9567-9573.
[17] WANG JM, GU Y, PAN CJ, et al. Isolation, culture and identification of human adipose-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(3):1039-1043.
[18] FANG B, LIU Y, ZHENG D, et al. The effects of mechanical stretch on the biological characteristics of human adipose-derived stem cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(6):4244-4255.
[19] SHEYKHHASAN M, WONG J, SEIFALIAN AM. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells with great Therapeutic Potential. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(7):532-548.
[20] ZHAO Z, YU H, FAN C, et al. Differentiate into urothelium and smooth muscle cells from adipose tissue-derived stem cells for ureter reconstruction in a rabbit model. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(9):3757-3768.
[21] WANG Y, ZHOU S, YANG R, et al. Bioengineered bladder patches constructed from multilayered adipose-derived stem cell sheets for bladder regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019;85:131-141.
[22] WANG Q, XIAO DD, YAN H, et al. The morphological regeneration and functional restoration of bladder defects by a novel scaffold and adipose-derived stem cells in a rat augmentation model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):149.
[23] CHAN YY, SANDLIN SK, KURZROCK EA, et al. The Current Use of Stem Cells in Bladder Tissue Regeneration and Bioengineering. Biomedicines. 2017;5(1):4.
[24] LI H, XU Y, FU Q, et al. Effects of multiple agents on epithelial differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells in 3D culture Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(17-18):1760-1770.
[25] SHI JG, FU WJ, WANG XX, et al. Transdifferentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells into urothelial cells: potential for urinary tract tissue engineering. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;47(3):737-746.
[26] GASANZ C, RAVENTOS C, MOROTE J. Current status of tissue engineering applied to bladder reconstruction in humans. Actas Urol Esp. 2018;42(7):435-441.
[27] PEREZ JR, KOUROUPIS D, LI DJ, et al. Tissue Engineering and Cell-Based Therapies for Fractures and Bone Defects. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018;6:105.
[28] PETERS JJ, SHINGLETON WB, MORGAN D, et al. Neointimized Gore-Tex graft for ureteral prosthesis in the dog. Urology. 1996;48(3):379-382.
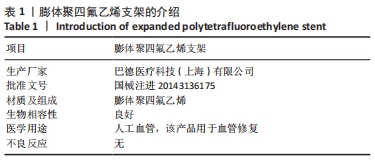
[29] SABANEGH EJ, DOWNEY JR, SAGO AL. Long-segment ureteral replacement with expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts. Urology. 1996;48(2):312-316.
[30] DAS S, GORDIAN-VELEZ WJ, LEDEBUR HC, et al. Innervation: the missing link for biofabricated tissues and organs. NPJ Regen Med. 2020;5:11.
|