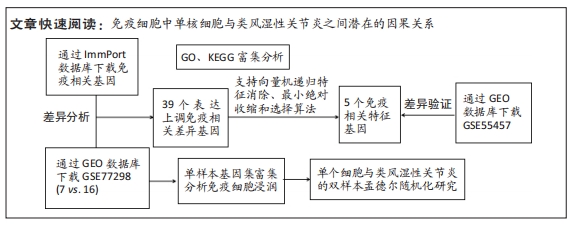
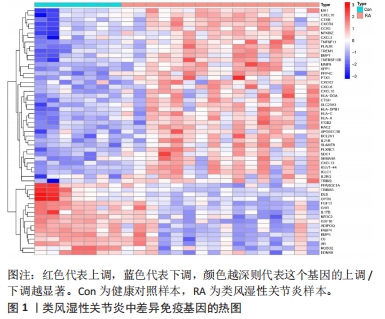
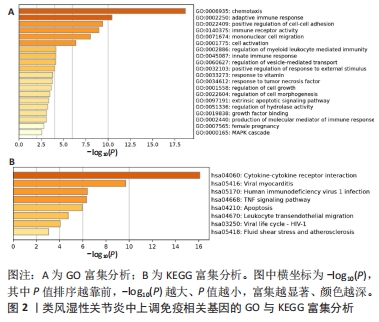
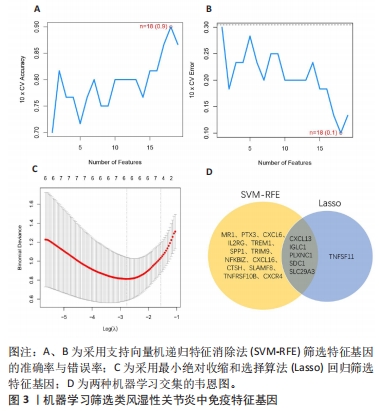
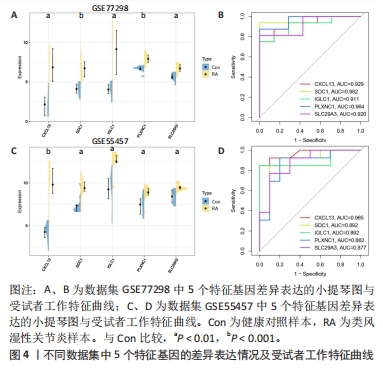
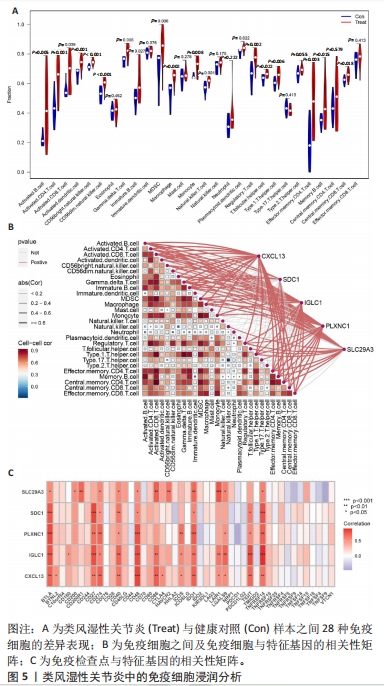
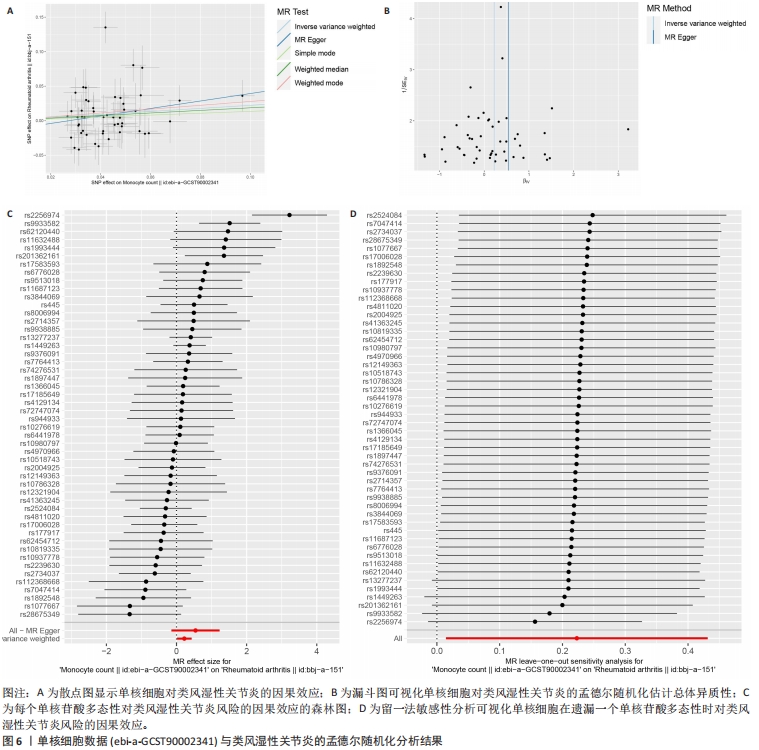
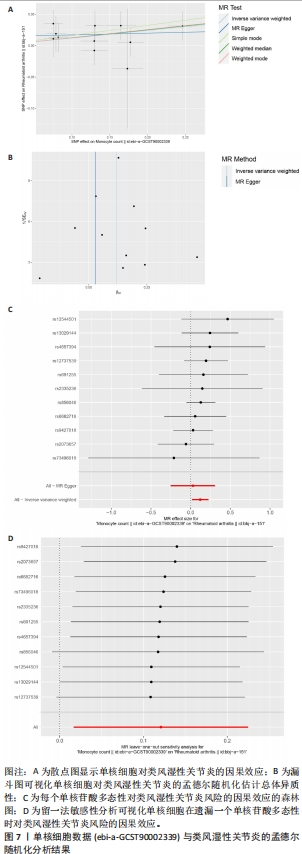
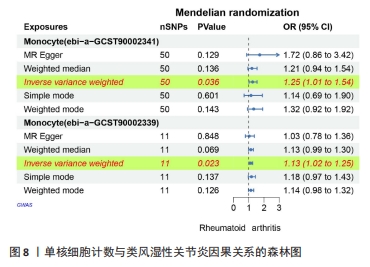
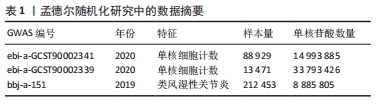
[1] WU R, LONG L, ZHOU Q, et al. Identification of hub genes in rheumatoid arthritis through an integrated bioinformatics approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):1-9.
[2] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the pathomechanism, diagnosis, and treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880.
[3] SMOLEN JS. Insights into the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a paradigm in medicine. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102425.
[4] REN C, LI M, DU W, et al. Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis reveals hub genes and inflammation state of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6943103.
[5] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic roles of diverse immune cells. Int J Mol. 2022;23(2):905.
[6] NEWMAN AM, ALIZADEH AA. High-throughput genomic profiling of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;41:77-84.
[7] ZUO S, WEI M, WANG S, et al. Pan-cancer analysis of immune cell infiltration identifies a prognostic immune-cell characteristic score (ICCS) in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1218.
[8] BOEHM FJ, ZHOU X. Statistical methods for Mendelian randomization in genome-wide association studies: A review. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022;20:2338-2351.
[9] LAMINA C. Mendelian Randomization: Principles and its usage in Lp (a) research. Atherosclerosis. 2022;349:36-41.
[10] XU J, ZHANG S, TIAN Y, et al. Genetic causal association between iron status and osteoarthritis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization. Nutrients. 2022;14(18):3683.
[11] BROEREN MGA, DE VRIES M, BENNINK MB, et al. Disease-regulated gene therapy with anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 under the control of the CXCL10 promoter for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(3):244-254.
[12] NAKAO H, IMAOKA M, HIDA M, et al. Determination of individual factors associated with hallux valgus using SVM-RFE. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):534.
[13] LI Y, LU F, YIN Y. Applying logistic LASSO regression for the diagnosis of atypical Crohn’s disease. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):11340.
[14] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16:1-22.
[15] ZENG Y, CAO S, CHEN M. Integrated analysis and exploration of potential shared gene signatures between carotid atherosclerosis and periodontitis. BMC Med Genomics. 2022;15(1):1-15.
[16] HU FF, LIU CJ, LIU LL, et al. Expression profile of immune checkpoint genes and their roles in predicting immunotherapy response. Brief Bioinform. 2021;22(3):bbaa176.
[17] ROSZKOWSKI L, CIECHOMSKA M. Tuning monocytes and macrophages for personalized therapy and diagnostic challenge in rheumatoid arthritis. Cells. 2021;10(8):1860.
[18] HENRY A, GORDILLO-MARAÑÓN M, FINAN C, et al. Therapeutic targets for heart failure identified using proteomics and Mendelian randomization. Circulation. 2022;145(16):1205-1217.
[19] LIN L, LUO P, YANG M, et al. Causal relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1011246.
[20] SHU MJ, LI JR, ZHU YC, et al. Migraine and ischemic stroke: a Mendelian randomization study. Neurol Ther. 2022;11(1):237-246.
[21] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32: 377-389.
[22] GUDERUD K, SUNDE LH, FLÅM ST, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients, both newly diagnosed and methotrexate treated, show more DNA methylation differences in CD4+ memory than in CD4+ naïve T cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:194.
[23] KONDO N, KURODA T, KOBAYASHI D. Cytokine networks in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):10922.
[24] PAN Z, ZHU T, LIU Y, et al. Role of the CXCL13/CXCR5 axis in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2022;13:850998.
[25] GREISEN SR, SCHELDE KK, RASMUSSEN TK, et al. CXCL13 predicts disease activity in early rheumatoid arthritis and could be an indicator of the therapeutic ‘window of opportunity’. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):1-9.
[26] VAN RAEMDONCK K, UMAR S, PALASIEWICZ K, et al. Interleukin‐34 Reprograms Glycolytic and Osteoclastic Rheumatoid Arthritis Macrophages via Syndecan 1 and Macrophage Colony‐Stimulating Factor Receptor. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(11):2003-2014.
[27] ALZOUBI O, MEYER A, GONZALEZ TP, et al. Significance of IL-34 and SDC-1 in the pathogenesis of RA cells and preclinical models. Clin Immunol. 2023;251:109635.
[28] NI Z, HUANG C, ZHAO H, et al. PLXNC1: A novel potential immune-related target for stomach adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:662707.
[29] COMEAU MR, JOHNSON R, DUBOSE RF, et al. A poxvirus-encoded semaphorin induces cytokine production from monocytes and binds to a novel cellular semaphorin receptor, VESPR. Immunity. 1998;8(4):473-482.
[30] WALZER T, GALIBERT L, COMEAU MR, et al. Plexin C1 engagement on mouse dendritic cells by viral semaphorin A39R induces actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and inhibits integrin-mediated adhesion and chemokine-induced migration. J Immunol. 2005;174(1):51-59.
[31] NOAVAR S, BEHROOZI S, TATARCHEH T, et al. A novel homozygous frame-shift mutation in the SLC29A3 gene: a new case report and review of literature. BMC Med Gene. 2019;20(1):1-7.
[32] ALANSARI S, ALSALEEM A, ALZAID T, et al. The SLC29A3 variant, neutrophilic dermatosis, and hyperferritinemia imitate systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis in a Saudi child: a case report. J Rheum Dis. 2023;30(2):133-137.
[33] STEINZ MM, EZDOGLIAN A, KHODADUST F, et al. Folate receptor beta for macrophage imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 819163.
[34] YANG S, ZHAO M, JIA S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1080310.
[35] NING Z, LIU K, XIONG H. Roles of BTLA in immunity and immune disorders. Front Immunol. 2021;12:654960.
[36] YANG B, HUANG Z, FENG W, et al. The Expression of BTLA Was Increased and the Expression of HVEM and LIGHT Were Decreased in the T Cells of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [corrected]. PLoS One. 2016;11(5): e0155345.
[37] KAPELLOS TS, BONAGURO L, GEMÜND I, et al. Human monocyte subsets and phenotypes in major chronic inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2035.
[38] PRAJZLEROVÁ K, KRYŠTŮFKOVÁ O, KOMARC M, et al. The dysregulation of monocyte subpopulations in individuals at risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2021;60(4):1823-1831.
[39] TSUKAMOTO M, SETA N, YOSHIMOTO K, et al. CD14brightCD16+ intermediate monocytes are induced by interleukin-10 and positively correlate with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):1-10.
[40] ZHAO J, GUO S, SCHRODI SJ, et al. Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Front Immunol. 2021;12:790122.
[41] YANG M, WAN X, ZHENG H, et al. No evidence of a genetic causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and gut microbiota: A two-sample mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023;15(4):1057. |